JDBC介绍
JDBC(Java DataBase Connectivity)是Java和数据库之间的一个桥梁,是一个规范而不是一个实现,能够执行SQL语句。它由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成。各种类型的的数据库都有相应的实现,本文中的代码都是针对MySQL数据库实现的。

JDBC编程步骤
1、装载相应数据库的JDBC驱动并进行初始化
1.1导入专用的JAR包(不同的数据库需要的JAR包不同)
访问MySQL数据库需要用到第三方的类,这些第三方的类,都被压缩在一个.jar的文件里。mysql-connector-java-xxxx-bin.jar包可以在网上下载,或者在MySQL的安装目录下找。通常下载到该jar报纸后将其放到在项目的lib项目下,在本例会放在这个位置,然后在IDEA中导入这个jar包。
使用IDEA新建一个MAVEN项目,
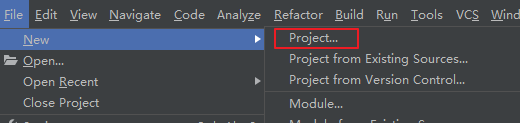
然后
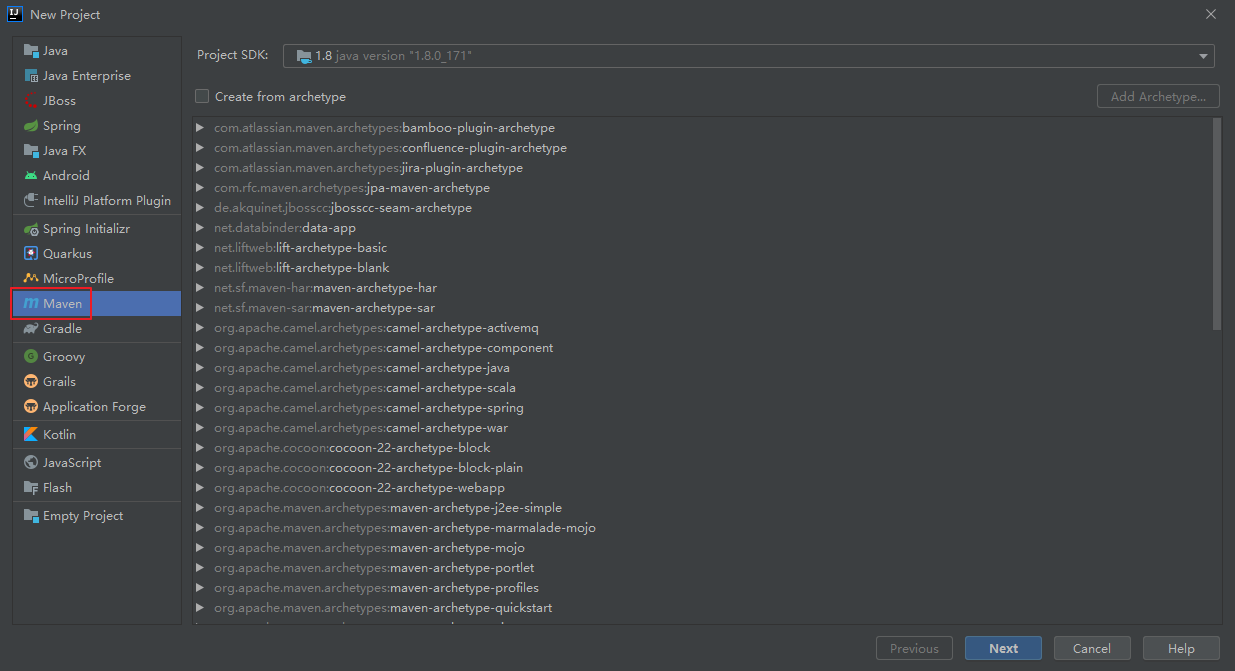
然后

