2020/02/01
Java编码中,平方的计算需要注意的问题!
【不能使用^符号,要用Math.pow()函数做平方计算】
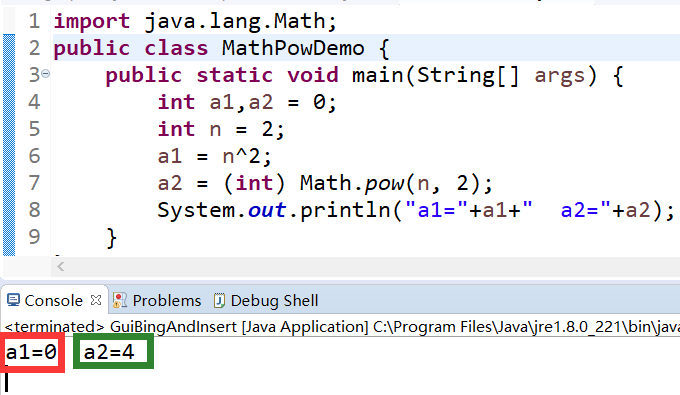
在计算一个数平方,发现和预期的结果不一致:
如下:
计算 n2 当n=1时,代码 n^2=3 !!!
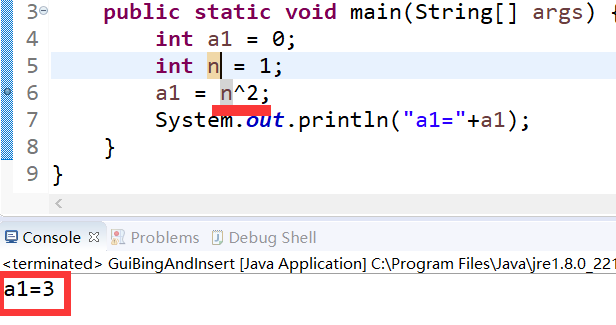
查找到的原因
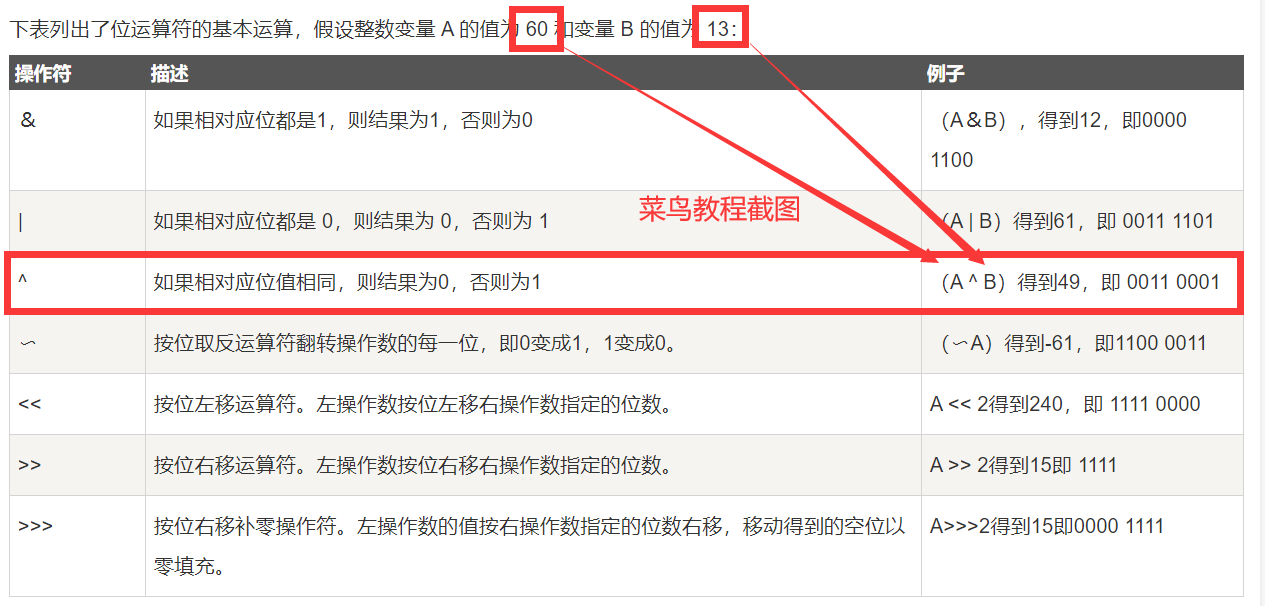
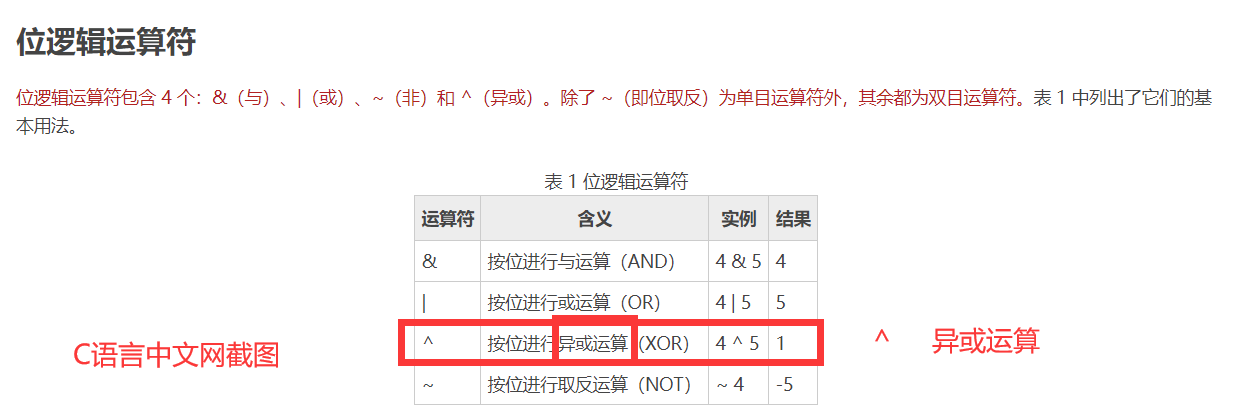
则本次编码中用到的 1^2 的实际运算过程为:
| 0001 | |
| ⊕ 0010 | |
| 0011 |
根据异或的计算规则:位 相同为0,不同为1,得到2进制的0011,即10进制的3。
得证!
