package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 定义一个ManKind类,包括 成员变量int sex和int salary; 方法void manOrWoman():根据sex的值显示“man”(sex==1)或者“woman”(sex==0); 方法void employeed():根据salary的值显示“no job”(salary==0)或者“ job”(salary!=0)。 */ public class ManKind { private int sex;//性别 private int salary;//薪资 public ManKind() { } public ManKind(int sex, int salary) { this.sex = sex; this.salary = salary; } public void manOrWoman(){ if(sex == 1){ System.out.println("man"); }else if(sex == 0){ System.out.println("woman"); } } public void employeed(){ // if(salary == 0){ // System.out.println("no job"); // }else{ // System.out.println("job"); // } //或 String jobInfo = (salary == 0)? "no job" : "job"; System.out.println(jobInfo); } public int getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(int sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary(int salary) { this.salary = salary; } }
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 定义类Kids继承ManKind,并包括 成员变量int yearsOld; 方法printAge()打印yearsOld的值。 */ public class Kids extends ManKind{ private int yearsOld; public Kids() { } public Kids(int yearsOld) { this.yearsOld = yearsOld; } public void printAge(){ System.out.println("I am " + yearsOld + " years old."); } public int getYearsOld() { return yearsOld; } public void setYearsOld(int yearsOld) { this.yearsOld = yearsOld; } /* * 修改练习1.2中定义的类Kids,在Kids中重新定义employeed()方法, * 覆盖父类ManKind中定义的employeed()方法, * 输出“Kids should study and no job.” */ public void employeed() { System.out.println("Kids should study and no job."); } }
package com.atguigu.exer; /* * 定义类KidsTest,在类的main方法中实例化Kids的对象someKid,用该对象访问其父类的成员变量及方法。 */ public class KidsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Kids someKid = new Kids(12); someKid.printAge(); someKid.setSalary(0); someKid.setSex(1); someKid.employeed(); someKid.manOrWoman(); } }
package com.atguigu.exer1; public class Circle { private double radius;//半径 public Circle(){ radius = 1.0; } // public Circle(double radius){ this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } //返回圆的面积 public double findArea(){ return Math.PI * radius * radius; } }
package com.atguigu.exer1; public class Cylinder extends Circle{ private double length;//高 public Cylinder(){ length = 1.0; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } //返回圆柱的体积 public double findVolume(){ // return Math.PI * getRadius() * getRadius() * getLength(); return super.findArea() * getLength(); } @Override public double findArea() {//返回圆柱的表面积 return Math.PI * getRadius() * getRadius() * 2 + 2 * Math.PI * getRadius() * getLength(); } }
package com.atguigu.exer1; public class CylinderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Cylinder cy = new Cylinder(); cy.setRadius(2.1); cy.setLength(3.4); double volume = cy.findVolume(); System.out.println("圆柱的体积为:" + volume); //没有重写findArea()时: // double area = cy.findArea(); // System.out.println("底面圆的面积:" + area); //重写findArea()以后: double area = cy.findArea(); System.out.println("圆柱的表面积:" + area); System.out.println("******************"); Cylinder cy1 = new Cylinder(); double volume1 = cy1.findVolume(); System.out.println("圆柱的体积为:" + volume1); } }



package com.atguigu.java; /* * 如何调试程序: * 1. System.out.println(). * 2. Eclipse - Debug调试 * */ public class DebugTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 10; int j = 20; System.out.println("i = " + i + ", j = " + j); DebugTest test = new DebugTest(); int max = test.getMax(i, j); System.out.println("max = " + max); } private int getMax(int k, int m) { int max = 0; if (k < m) { max = k; } else { max = m; } return max; } }
package com.atguigu.java; public class DebugTest1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5}; System.out.println(arr);//地址值 char[] arr1 = new char[] {'a','b','c'}; System.out.println(arr1);//abc } }
