一、LINQ 与 EF
从前面的讨论,可以看到 Code First 模型比 EF 设计模式要精简很多,在实际项目开发中,也建议直接采用 Code First 模式。
因此,接下来的示例我们都采用 Code First 模式来展开讨论。
1、Select 语句
首先,创建 LINQDemo 项目,然后添加 ADO.Net 实体数据模型,选择 Code First 模式,选择事先创建好的数据库。
接下来,在 Main 方法中写一个 LINQ 的 Select 语句:
using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { var stus = from stu in context.Student select stu; foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine(stu.Name); } } Console.ReadKey();
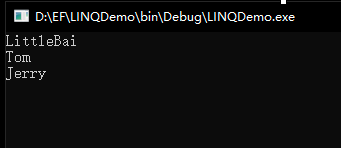
在 LINQ 中,Select 语句负责查询结果,除了查询完整的对象、单个或特定的属性成员外,同时它还支持功能强大的类型转换功能。
通过该功能,我们可以借助 LINQ 查询选择的对象集合来创建一组全新的类型(类型转换):
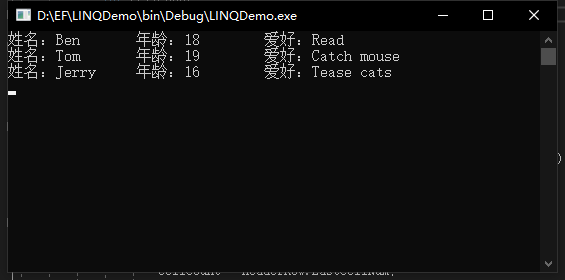
using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { var stus = from stu in context.Student select stu; foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{stu.Name} 年龄:{stu.Age} 爱好:{stu.Hobby}"); } } Console.ReadKey();
a、类型转换
基于上面输出的查询结果,我们可以进行指定属性查询:
新建一个 SelectResult.cs 类。
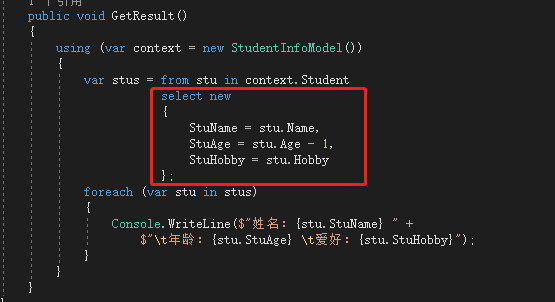
using System; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo { class SelectResult { public void GetResult() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { var stus = from stu in context.Student select new { stu.Name, stu.Age, stu.Hobby }; foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{stu.Name} 年龄:{stu.Age} 爱好:{stu.Hobby}"); } } } } }
然后回到主程序(Main 方法)中调用该方法:

在 Select 语句中获取了指定的 Name、Age、Hobby属性之后,通过 new 关键字创建了新的返回对象。

如你所见,只要通过适当的 LINQ 语句,我们就可以取出特定的数据。
我们还可以为属性指定标识名:
Select 语句中,在创建的新对象中逐一为属性指定了映射名,同时将原来的年龄减去了 1 岁。
可以看出,Select 语句除了选择数据外,还进一步转换了结果,创建了新的结果对象类型。创建对象的过程就是所谓的映射。
在实际开发中,针对特定的数据处理,我们会定义实体类,以支持更进一步的强类型数据操作。
所以,接下来我们需要定义一个实体类对象,用以存储查询结果及数据处理:
using System; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo { class SelectResult { public void GetResult() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { IQueryable<ResultObj> stus = from stu in context.Student select new ResultObj() { SID = stu.Id, StuID = "2020" + stu.Id.ToString(), StuName = stu.Name, StuAge = stu.Age - 1, StuHobby = stu.Hobby }; foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine($"ID:{stu.SID} 编号:{stu.StuID} 姓名:{stu.StuName} 年龄:{stu.StuAge} 爱好:{stu.StuHobby}"); } } } class ResultObj { public int? SID { get; set; } public string StuID { get; set; } public string StuName { get; set; } public int? StuAge { get; set; } public string StuHobby { get; set; } } } }
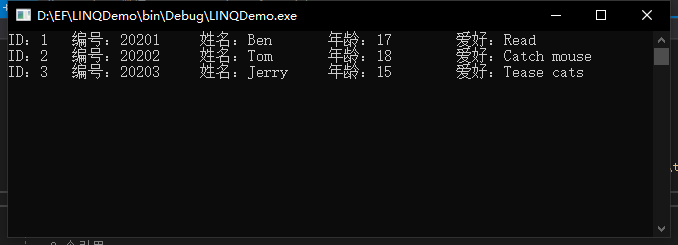
这么看来,感觉 Select 语句有点儿复杂,有什么方法可以简化么?
当然,我们可以把 new 对象的逻辑单独的放到独立的方法(或函数)中:
public void GetResult() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { IEnumerable<ResultObj> stus = from stu in context.Student.ToList() select ConvertToResultObj(stu); foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine($"ID:{stu.SID} 编号:{stu.StuID} 姓名:{stu.StuName} 年龄:{stu.StuAge} 爱好:{stu.StuHobby}"); } } } ResultObj ConvertToResultObj(Student stu) { return new ResultObj() { SID = stu.Id, StuID = "2020" + stu.Id.ToString(), StuName = stu.Name, StuAge = stu.Age - 1, StuHobby = stu.Hobby }; }
2、多重 from 与 SelectMany
了解了 Select 语句后,再来学习 SelectMany 就会容易许多,因为 SelectMany 只是搭配了多重 from 子句的 Select 方法。
// 第二个参数 Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TResult>> selector
// IEnumerable<TResult> 这个表示将 IEnumerable 对象当做参数传入做进一步处理,构成了多重 from 运算。
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source,
Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TResult>> selector);
在学习 SelectMany 方法之前,先来看两个多重 from 语句的例子:
using System; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] weekMonth = { "January,February,March,April,May,June,July,August,September,October,November,December", "Monday,Tusday,Wednesday,Thursday,Friday,Saturday,Sunday" }; var enumMonth = from wm in weekMonth from daywm in wm.Split(',') select new { week = daywm.Contains("day") ? daywm.Substring(0, 3):"", month = !daywm.Contains("day") ? daywm.Substring(0, 3):"", }; string month = "星期的缩写: "; foreach (var mon in enumMonth) { if(mon.week!="") month += mon.week + " "; } Console.WriteLine(month); month = "月份的缩写: "; foreach (var mon in enumMonth) {
month += mon.month + " ";
} Console.WriteLine(month); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
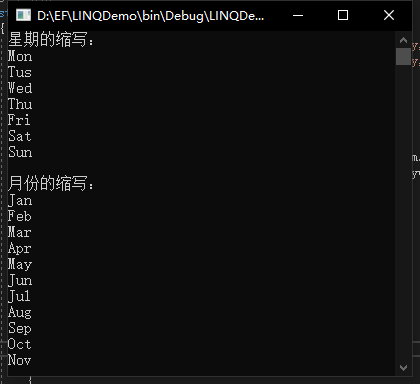
上面的例子是将数组中的数据提取成缩写形式并输出!用了嵌套 from 语句。
第一个 from 语句是将月份和星期提取出来,第二个 from 将提取出来的对象通过 ‘,’ 将其分解,然后再挨个处理数组中的数据;
最后返回一个由 week 和 month 属性组成的匿名对象。像这种就是嵌套查询了。
接下来,咱们用 LINQ 结合 EF 实体数据结构,来看看多重 from 是怎么操作的?