结论
要想使用数学中的平方计算,需要用到java.lang.Math包中的pow函数
其函数源码:
1 public static double pow(double a, double b) {
2 return StrictMath.pow(a, b); // default impl. delegates to StrictMath
3 }
其函数源码注释:
1 * Returns the value of the first argument raised to the power of the 2 * second argument. Special cases: 3 * 4 * <ul><li>If the second argument is positive or negative zero, then the 5 * result is 1.0. 6 * <li>If the second argument is 1.0, then the result is the same as the 7 * first argument. 8 * <li>If the second argument is NaN, then the result is NaN. 9 * <li>If the first argument is NaN and the second argument is nonzero, 10 * then the result is NaN. 11 * 12 * <li>If 13 * <ul> 14 * <li>the absolute value of the first argument is greater than 1 15 * and the second argument is positive infinity, or 16 * <li>the absolute value of the first argument is less than 1 and 17 * the second argument is negative infinity, 18 * </ul> 19 * then the result is positive infinity. 20 * 21 * <li>If 22 * <ul> 23 * <li>the absolute value of the first argument is greater than 1 and 24 * the second argument is negative infinity, or 25 * <li>the absolute value of the 26 * first argument is less than 1 and the second argument is positive 27 * infinity, 28 * </ul> 29 * then the result is positive zero. 30 * 31 * <li>If the absolute value of the first argument equals 1 and the 32 * second argument is infinite, then the result is NaN. 33 * 34 * <li>If 35 * <ul> 36 * <li>the first argument is positive zero and the second argument 37 * is greater than zero, or 38 * <li>the first argument is positive infinity and the second 39 * argument is less than zero, 40 * </ul> 41 * then the result is positive zero. 42 * 43 * <li>If 44 * <ul> 45 * <li>the first argument is positive zero and the second argument 46 * is less than zero, or 47 * <li>the first argument is positive infinity and the second 48 * argument is greater than zero, 49 * </ul> 50 * then the result is positive infinity. 51 * 52 * <li>If 53 * <ul> 54 * <li>the first argument is negative zero and the second argument 55 * is greater than zero but not a finite odd integer, or 56 * <li>the first argument is negative infinity and the second 57 * argument is less than zero but not a finite odd integer, 58 * </ul> 59 * then the result is positive zero. 60 * 61 * <li>If 62 * <ul> 63 * <li>the first argument is negative zero and the second argument 64 * is a positive finite odd integer, or 65 * <li>the first argument is negative infinity and the second 66 * argument is a negative finite odd integer, 67 * </ul> 68 * then the result is negative zero. 69 * 70 * <li>If 71 * <ul> 72 * <li>the first argument is negative zero and the second argument 73 * is less than zero but not a finite odd integer, or 74 * <li>the first argument is negative infinity and the second 75 * argument is greater than zero but not a finite odd integer, 76 * </ul> 77 * then the result is positive infinity. 78 * 79 * <li>If 80 * <ul> 81 * <li>the first argument is negative zero and the second argument 82 * is a negative finite odd integer, or 83 * <li>the first argument is negative infinity and the second 84 * argument is a positive finite odd integer, 85 * </ul> 86 * then the result is negative infinity. 87 * 88 * <li>If the first argument is finite and less than zero 89 * <ul> 90 * <li> if the second argument is a finite even integer, the 91 * result is equal to the result of raising the absolute value of 92 * the first argument to the power of the second argument 93 * 94 * <li>if the second argument is a finite odd integer, the result 95 * is equal to the negative of the result of raising the absolute 96 * value of the first argument to the power of the second 97 * argument 98 * 99 * <li>if the second argument is finite and not an integer, then 100 * the result is NaN. 101 * </ul> 102 * 103 * <li>If both arguments are integers, then the result is exactly equal 104 * to the mathematical result of raising the first argument to the power 105 * of the second argument if that result can in fact be represented 106 * exactly as a {@code double} value.</ul> 107 * 108 * <p>(In the foregoing descriptions, a floating-point value is 109 * considered to be an integer if and only if it is finite and a 110 * fixed point of the method {@link #ceil ceil} or, 111 * equivalently, a fixed point of the method {@link #floor 112 * floor}. A value is a fixed point of a one-argument 113 * method if and only if the result of applying the method to the 114 * value is equal to the value.) 115 * 116 * <p>The computed result must be within 1 ulp of the exact result. 117 * Results must be semi-monotonic. 118 * 119 * @param a the base. 120 * @param b the exponent. 121 * @return the value {@code a}<sup>{@code b}</sup>. 122 */
最终结果: