模拟锁情况无效
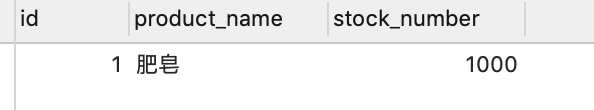
1.创建一个表
SET NAMES utf8mb4; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `demo`; CREATE TABLE `demo` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `product_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `stock_number` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `index_name` (`product_name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=31 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; BEGIN; INSERT INTO `demo` VALUES (1, '肥皂', 1000); COMMIT; SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
2.创建一个下单扣除的方法防止并发导致超买超卖以及脏读加锁
ps 我这里用的redis实现的分布式锁可以直接替换成synchronized测试
//事物方法 保证一致性 @Transactional public boolean deductNumber(Long id,int i){ //定义锁 库存id为id的数据 RLock[] locks = new RLock[]{redissonClient.getLock(String.valueOf(id))}; RedissonMultiLock redissonMultiLock = null; redissonMultiLock = new RedissonMultiLock(locks); boolean getLock = false; try { if (redissonMultiLock != null) { //尝试获得锁 getLock = redissonMultiLock.tryLock(); if (!getLock) { return false;//系统繁忙请重试 } } RowMapper<Demo> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Demo>(Demo.class); //获得指定产品的库存 Demo demo= jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from demo where id=?",rowMapper,id); //判断库存是否充足 if(demo.getStockNumber()<i){ return false;//库存不足 剩余库存demo.getStockNumber() } //库存扣除 demo.setStockNumber(demo.getStockNumber()-i); //持久化到数据 jdbcTemplate.update("update demo set stock_number=? where id=?",demo.getStockNumber(),demo.getId()); } catch (Exception e) { return false; } finally { //释放锁 if (redissonMultiLock != null && getLock) { redissonMultiLock.unlock(); } } return true; }
这里分为五步 1获得锁 2查询数据判断库存是否充足 3.库存扣除 4.持久化到数据库 5.释放锁
3.测试并发场景
/** * 模拟50个人下单 同时扣除库存 */ @Test public void run() { int threand = 50;//定义50个线程 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threand); List<Future<Integer>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<Integer>>(); for (int i = 0; i < threand; i++) { futures.add(executorService.submit(new Callable<Integer>() { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int succeedCount = 0; //重复扣除1000次 for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) { boolean isSuccess = tbDmsBasisCompanyConfigureService.deductNumber(1L, 1); //如果扣除成功+1 if (isSuccess) { succeedCount++; } } return succeedCount; } })); } int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < futures.size(); i++) { try { count += futures.get(i).get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //打印成功的数量 System.out.println(count); }
4.验证结果
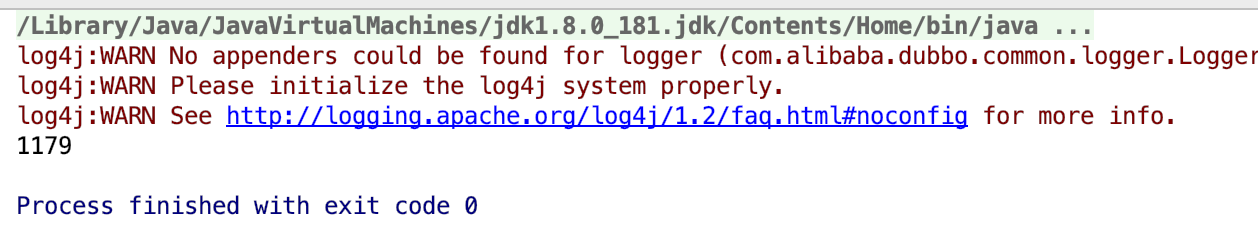
可以发现超卖了 我们库存1000 但是现在卖出1179 再看我们的库存

189 数据也是异常的
导致异常的分析
由于我们的事物开启和关闭是由spring托管的 spring事物管理是根据代理模式实现的 我可以把spring的代理方法简单看成以下
ps:大致这样 有空看完源码再回来补充
public boolean invoke(){ //开启事物 ...... boolean result= tbDmsBasisCompanyConfigureService.deductNumber(1L, 1); //根据事物状态提交和回滚事物 ...... return result }
用户1 1获得锁 2查询数据判断库存是否充足 3.库存扣除 4.持久化到数据库 5.释放锁 库存还剩999 (并发情况spring还没来得及提交事物)