首先,需要添加一个年级表,学生表能添加一个关联年级表的ID,表结果如下:
Student 表:
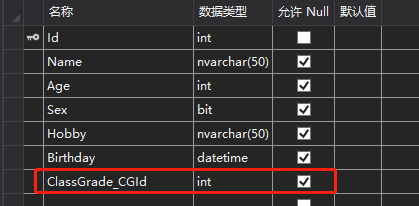
ClassGrade 表:

年级表和学生表 是一对多的关系。
接下来我们尝试用 LINQ 语句,将学生用年级来分组并输出:
using System; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo { class SelectMany { public void ClassToStu() { using(var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { var stus = from classes in context.CGrade from stu in classes.Students orderby classes.GradeNum,classes.ClassNum select new { classes.GradeNum, classes.ClassNum, stu.Name }; foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine($"{stu.GradeNum}年级{stu.ClassNum}班: {stu.Name}"); } } } } }
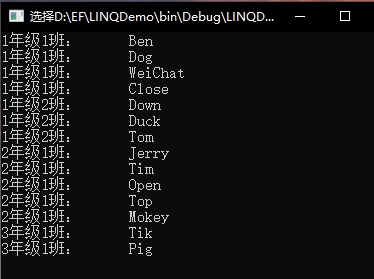
我们通过 LINQ 实现了归组链表查询,接下来看看如何把上面的 LINQ 语句通过 SelectMany() 方法来实现:
using System; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo { class SelectMany { public void ClassToStu() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { var students = context.CGrade.SelectMany( s => s.Students.Select( st => new { s.GradeNum, s.ClassNum, st.Name })).OrderBy(s => s.GradeNum).ThenBy(s => s.ClassNum); foreach (var stu in students) { Console.WriteLine($"{stu.GradeNum}年级{stu.ClassNum}班: {stu.Name}"); } } } } }
我们还可以通过 where 方法来过滤出我们想要查询的数据,比如 我想查出属于一年级的同学:
var stus = from classes in context.CGrade where classes.GradeNum == 1 from stu in classes.Students orderby classes.GradeNum, classes.ClassNum select new { classes.GradeNum, classes.ClassNum, stu.Name }; var students = context.CGrade.Where(s => s.GradeNum == 1).SelectMany( s => s.Students.Select( st => new { s.GradeNum, s.ClassNum, st.Name })).OrderBy(s => s.GradeNum).ThenBy(s => s.ClassNum);
3、Where 与数据筛选
数据筛选过滤运算是针对集合中的对象元素,根据指定的条件返回符合此条件值的数据记录。
与数据的筛选运算有关的方法有两个,它们分别是 where 与 OfType。
我们先来看看 where,下面示例过滤出 15 到 17 岁的童鞋:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace LINQDemo { class Where { public void GetWhereData() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { Console.WriteLine("LINQ 语句:"); var students = from stu in context.Student where stu.Age >= 15 && stu.Age <= 17 select stu; foreach (var stu in students) { Console.WriteLine($"{stu.Name}: {stu.Age}"); } Console.WriteLine(" Where 方法:"); students = context.Student.Where(s => s.Age >= 15 && s.Age <= 17); foreach (var stu in students) { Console.WriteLine($"{stu.Name}: {stu.Age}"); } } } } }
如你所见,LINQ 已完美整合进 C# 语法中,我们可以再套用标准的 C# 语法或其他的 C# 运算符,进而建立更为复杂的筛选表达式。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo { class Where { public void DoWhere() { int[] numberQuery = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 }; string source = "列表数据:"; foreach (var num in numberQuery) { source += num + ","; } Console.WriteLine(source + " "); IEnumerable<int> enumNumbers = from number in numberQuery where number <= 20 && number >= 10 select number; string result = "查询10-20之间的数字:"; foreach (var num in enumNumbers) { result += num + ","; } Console.WriteLine(result + " "); enumNumbers = from number in numberQuery where IsEven(number) select number; result = "查询偶数:"; foreach (var num in enumNumbers) { result += num + ","; } Console.WriteLine(result); } public bool IsEven(int value) { bool val = (value % 2) == 0; return val; } } }
可以看到 where 条件中调用了 IsEven 方法,来判断传值是否为偶数并返回结果,程序会根据此结果决定筛选的数据。
但是,当 LINQ 计算的数据记录是直接连接到底层数据进行存取时,由于牵涉 SQL 语句的转换问题,所以在 where
子句中引用独立函数时会出现无法解析的问题,因此必须将数据完全载入之后才能进一步运算。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace LINQDemo { class Where { public void DoWhere() { using(var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { IEnumerable<Student> students = from stu in context.Student where IsAgeRange(stu.Age) select stu; Console.WriteLine("查询 16-18 岁的学生:"); foreach (var stu in students) { Console.WriteLine($"{stu.Name} {stu.Age}"); } } } private bool IsAgeRange(int? age) { bool b = age >= 16 && age <= 18; return b; } } }
如同上面的示例,因为 IsAgeRange 方法无法被解析,所以就会出现如下错误:
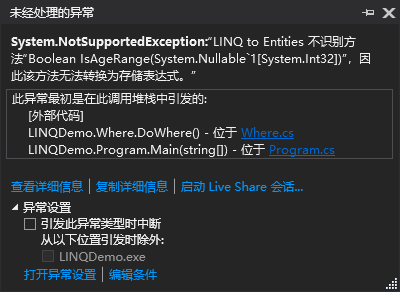
我们需要将 LINQ 语句进行 ToList 转换,以确保程序的正常运行:
IEnumerable<Student> students = from stu in context.Student.ToList() where IsAgeRange(stu.Age) select stu;
这么一来,由于数据完成了转换,所以程序得以正常运行:

4、OfType 方法
如果想要通过类型来筛选集合对象,可以通过引用 IEnumerable 的扩充方法 OfType 来实现。
对未导入泛型技术的旧型项目进行维护时,通过 OfType 可以很方便地对特定类型进行筛选。
实践出真知,上例子:
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class OfType { public void OfTypeDemo() { ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList() { "Mon","Tue","Wed","Thu","Fri","Sat","Sun", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", 1,2,3,4,5,6,7, }; Console.WriteLine("ArrayList 中的数据:"); foreach (var al in arrayList) { Console.WriteLine(al.ToString() + ","); } IEnumerable<string> arrList = arrayList.OfType<string>(); IEnumerable<string> strList = from strl in arrList select strl; Console.WriteLine(" OfType<string> 的筛选结果:"); foreach (var al in strList) { Console.WriteLine(al.ToString() + ","); } } } }
OfType 方法可以将传统的集合转换成支持 LINQ 查询的 IEnumerable 对象,它会只筛选符合类型的对象。
这个方法相当实用, 现在结合实体数据模型进行
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class OfType { public void DoOfType() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { var grands = from cg in context.CGrade.ToList() select GetStudent(cg); IEnumerable<rStudent> rStudents = grands.OfType<rStudent>(); foreach (var stus in rStudents) { Console.WriteLine($"{stus.Name} 的全部学生:"); foreach (var st in stus.Stus) { Console.WriteLine($" {st.Name}"); } } } } private object GetStudent(ClassGrade cg) { if (cg.GradeNum == 1) { rStudent rStudent = new rStudent() { Id = cg.CGId, Name = $"{cg.GradeNum}年级{cg.ClassNum}班", Stus = cg.Students }; return rStudent; }else { return cg; } } public class rStudent { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public IEnumerable<Student> Stus { get; set; } } } }