创建完成
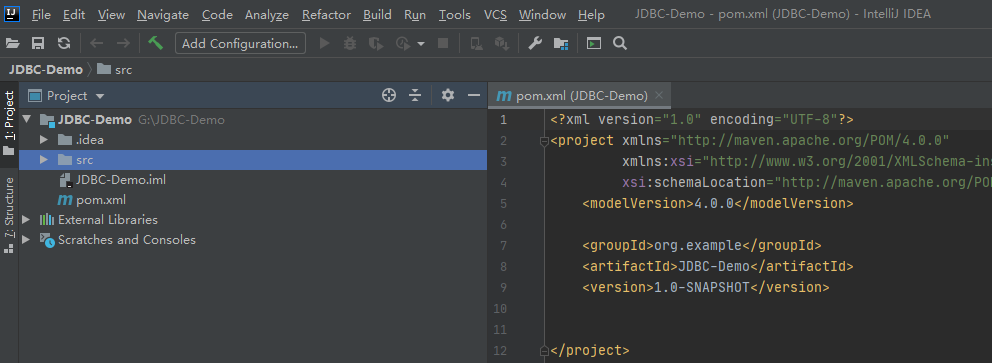
删除src文件夹

然后创建模块

然后

在JDBC-Demo的项目的pom.xml文件中加入mysql相关的包
<dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.47</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
使用Statement接口
package com.logan.jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; /** * 使用Statement接口 * Statement接口创建之后,可以执行SQL语句,完成对数据库的增删改查。其中,增删改只需要改变SQL语句的内容就能完成,然而查询略显复杂。 * 在Statement中使用字符串拼接的方式,该方式存在句法复杂,容易犯错等缺点,具体在下文中对比介绍。所以Statement在实际使用过程中用的非常少 * 所以具体的放到PreparedStatement那里给出详细代码。 * 字符串拼接方式的SQL语句是非常繁杂的,中间有很多的单引号和双引号的昏庸,极易出错。 */ public class JDBCDemo1 { public static Connection getConnection(){ Connection conn = null; try{ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/school?characterEncoding=UTF-8", "root", "logan123"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } return conn; } public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { Connection conn = getConnection(); Statement st = conn.createStatement(); String sql = "insert into course (CId,Cname,TId) values ('04','历史','04')"; st.execute(sql); System.out.println("执行插入语句成功"); } }
使用PreparedStatement接口
package com.logan.jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * 使用PreparedStatement接口 * 与Statement一样,PreparedStatement也是用来执行sql语句的,与Statement不同的是,需要根据SQL语句创建PreparedStatement。 * 除此之外,还能够通过设置参数,执行相应的值,而不是Statement那样使用字符串拼接。 * */ public class JDBCDemo2 { public static Connection getConnection(){ Connection conn = null; try{ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/school?characterEncoding=UTF-8", "root", "logan123"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } return conn; } //增加一条记录 public static void addCourse(String courseName) throws SQLException { String sql = "insert into course (CId,Cname,TId) values (?,?,?)"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try { conn = getConnection(); pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString(1,"05"); pstmt.setString(2,courseName); pstmt.setString(3,"05"); pstmt.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { conn.close(); } } //删除一条记录 public static void delCourse(String courseId) throws SQLException { String sql = "delete from course where CId = ?"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try{ conn = getConnection(); pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString(1,courseId); pstmt.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { conn.close(); } } //修改一条记录 public static void modifyCourse(String courseId) throws SQLException { String sql = "update course set Cname=? where CId=?"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try{ conn = getConnection(); pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); pstmt.setString(1,"物理"); pstmt.setString(2,courseId); pstmt.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { conn.close(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { delCourse("05"); } }
从上面的增删改程序可以看出,他们的代码都是大同小异的,主要是SQL语句存在差异,其他地方几乎是完全相同的。其中有几个地方需要注意:
1、使用PreparedStatement时,它的SQL语句不采用字符串拼接的方式,而是采用占位符的方式。“?”在这里就起到占位符的作用,这种方式除了避免了statement拼接字符串的繁琐之外,还能够提高性能。
每次SQL语句都是一样的,java类就不会再次编译,这样能够显著提高性能。
后面需要用到PreparedStatement接口创建的pstmt的set方法给占位符进行赋值。
注意一点,这里的参数索引是从1开始的。
增删改都使用pstmt.executeUpdate()语句进行SQL语句的提交。下文的查询会有所不同,请注意。
2、在添加的过程中,如果添加的数据量比较大的话,可以使用批量添加。
PreparedStatement接口提供了相应的批量操作的方法。
public static void addCourse(String courseName) throws SQLException { String sql = "insert into course (CId,Cname,TId) values (?,?,?)"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try { conn = getConnection(); pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 1;i<100;i++){ pstmt.setString(1,"05"); pstmt.setString(2,courseName); pstmt.setString(3,"05"); pstmt.addBatch(); if (i%10 == 0){ pstmt.executeBatch(); } } } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { conn.close(); } }
下面我们来看看稍微麻烦一点的查询操作:
public static List<Course> findCourseList() throws SQLException { String sql = "select * from course order by CId"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pstmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; List<Course> courseList = new ArrayList<Course>(); try { conn = getConnection(); pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); while (rs.next()){ String courseId = rs.getString("CId"); String courseName = rs.getString("Cname"); String TId = rs.getString("TId"); Course course = new Course(); course.setCId(courseId); course.setCname(courseName); course.setTId(TId); courseList.add(course); } } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); }finally { conn.close(); } return courseList; } public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { List<Course> courseList = findCourseList(); for (Course course:courseList){ System.out.println(course); } }
4、处理和显示结果
执行查询语句,并把结果集返回给集合ResultSet
利用While(ResultSet.next()){}循环将集合ResultSet中的结果遍历出来。
5、释放资源
在JDBC编码的过程中我们创建了Connection、ResultSet等资源,这些资源在使用完毕之后是一定要进行关闭的,关闭的过程中遵循从里到外的原则,因为在增删改查的操作中都要用到这样的关闭操作,为了使代码简单,增加其重复性,这里我将这些关闭的操作写成一个方法和建立连接的方法一起放到一份工具类中。
package com.logan.utils; import java.sql.*; public class DbUtil { public static Connection getConnection(){ Connection conn = null; try{ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/school?characterEncoding=UTF-8", "root", "logan123"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } return conn; } public static void close(PreparedStatement pstmt){ if(pstmt != null){ try{ pstmt.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void close(Connection conn){ if(conn != null){ try{ conn.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void close(ResultSet rs){ if(rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException throwables) { throwables.printStackTrace(); } } } }
JDBC编程的内容就这些了。
还有涉及到事务、获取自增、获取元数据、ORM、DAO、数据连接池等内容
Statement和PreparedStatement的异同及优缺点
同:两者都是用来执行SQL语句的
异:PreparedStatement需要根据SQL语句来创建,他能够通过设置参数,指定相应的值,不是像Statement那样使用字符串拼接的方式。
PreparedStatement的优点:
1、使用参数设置,可读性好,不易记错。在Statement中使用字符串拼接,可读性差和维护性比较差。
2、具有预编译机制,性能比Statement更快。
3、能够有效防止SQL注入攻击。
execute和executeUpdate的区别
相同点:二者都能够执行增加、删除、修改等操作。
不同点:
1、execute可以执行查询语句,然后通过getResult把结果取出来。executeUpdate不能执行查询语句。
2、execute返回Boolean类型,true表示执行的是查询语句,false表示执行的insert、delete、update等。executeUpdate的返回值是int,表示有多少条数据受到了影响。