refer to: https://www.algoexpert.io/questions/Multi%20String%20Search
Input: a big string and an array of small strings, the length of every string in the array is smaller than the length of the big string
Output: a boolean string, which every index represents the particular small string is contained in the big string or not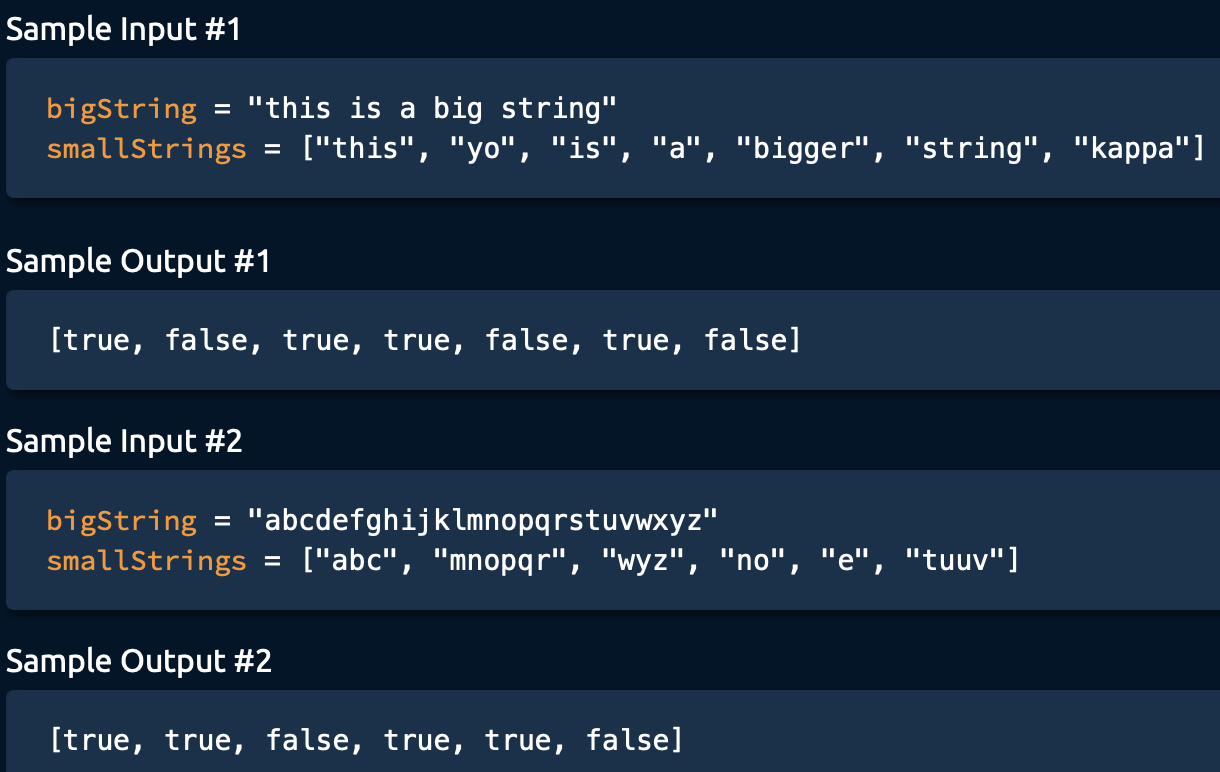
Analysis
Approach 1
naive approach, iterate through all of the small strings, for every small string, traverse the whole big string, time complexity: O(mnl), where m is the length of the array of small strings, n is the length of the big string, and l is the biggest length of small string. Space complexity is O(m) -> the size of the output array.

code
def multiStringSearch(bigString, smallStrings): return [isInBigString(bigString, smallString) for smallString in smallStrings] def isInBigString(bigString, smallString): for i in range(len(bigString)): if i + len(smallString) > len(bigString): break if isInBigStringHelper(bigString, smallString, i): return True return False def isInBigStringHelper(bigString, smallString, startIdx): # compare the two strings from startIdx leftBigIdx = startIdx rightBigIdx = startIdx + len(smallString) - 1 leftSmallIdx = 0 rightSmallIdx = len(smallString) - 1 while leftBigIdx <= rightBigIdx: if bigString[leftBigIdx] != smallString[leftSmallIdx] or bigString[rightBigIdx] != smallString[rightSmallIdx]: return False leftBigIdx += 1 rightBigIdx -= 1 leftSmallIdx += 1 rightSmallIdx -= 1 return True
Approach 2
build a suffix-trie containing all of the big string's suffixes. 后缀树,to build this suffix trie like data structrue, it takes O(n^2) time and O(n^2) space, where n is the length of the big string.
To check if a sring is contained in a suffixex trie, it takes O(len(string)) time. In this case, it takes O(biggest length of small string) for check if a string is contained in the big string. To finish checking the whole array of small strings, we will take O(ml) time to check the whole array of strings, where m is the length of the array, l is the biggest length of small string. In total, we will take O(n^2 + ml) time, where O(n^2) is the suffix trie construction and O(ml) is the checking step. Space complexity is O(n^2 + m). O(n^2) is the space for suffix trie, O(m) is to store the output array.

Code
def multiStringSearch(bigString, smallStrings): modifiedSuffixTrie = ModifiedSuffixTrie(bigString)# construct the suffix trie return [modifiedSuffixTrie.contains(string) for string in smallStrings] # check every string is in the suffix trie class ModifiedSuffixTrie: def __init__(self, string): self.root = {} self.populateModifiedSuffixTrieFrom(string) # add string into the suffix trie def populateModifiedSuffixTrieFrom(self, string): # for each string, add each suffix trie, start indices included. for i in range(len(string)): self.insertSubstringStartingAt(i, string) def insertSubstringStartingAt(self, i, string): # given a start index, insert the substring in the suffix trie node = self.root for j in range(i, len(string)): # iterate erevy letter from index i letter = string[j] # the current letter if letter not in node: node[letter] = {} # create an empty hashmap to build a new root tree node = node[letter] # update the node, traverse down the tree def contains(self, string): # check a string is contained in the suffix tries node = self.root for letter in string: if letter not in node: return False node = node[letter] # update the node, traverse down the tree
return True
Approach 3
build a suffix trie based on array of small strings. suffix trie construction: O(ml) time, where m is the length of the array, l is the biggest length of small string; O(ml) space to store the suffix tries.
Search: O(nl), where n is the length of the big string, l is the longest small string in the array.
In total: time complexity: O(ml + nl). space complexity: O(ml + m)->O(ml)

code
def multiStringSearch(bigString, smallStrings): trie = Trie() for string in smallStrings: trie.insert(string) containedStrings = {} for i in range(len(bigString)): findSmallStringsIn(bigString, i, trie, containedStrings) return [string in containedStrings for string in smallStrings] def findSmallStringsIn(string, startIdx, trie, containedStrings): currentNode = trie.root for i in range(startIdx, len(string)): currentChar = string[i] if currentChar not in currentNode: break currentNode = currentNode[currentChar] if trie.endSymbol in currentNode: containedStrings[currentNode[trie.endSymbol]] = True class Trie: def __init__(self): self.root = {} self.endSymbol = "*" def insert(self, string): current = self.root for i in range(len(string)): if string[i] not in current: current[string[i]] = {} current = current[string[i]] current[self.endSymbol] = string
Comparing
appoach 1: O(mnl)
appoach 2: O(n^2 + ml)
appoach 3: O(nl + ml)
compare l and n, where n is the length of the big string, l is the longest length of small strings
In the problem description, we know that the length of every string in the array is smaller than the length of the big string, so appoach 3 is better than approach 2.