上面的例子通过 OfType 方法过滤出了属于一年级每个班级的童鞋:

5、排序
排序是查询操作中非常普遍的行为,LINQ 根据指定的对象属性对集合元素进行排序。
LINQ 中的排序方法:
OrderBy (升序排序)、OrderByDescending(降序排序)、ThenBy(二次升序排序)、ThenByDescending(二次降序排序)以及
Reverse(反转集合中的对象排列顺序)
屏上得来终觉浅,觉知此事得执行:
using System; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class OrderBy { public void GetDataOrderBy() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { // LINQ 语句 var stus = from stu in context.Student orderby stu.Age, stu.Name select stu; //OrderBy、ThenBy方法 var stu_met = context.Student.OrderBy(s => s.Age).ThenBy(s => s.Name); foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{stu.Name} 年龄:{stu.Age}"); } } } } }
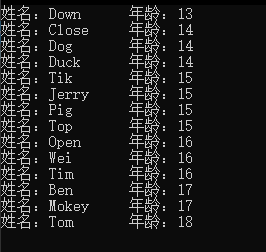
看下执行结果,如果没有出错的话,大概是按照年龄升序进行排序的:
降序排序只需在字段后面加上 descending 即可:
// LINQ 语句
var stus = from stu in context.Student orderby stu.Age descending select stu;
//OrderByDescending 方法 var stu_met = context.Student.OrderByDescending(s => s.Age);
// LINQ 语句 var stus = from stu in context.Student orderby stu.Age descending, stu.Name descending select stu; //OrderBy、ThenBy方法 var stu_met = context.Student.OrderByDescending(s => s.Age).ThenByDescending(s => s.Name);
多字段进行排序的话,需用 “,” (逗号) 进行分隔(先以年龄排序,再通过名称排序):
// LINQ 语句 var stus = from stu in context.Student orderby stu.Age, stu.Name select stu; //OrderBy、ThenBy方法 var stu_met = context.Student.OrderBy(s => s.Age).ThenBy(s => s.Name);
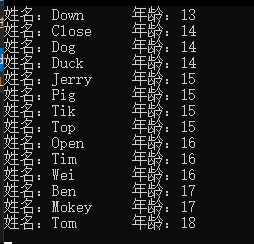
排序的痕迹有没有很明显?
反转输出
Reverse 是排序的方法之一,不过它并没有对应的 C# 语句,必须直接进行引用。
Reverse 方法不需要任何参数。
心动么?行动吧,再不行动,女神都老啦:
using System; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class Reverse { public void DoReverse() { using(var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { var stus = context.Student.OrderBy(s => s.Age).ToList(); stus.Reverse(); foreach (var stu in stus) { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{stu.Name} 年龄:{stu.Age}"); } } } } }
6、分组
分组通过一个指定的 key 返回分组化的数据内容,相关的语句有两种:group-by 和 group-by-into。
① group-by
group 表示将要查询的数据源进行分组,其后必须连接所要搜索的集合对象,by 则是指定作为分组依据的条件值。
分组运算返回的是一种 IGrouping<TKey, TElement> 类对象,表示一系列具有共同键值的对象集合,集合元素则
通过此键值辨识元素所属分组,因此我们可以通过分组运算来自定义逻辑,以达到将集合中的对象进行分类的目的。
干就完了:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class GroupDemo { public void DoGroup() { List<int> monthList = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 }; // LINQ IEnumerable<IGrouping<int, int>> query = from month in monthList group month by checkMonth(month); // GroupBy 方法 IEnumerable<IGrouping<int, int>> query2 = monthList.GroupBy(month => checkMonth(month)); foreach (var group in query) { Console.WriteLine(group.Key > 30 ? "每月31天" : group.Key < 30 ? "二月" : "每月30天"); foreach (var i in group) { Console.WriteLine($"{i}-{group.Key.ToString()}"); } Console.WriteLine(" "); } } public int checkMonth(int month) { int resultDays; resultDays = DateTime.DaysInMonth(2020, month); return resultDays; } } }