package com.atguigu.java1; /* * 方法的重写(override / overwrite) * * 1.重写:子类继承父类以后,可以对父类中同名同参数的方法,进行覆盖操作 * * 2.应用:重写以后,当创建子类对象以后,通过子类对象调用子父类中的同名同参数的方法时,实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法。 * * 3. 重写的规定: * 方法的声明: 权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(形参列表) throws 异常的类型{ * //方法体 * } * 约定俗称:子类中的叫重写的方法,父类中的叫被重写的方法 * ① 子类重写的方法的方法名和形参列表与父类被重写的方法的方法名和形参列表相同 * ② 子类重写的方法的权限修饰符不小于父类被重写的方法的权限修饰符 * >特殊情况:子类不能重写父类中声明为private权限的方法 * ③ 返回值类型: * >父类被重写的方法的返回值类型是void,则子类重写的方法的返回值类型只能是void * >父类被重写的方法的返回值类型是A类型,则子类重写的方法的返回值类型可以是A类或A类的子类 * >父类被重写的方法的返回值类型是基本数据类型(比如:double),则子类重写的方法的返回值类型必须是相同的基本数据类型(必须也是double) * ④ 子类重写的方法抛出的异常类型不大于父类被重写的方法抛出的异常类型(具体放到异常处理时候讲) * ********************************************************************** * 子类和父类中的同名同参数的方法要么都声明为非static的(考虑重写),要么都声明为static的(不是重写)。 * * #区分方法的重载与重写 */ public class PersonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s = new Student("计算机科学与技术"); s.eat(); s.walk(10); System.out.println("**************"); s.study(); Person p1 = new Person(); p1.eat(); } }
package com.atguigu.java1; public class Person { String name; int age; public Person(){ } public Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } void eat(){ System.out.println("吃饭"); } public void walk(int distance){ System.out.println("走路,走的距离是:" + distance + "公里"); show(); eat(); } private void show(){ System.out.println("我是一个人"); } public Object info(){ return null; } public double info1(){ return 1.0; } }
package com.atguigu.java1; public class Student extends Person{ String major; public Student(){ } public Student(String major){ this.major = major; } public void study(){ System.out.println("学习。专业是:" + major); } //对父类中的eat()进行了重写 public void eat(){ System.out.println("学生应该多吃有营养的食物"); } public void show(){ System.out.println("我是一个学生"); } public String info(){ return null; } // public int info1(){ // return 1; // } // public void walk(int distance){ // System.out.println("重写的方法"); // } public void walk(int distance) { System.out.println("重写的方法"); } }
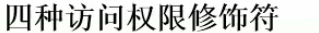
package com.atguigu.java2; /* * 体会4种不同的权限修饰 * * */ public class Order { private int orderPrivate; int orderDefault; protected int orderProtected; public int orderPublic; private void methodPrivate(){ orderPrivate = 1; orderDefault = 2; orderProtected = 3; orderPublic = 4; } void methodDefault(){ orderPrivate = 1; orderDefault = 2; orderProtected = 3; orderPublic = 4; } protected void methodProtected(){ orderPrivate = 1; orderDefault = 2; orderProtected = 3; orderPublic = 4; } public void methodPublic(){ orderPrivate = 1; orderDefault = 2; orderProtected = 3; orderPublic = 4; } }
package com.atguigu.java2; public class OrderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Order order = new Order(); order.orderDefault = 1; order.orderProtected = 2; order.orderPublic = 3; order.methodDefault(); order.methodProtected(); order.methodPublic(); //同一个包中的其他类,不可以调用Order类中私有的属性、方法 // order.orderPrivate = 4; // order.methodPrivate(); } }
package com.atguigu.java3; import com.atguigu.java2.Order; public class SubOrder extends Order { public void method(){ orderProtected = 1; orderPublic = 2; methodProtected(); methodPublic(); //在不同包的子类中,不能调用Order类中声明为private和缺省权限的属性、方法 // orderDefault = 3; // orderPrivate = 4; // // methodDefault(); // methodPrivate(); } }
package com.atguigu.java3; import com.atguigu.java2.Order; public class OrderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Order order = new Order(); order.orderPublic = 1; order.methodPublic(); //不同包下的普通类(非子类)要使用Order类,不可以调用声明为private、缺省、protected权限的属性、方法 // order.orderPrivate = 2; // order.orderDefault = 3; // order.orderProtected = 4; // // order.methodPrivate(); // order.methodDefault(); // order.methodProtected(); } public void show(Order order){ order.orderPublic = 1; order.methodPublic(); //不同包下的普通类(非子类)要使用Order类,不可以调用声明为private、缺省、protected权限的属性、方法 // order.orderPrivate = 2; // order.orderDefault = 3; // order.orderProtected = 4; // // order.methodPrivate(); // order.methodDefault(); // order.methodProtected(); // } }
