网易云音乐链接 : 点我听歌.
练习:
一、继承与派生——公有
实例:
#include<iostream.h>
class A //A类
{
private :
int a;
public :
void inita(int n) //初始化A类的成员变量
{
a=n;
}
int geta() //访问获取A类的值
{
return a;
}
};
class B:public A //B类继承A类
{
private:
int b;
public:
void initb(int m) //初始化B类的成员变量
{
b=m;
}
int getb() //访问获取B类的值跟A类的成员变量相乘并返回结果
{
return b*geta();
}
};
void main()
{
int s; //存取后续的值
B ob; //创建一个B类的对象ob
//oa.inita(5);
ob.A::inita(5); //初始化a的值(派生类拥有基类的成员特性)
ob.initb(8); //初始化内部b的值
s=ob.getb(); //调用函数并返回值给 s
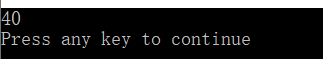
cout<<s<<endl; //打印输出
}
运行结果:
二、继承与派生–私有
实例:
#include<iostream.h>
class A //A类
{
private :
int a;
public :
void inita(int n) //初始化成员变量
{
a=n;
}
int geta() //返回成员变量的值
{
return a;
}
};
class B:private A //B继承A(私有继承)---私有特性
{
private:
int b;
public:
void initb(int m,int n) //由于私有继承,需要公有函数来访问并初始化基类
{
b=m;
inita(n); //初始化A类的成员变量
}
int getb() //获取成员变量与基类成员变量的积
{
return b*geta();
}
};
void main()
{
int s; //用于存放返回值
B ob; //创建一个对象ob
ob.initb(8,5); //初始化成员变量
s=ob.getb(); //返回乘积
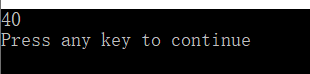
cout<<s<<endl; //打印
}
运行结果:
三、子类的构造函数、析构函数
定义人类 学生类 老师类
实例:
#include<iostream.h>
class person //创建person类
{
public:
int age; //年龄
char *name; //名字指针
public:
void eat();
void run(); //功能函数(人能干什么)
person(int x,char *s); //构造函数---初始化成员变量
~person(); //析构函数(与构造函数成对存在)
};
void person::eat() //人类“吃”函数
{
cout<<"人类吃饭"<<endl;
}
void person::run() //人类“运动”函数
{
cout<<"人类运动"<<endl;
}
person::person(int x,char *s) //构造函数初始化
{
age=x;
name=s;
cout<<"人类构造函数"<<endl;
}
person::~person() //析构函数
{
cout<<"人类析构函数"<<endl;
}
class student:public person //学生student类公有继承person
{
public:
char *sno; //学生标志(可以填学号)
public:
void study(); //学生功能函数
student(int x,char *s,char *s1):person(x,s)//子类的构造函数---参数列表(给基类成员变量初始化)
{
sno=s1;
cout<<"学生类构造函数"<<endl;
}
~student(); //子类析构函数
};
void student::study() //功能函数
{
cout<<"学生学习"<<endl;
}
student::~student() //
{
cout<<"学生类析构函数"<<endl;
}
class teacher:public person //老师teacher类公有继承person类
{
public:
char *tno; //老师标志位(工号)
public:
void teach(); //老师功能函数
teacher(int x,char *s,char *s1):person(x,s)//子类的构造函数
{
tno=s1;
cout<<"教师类构造函数"<<endl;
}
~teacher();
};
void teacher::teach()
{
cout<<"教师教书"<<endl;
}
teacher::~teacher()
{
cout<<"教师类析构函数"<<endl;
}
void main()
{
person p1(20,"xiaoming"); //基类对象
student s1(20,"xiaoli","2018110110"); //student类对象
teacher t1(20,"fubw","2540"); //teacher类对象
//p1.age=20;
//p1.name="小明";
cout<<p1.age<<endl; //打印p1基类对象的年龄
cout<<p1.name<<endl; //打印p1基类对象的名字
p1.eat();
p1.run(); //打印p1基类对象的功能
cout<<s1.age<<endl; //打印s1学生类对象的年龄
cout<<s1.name<<endl; //打印s1学生类对象的名字
cout<<s1.sno<<endl; //打印s1学生类对象的学号
s1.person::eat();
s1.eat();
s1.person::run();
s1.study(); //打印s1学生类对象的功能
t1.teach(); //打印t1老师类对象的功能
cout<<t1.age<<endl; //打印t1老师类对象的年龄
cout<<t1.name<<endl; //打印t1老师类对象的名字
cout<<t1.tno<<endl; //打印t1老师类对象的工号
}
运行结果:

四、多重继承
存在问题的实例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person //Person类
{
public:
void sleep()
{cout << "sleep" << endl;}
void eat()
{cout << "eat" << endl;}
};
class Author : public Person //Author继承自Person
{
public:
void writeBook()
{cout << "write Book" << endl;}
};
class Programmer : public Person //Programmer继承自Person
{
public:
void writeCode()
{cout << "write Code" << endl;}
};
class Programmer_Author : public Programmer, public Author //多重继承
{
};
int main()
{
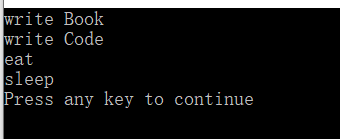
Programmer_Author pa;
pa.writeBook(); //调用基类Author的方法
pa.writeCode(); //调用基类Programmer的方法
pa.eat(); //编译错误,eat()定义不明确 在Author 和Programmer继承时添加virtual
pa.sleep(); //编译错误,sleep()定义不明确
//pa.Author::eat();//指定到底是哪个基类的方法
return 0;
}
报错:

修改:
在继承Person类的两个类前面加上 virtual
class Author : virtual public Person
class Programmer : virtual public Person
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person //Person类
{
public:
void sleep()
{cout << "sleep" << endl;}
void eat()
{cout << "eat" << endl;}
};
class Author : virtual public Person //Author继承自Person
{
public:
void writeBook()
{cout << "write Book" << endl;}
};
class Programmer : virtual public Person //Programmer继承自Person
{
public:
void writeCode()
{cout << "write Code" << endl;}
};
class Programmer_Author : public Programmer, public Author //多重继承
{
};
int main()
{
Programmer_Author pa;
pa.writeBook(); //调用基类Author的方法
pa.writeCode(); //调用基类Programmer的方法
pa.eat(); //编译错误,eat()定义不明确 在Author 和Programmer继承时添加virtual
pa.sleep(); //编译错误,sleep()定义不明确
//pa.Author::eat();//指定到底是哪个基类的方法
return 0;
}
运行结果:
五、虚基类
虚基类:解决继承中 间接多次继承同一个类 所出现的二义性问题
主要看看构造函数的加载先后顺序
父类-----子类------孙类
实例:
#include<iostream.h>
class p
{
public :
char *name;
public :
p()
{
name="xiaoming";
cout<<"p类的构造函数 "<<name<<endl;
};
};
class s:virtual public p
{
public :
s()
{
cout<<"s类的构造函数 "<<name<<endl;
}
};
class w :virtual public p
{
public :
w()
{
cout<<"w类的构造函数 "<<name<<endl;
}
};
class sw: public s, public w
{
public :
sw()
{
cout<<"sw类的构造函数 "<<name<<endl;
}
};
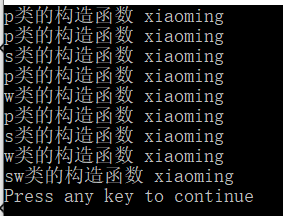
void main()
{
p p1;
s s1;
w w1;
sw sw1;
}
运行结果:
作业:
一、选择题:
1、定义派生类时,若不使用关键字显式地规定采用体积继承方式,则默认方式是______。
A.私有继承 B.非私有继承 C.保护继承 D.公有继承