上面示例给每个月按照天数进行了分组归类:

② group-by-into
into 表示指定一个暂存的标识变量,用来存储每一个分组后的结果,然后针对每一个分组结果进一步执行其他的查询运算。
into 最后会将分组的结果存储于指定的标识变量中,因此一旦启用 into 就必须进一步在其后编写处理表达式,然后以 select
或另一个 group 作为结束。
把上例中的 LINQ 语句进行调整下:
// LINQ IEnumerable<IGrouping<int, int>> query = from month in monthList group month by checkMonth(month) into o orderby o.Key select o; //into 把分组结果的引用存储给了指定变量 o,然后通过 Key 对其进行了排序。 // GroupBy 方法 用 Select 实现 into 的功能 IEnumerable<IGrouping<int, int>> query2 = monthList.GroupBy(month => checkMonth(month)).Select(g => g).OrderBy(g => g.Key);

可以看到月份分组按照天数进行排序了。
接下来,结合 ADO.NET 实体数据模型来探讨下数据库的分组操作。
直接看示例吧:
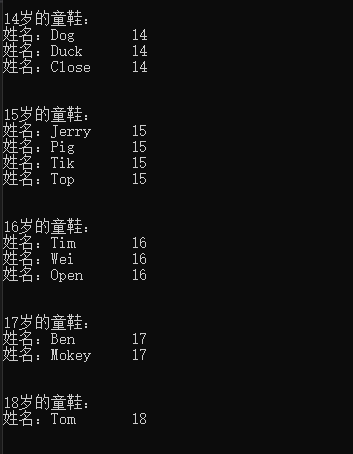
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class GroupDemo { public void DoADOGroup() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { IEnumerable<IGrouping<int?, Student>> groups = from stu in context.Student group stu by stu.Age; foreach (var gp in groups) { Console.WriteLine(gp.Key + "岁的童鞋:"); foreach (var stu in gp) { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{stu.Name} {stu.Age}"); } Console.WriteLine(" "); } } } } }
还是看结果吧:
我们还可以将分组的规则进行进一步的封装,以便简化 LINQ 语句:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class GroupDemo { public void DoGroupToMethod() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { IEnumerable<IGrouping<string, Student>> gps = from stu in context.Student.ToList() group stu by CheckAge(stu.Age ?? 0); foreach (var gp in gps) { Console.WriteLine(gp.Key); foreach (var stu in gp) { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{stu.Name} 年龄:{stu.Age}"); } Console.WriteLine(" "); } } } string CheckAge(int age) { if (age >= 18) return "成年"; else if (age >= 16 && age <= 18) return "青年"; else return "少年"; } } }
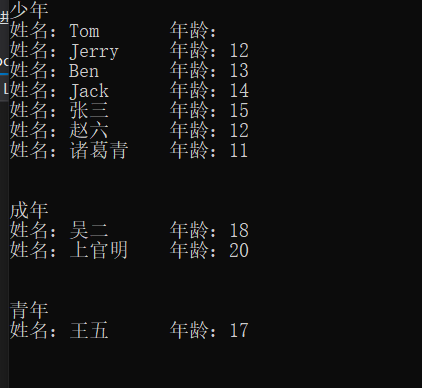
通过这种方式我们可以写更复杂的分组处理逻辑。
group-by-into 同样也可以结合 ADO.NET 实体数据模型来处理数据。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace LINQDemo.Demo { class GroupDemo { public void GroupInto() { using (var context = new StudentInfoModel()) { IEnumerable<IGrouping<int, ClassGrade>> gps = from cg in context.CGrade.ToList() group cg by cg.GradeNum into cgp orderby cgp.Key select cgp; foreach (var gp in gps) { Console.WriteLine($"{gp.Key}年级:"); foreach (var cg in gp) { foreach (var stu in cg.Students) { Console.WriteLine($"姓名:{stu.Name} 班级:{cg.ClassNum}班"); } } Console.WriteLine(" "); } } } } }
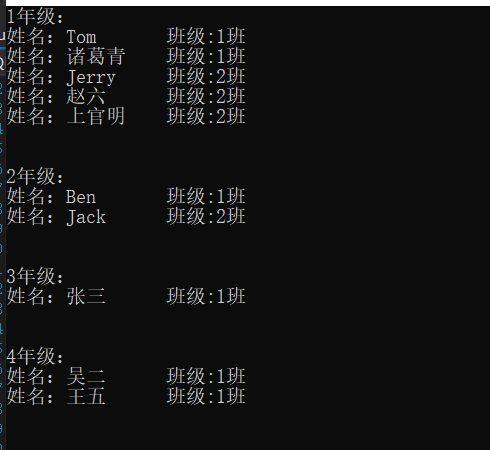
OK,篇幅过长…来日方长!拜了个拜!