package com.atguigu.java3; /* * super关键字的使用 * 1.super理解为:父类的 * 2.super可以用来调用:属性、方法、构造器 * * 3.super的使用:调用属性和方法 * * 3.1 我们可以在子类的方法或构造器中。通过使用"super.属性"或"super.方法"的方式,显式的调用 * 父类中声明的属性或方法。但是,通常情况下,我们习惯省略"super." * 3.2 特殊情况:当子类和父类中定义了同名的属性时,我们要想在子类中调用父类中声明的属性,则必须显式的 * 使用"super.属性"的方式,表明调用的是父类中声明的属性。 * 3.3 特殊情况:当子类重写了父类中的方法以后,我们想在子类的方法中调用父类中被重写的方法时,则必须显式的 * 使用"super.方法"的方式,表明调用的是父类中被重写的方法。 * * 4.super调用构造器 * 4.1 我们可以在子类的构造器中显式的使用"super(形参列表)"的方式,调用父类中声明的指定的构造器 * 4.2 "super(形参列表)"的使用,必须声明在子类构造器的首行! * 4.3 我们在类的构造器中,针对于"this(形参列表)"或"super(形参列表)"只能二选一,不能同时出现 * 4.4 在构造器的首行,没有显式的声明"this(形参列表)"或"super(形参列表)",则默认调用的是父类中空参的构造器:super() * 4.5 在类的多个构造器中,至少有一个类的构造器中使用了"super(形参列表)",调用父类中的构造器 */ public class SuperTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s = new Student(); s.show(); System.out.println(); s.study(); Student s1 = new Student("Tom", 21, "IT"); s1.show(); System.out.println("************"); Student s2 = new Student(); } }
package com.atguigu.java3; public class Person { String name; int age; int id = 1001;//身份证号 public Person(){ System.out.println("我无处不在!"); } public Person(String name){ this.name = name; } public Person(String name,int age){ this(name); this.age = age; } public void eat(){ System.out.println("人:吃饭"); } public void walk(){ System.out.println("人:走路"); } }
package com.atguigu.java3; public class Student extends Person{ String major; int id = 1002;//学号 public Student(){ super(); } public Student(String major){ super(); this.major = major; } public Student(String name,int age,String major){ // this.name = name; // this.age = age; super(name,age); this.major = major; } @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("学生:多吃有营养的食物"); } public void study(){ System.out.println("学生:学习知识"); this.eat(); super.eat(); walk(); } public void show(){ System.out.println("name = " + name + ", age = " + age); System.out.println("id = " + this.id); System.out.println("id = " + super.id); } }
package com.atguigu.java3; /* * 子类对象实例化的全过程 * * 1. 从结果上来看:(继承性) * 子类继承父类以后,就获取了父类中声明的属性或方法。 * 创建子类的对象,在堆空间中,就会加载所有父类中声明的属性。 * * 2. 从过程上来看: * 当我们通过子类的构造器创建子类对象时,我们一定会直接或间接的调用其父类的构造器,进而调用父类的父类的构造器,... * 直到调用了java.lang.Object类中空参的构造器为止。正因为加载过所有的父类的结构,所以才可以看到内存中有 * 父类中的结构,子类对象才可以考虑进行调用。 * * * 明确:虽然创建子类对象时,调用了父类的构造器,但是自始至终就创建过一个对象,即为new的子类对象。 * */ public class InstanceTest { }
package com.atguigu.exer2; public class Account { private int id;//账号 private double balance;//余额 private double annualInterestRate;//年利率 public Account(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate) { super(); this.id = id; this.balance = balance; this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(double balance) { this.balance = balance; } public double getAnnualInterestRate() { return annualInterestRate; } public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) { this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate; } //返回月利率 public double getMonthlyInterest(){ return annualInterestRate / 12; } //取钱 public void withdraw (double amount){ if(balance >= amount){ balance -= amount; return; } System.out.println("余额不足"); } //存钱 public void deposit (double amount){ if(amount > 0){ balance += amount; } } }
package com.atguigu.exer2; /* * 写一个用户程序测试Account类。在用户程序中, * 创建一个账号为1122、余额为20000、年利率4.5%的Account对象。 * 使用withdraw方法提款30000元,并打印余额。 * 再使用withdraw方法提款2500元, * 使用deposit方法存款3000元,然后打印余额和月利率。 * */ public class AccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Account acct = new Account(1122, 20000, 0.045); acct.withdraw(30000); System.out.println("您的账户余额为:" + acct.getBalance()); acct.withdraw(2500); System.out.println("您的账户余额为:" + acct.getBalance()); acct.deposit(3000); System.out.println("您的账户余额为:" + acct.getBalance()); System.out.println("月利率为:" + (acct.getMonthlyInterest() * 100) +"%"); } }
package com.atguigu.exer2; /* * 创建Account类的一个子类CheckAccount代表可透支的账户,该账户中定义一个属性overdraft代表可透支限额。 * 在CheckAccount类中重写withdraw方法,其算法如下: 如果(取款金额<账户余额), 可直接取款 如果(取款金额>账户余额), 计算需要透支的额度 判断可透支额overdraft是否足够支付本次透支需要,如果可以 将账户余额修改为0,冲减可透支金额 如果不可以 提示用户超过可透支额的限额 * * */ public class CheckAccount extends Account{ private double overdraft;//可透支限额 public CheckAccount(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate,double overdraft){ super(id, balance, annualInterestRate); this.overdraft = overdraft; } public double getOverdraft() { return overdraft; } public void setOverdraft(double overdraft) { this.overdraft = overdraft; } @Override public void withdraw(double amount) { if(getBalance() >= amount){//余额就足够消费 // getBalance() -= amount; //方式一: // setBalance(getBalance() - amount); //方式二: super.withdraw(amount); }else if(overdraft >= amount - getBalance()){//透支额度+余额足够消费 overdraft -= (amount - getBalance()); // setBalance(0); //或 super.withdraw(getBalance()); }else{ System.out.println("超过可透支限额!"); } } }
package com.atguigu.exer2; /* * 写一个用户程序测试CheckAccount类。 * 在用户程序中,创建一个账号为1122、余额为20000、年利率4.5%,可透支限额为5000元的CheckAccount对象。 使用withdraw方法提款5000元,并打印账户余额和可透支额。 再使用withdraw方法提款18000元,并打印账户余额和可透支额。 再使用withdraw方法提款3000元,并打印账户余额和可透支额。 * */ public class CheckAccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { CheckAccount acct = new CheckAccount(1122, 20000, 0.045, 5000); acct.withdraw(5000); System.out.println("您的账户余额为:" + acct.getBalance()); System.out.println("您的可透支额度为:" + acct.getOverdraft()); acct.withdraw(18000); System.out.println("您的账户余额为:" + acct.getBalance()); System.out.println("您的可透支额度为:" + acct.getOverdraft()); acct.withdraw(3000); System.out.println("您的账户余额为:" + acct.getBalance()); System.out.println("您的可透支额度为:" + acct.getOverdraft()); } }
package com.atguigu.java4; /* * 面向对象特征之三:多态性 * * 1.理解多态性:可以理解为一个事物的多种形态。 * 2.何为多态性: * 对象的多态性:父类的引用指向子类的对象(或子类的对象赋给父类的引用) * * 3. 多态的使用:虚拟方法调用 * 有了对象的多态性以后,我们在编译期,只能调用父类中声明的方法,但在运行期,我们实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法。 * 总结:编译,看左边;运行,看右边。 * * 4.多态性的使用前提: ① 类的继承关系 ② 方法的重写 * * 5.对象的多态性,只适用于方法,不适用于属性(编译和运行都看左边) */ public class PersonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p1 = new Person(); p1.eat(); Man man = new Man(); man.eat(); man.age = 25; man.earnMoney(); //************************************************* System.out.println("*******************"); //对象的多态性:父类的引用指向子类的对象 Person p2 = new Man(); // Person p3 = new Woman(); //多态的使用:当调用子父类同名同参数的方法时,实际执行的是子类重写父类的方法 ---虚拟方法调用 p2.eat(); p2.walk(); // p2.earnMoney(); System.out.println(p2.id);//1001 } }
package com.atguigu.java4; public class Person { String name; int age; int id = 1001; public void eat(){ System.out.println("人:吃饭"); } public void walk(){ System.out.println("人:走路"); } }
package com.atguigu.java4; public class Man extends Person{ boolean isSmoking; int id = 1002; public void earnMoney(){ System.out.println("男人负责挣钱养家"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("男人多吃肉,长肌肉"); } public void walk(){ System.out.println("男人霸气的走路"); } }
package com.atguigu.java4; public class Woman extends Person{ boolean isBeauty; public void goShopping(){ System.out.println("女人喜欢购物"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("女人少吃,为了减肥"); } public void walk(){ System.out.println("女人窈窕的走路"); } }
package com.atguigu.java5; import java.util.Random; //面试题:多态是编译时行为还是运行时行为? //证明如下: class Animal { protected void eat() { System.out.println("animal eat food"); } } class Cat extends Animal { protected void eat() { System.out.println("cat eat fish"); } } class Dog extends Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("Dog eat bone"); } } class Sheep extends Animal { public void eat() { System.out.println("Sheep eat grass"); } } public class InterviewTest { public static Animal getInstance(int key) { switch (key) { case 0: return new Cat (); case 1: return new Dog (); default: return new Sheep (); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int key = new Random().nextInt(3); System.out.println(key); Animal animal = getInstance(key); animal.eat(); } }