用户2 因为用户1释放了锁 所以用户2成功获得锁 因为用户1事物还没来得及提交 RR(mysql默认)或者RC隔离级别 别的事物是不能读取到未提交的数据 所以用户2查询库存还是1000 这里脏读 后面导致超买超卖以及库存扣除
解决方式1
在外部加锁
/** * 模拟50个人下单 同时扣除库存 */ @Test public void run() { int threand = 50;//定义50个线程 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threand); List<Future<Integer>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<Integer>>(); for (int i = 0; i < threand; i++) { futures.add(executorService.submit(new Callable<Integer>() { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int succeedCount = 0; //重复扣除1000次 for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) { //定义锁 库存id为1的数据 RLock[] locks = new RLock[]{redissonClient.getLock("1")}; RedissonMultiLock redissonMultiLock = null; redissonMultiLock = new RedissonMultiLock(locks); boolean getLock = false; try { if (redissonMultiLock != null) { //尝试获得锁 getLock = redissonMultiLock.tryLock(); if (!getLock) { continue; } } boolean isSuccess = tbDmsBasisCompanyConfigureService.deductNumber(1L, 1); if (isSuccess) { succeedCount++; } } catch (Exception e) { continue; } finally { if (redissonMultiLock != null && getLock) { redissonMultiLock.unlock(); } } } return succeedCount; } })); } int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < futures.size(); i++) { try { count += futures.get(i).get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //打印成功的数量 System.out.println(count); }
测试结果
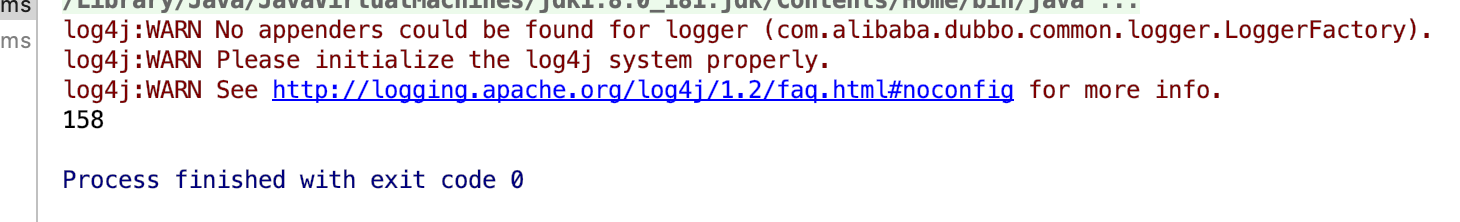
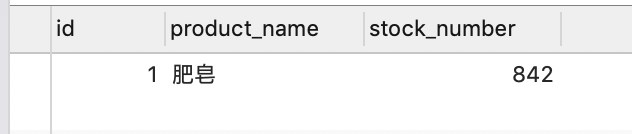
可以发现数据正确
这个时候可能有疑惑 不是50个人每个人下单1000吗 怎么库存不是0 因为并发情况 锁互斥 大部分都提示系统繁忙请稍后重试了
解决方式2(不推荐)
手动开启事物
//防止全局配置了 所以这里定义sprnig 不托管事物 @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED) public boolean deductNumber(Long id,int i){ //定义锁 库存id为id的数据 RLock[] locks = new RLock[]{redissonClient.getLock(String.valueOf(id))}; RedissonMultiLock redissonMultiLock = null; redissonMultiLock = new RedissonMultiLock(locks); boolean getLock = false; DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED);//设置事物传播行为 TransactionStatus status = null; try { if (redissonMultiLock != null) { //尝试获得锁 getLock = redissonMultiLock.tryLock(); if (!getLock) { return false;//系统繁忙请重试 } } //开启事物 开启事物一定要提交或者回滚 不然又不可预知的问题 status = transactionManager.getTransaction(def); RowMapper<Demo> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Demo>(Demo.class); //获得指定产品的库存 Demo demo= jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from demo where id=?",rowMapper,id); //判断库存是否充足 if(demo.getStockNumber()<i){ transactionManager.rollback(status); return false;//库存不足 剩余库存demo.getStockNumber() } //库存扣除 demo.setStockNumber(demo.getStockNumber()-i); //持久化到数据 jdbcTemplate.update("update demo set stock_number=? where id=?",demo.getStockNumber(),demo.getId()); //提交事务 transactionManager.commit(status); } catch (Exception e) { return false; } finally { //释放锁 if (redissonMultiLock != null && getLock) { redissonMultiLock.unlock(); } //保险起见加一个这个代码 如果事物没提交回滚 执行回滚 一般都是我们代码问题 if(status!=null&&!status.isCompleted()){ transactionManager.rollback(status); return false; } } return true; }
缺点
1.忘记提交或者回滚有不可预知问题 后面会分析
2.遇到其他事物方法调用这个方法 会有一致性问题 或者锁提前释放问题
不推荐