2、在一个派生类的成员函数中,试图调用其基类的成员函数“void f();”,但无法通过编译。这说明______。
A. f()是基类的私有成员 B.f()是基类的保护成员
C.派生类的继承方式是私有 D.派生类的继承方式为保护
3、已知基类Employee只有一个构造函数,其定义如下:
Employee::Employee( int n ) : id(n){}
Manager 是 Employee的派生类,则下列对Manager的构造函数定义中,正确的是______。
A.Manager :: Manager ( int n ) : id(n) {}
B.Manager :: Manager ( int n ) : {id=n}
C.Manager :: Manager ( int n ) : Employee(n) {}
D.Manager :: Manager ( int n ) { Employee(n);}
派生类构造函数提供了将参数传递给基类构造函数的途径,以保证在基类进行
初始化时能够获得必要的数据。基类的构造函数是带有参数的,需要在派生类的
构造函数名后面显式调用基类的构造函数。
4、关于虚基类的描述中,错误的是______。
A.使用虚基类可以消除由多继承产生的二义性
B.构造派生类对象时,虚基类的构造函数只被调用一次
C.声明“class B: virtual public A”,说明类B为虚基类
D.建立派生类对象时,首先调用虚基类的构造函数
答案:
1~4 A C C C
二、编程题
1、定义一个长方形Rect类,派生出长方体类Cub,计算派生类对象的表面积和体积。
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect //长方形类
{
private :
int rect_length;
int rect_width; //长宽
public :
Rect(int l, int w) //构造函数
{
rect_length = l;
rect_width = w;
}
int getl()
{return rect_length;}
int getw()
{return rect_width;}
~Rect()
{}
};
class Cub :public Rect //Cub类公有继承Rect类
{
private:
int cub_height; //高
public:
Cub(int l, int w, int h):Rect(l,w)
{
cub_height = h;
}
int surfaceArea() //返回表面积
{
return (2*(getl()*getw()+getl()*cub_height+getw()*cub_height));
}
int volume() //返回体积
{
return (getl()*getw()*cub_height);
}
~Cub() //析构函数
{}
};
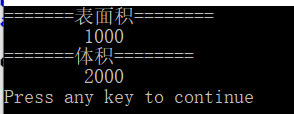
int main()
{
Rect objFir(10,20);
Cub objSec(10,20,10);
cout<<"=======表面积========
";
cout<<" "<<objSec.surfaceArea()<<endl;
cout<<"=======体积========
";
cout<<" "<<objSec.volume()<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2、定义一个Shap基类,并派生出圆球体(Sphere)和立方体类(Cube),分别求圆球体与立方体对象的表面积和体积。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define PI 3.14
class Shap //Shap基类
{
private :
int length;
public :
int getl()
{return length;}
};
class Sphere: public Shap //Sphere公有继承Shap基类
{
private:
int rad;
public :
Sphere(int r)
{
rad = r;
}
double surArea_1() //体积
{
return (4/3*PI*pow(rad,3));
}
double volume_1() //面积
{
return (4*PI*pow(rad,2));
}
~Sphere() //析构函数
{}
};
class Cube :public Shap //Cube类公有继承Shap基类
{
int len;
public:
Cube(int l)
{
len = l;
}
double surArea_2()
{
return (6*pow(len, 2));
}
double volume_2()
{
return (pow(len, 3));
}
~Cube() //析构函数
{}
};
int main()
{
//Shap objS; //基类对象
Sphere objSp(2); //半径为2的球体
Cube objC(5); //棱长为5的立方体
cout<<"球体的表面积:"<<objSp.surArea_1()<<" 体积为:"<<objSp.volume_1()<<endl;
cout<<"立方体的表面积:"<<objC.surArea_2()<<" 体积为:"<<objC.volume_2()<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
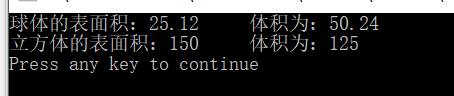
指正在求球体的表面积和体积的时候,对应输出 表面积跟体积相反了(看注释)