1.GitHub项目网址:
项目语言:Java;编译运行平台:IntelliJ IDEA;Github网址:https://github.com/DuoRouLongShu/WordCount
2.个人PSP
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
|
|
·Estimate |
·估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
|
|
Development |
开发 |
1600 |
|
|
·Analysis |
·需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
|
|
·Design Spec |
·生成设计文档 |
20 |
|
|
·Design Review |
·设计复审(和同事审核设计文档) |
50 |
|
|
·Coding Standard |
·代码规范(为目前的开发指定合适的规范) |
30 |
|
|
·Design |
·具体设计 |
80 |
|
|
·Coding |
·具体编码 |
150 |
|
|
·Code Review |
·代码复审 |
30 |
|
|
·Test |
·测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
|
|
Reporting |
报告 |
60 |
|
|
·Test Report |
·测试报告 |
75 |
|
|
·Size Measurement |
·计算工作量 |
10 |
|
|
·Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 |
15 |
|
|
Total |
合计 |
2765 |
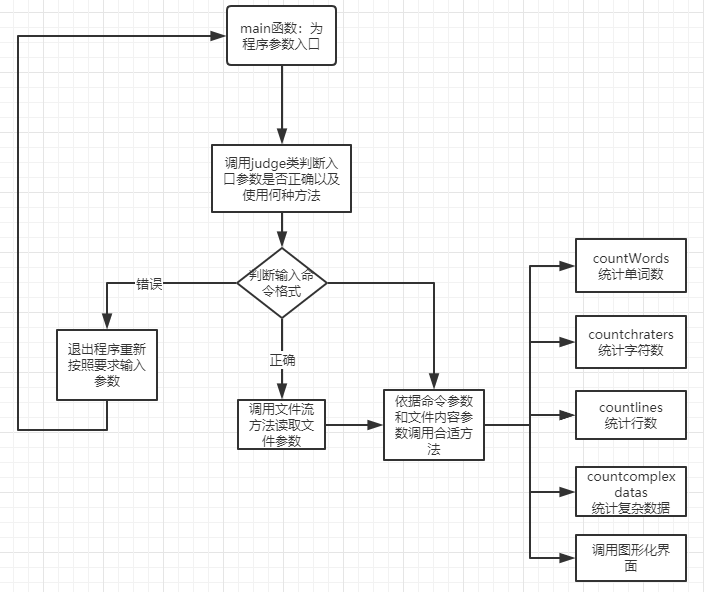
3.题目介绍与解题思路
3.1题目:
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。 具体功能要求: 程序处理用户需求的模式为:wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
扩展功能: -s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。 -a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”。
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。一个有趣的例子是有些程序员会在单字符后面加注释:
} //注释 在这种情况下,这一行属于注释行。
高级功能:
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。
需求举例: wc.exe -s -a .c
返回当前目录及子目录中所有.c 文件的代码行数、空行数、注释行数。
3.2解题思路
3.2.1需求分析
-
简单思路
-
拿到题目我想到用Java实现的话,应该分成两大模块,一是各个统计功能的代码实现,二是怎样获取到所需文件。初步想法是文件的获取录入采用文件流的思想,逐步获取到所需文件;然后将获取到的文件里面的内容按照要求的功能调用相关的方法
-
这样的话应该先把各个统计功能先实现,因为这是整个程序的核心。应该可以用到上课学的,单元测试,单元开发,这样就不用一个点设计错误全盘错误
-
-
找资料
这是最头痛的,因为很多很多自己都还没学过,直接上手这样一个Java项目着实吓到我了
-
查了正则表达式,因为觉得它好像是能具体字符出什么是什么,会对统计功能实现起到极方便的作用
-
查了单元测试,基于idea平台该如何进行,确实会帮到你开发,具体的junit链接都放在CSDN收藏夹。
-
查了如何将Java程序转成exe,因为看着需求确实不明白该怎样输入程序,以及自己的知识盲区图形化GUI界面这些
-
3.2.1程序框架
4.设计实现过程
4.1项目总体布局
-
WordCountDemo是入口参数类,用以处理入口参数判断以及选择具体统计功能的主类
-
TooltoCount是统计工具类,用以调用具体的文件流方法,以及统计功能方法
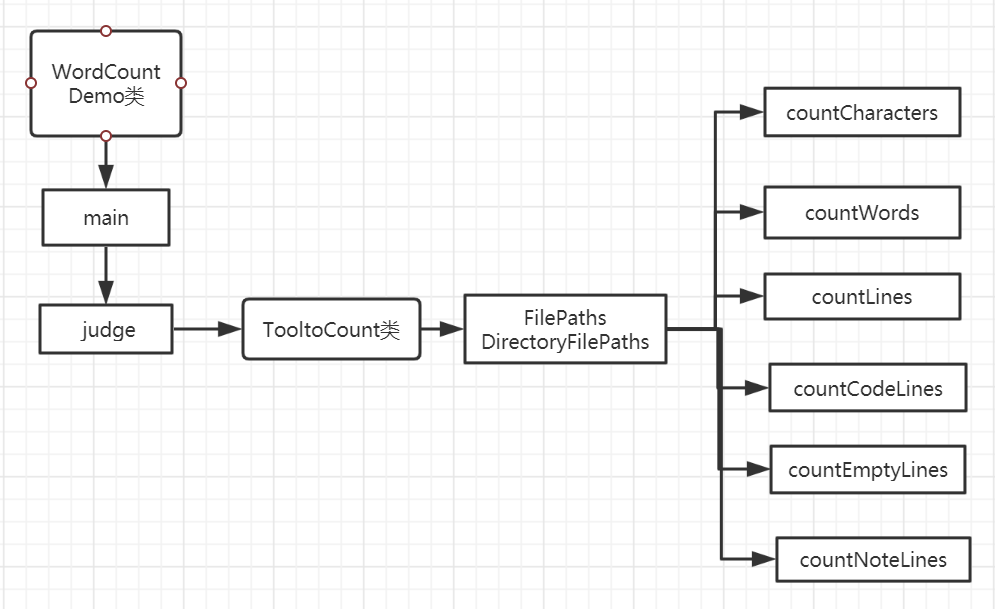
4.2具体类与具体函数与其之间的调用
-
WordCountDemo类里面的函数:public static void main(String[] args)和public String judge(String[] args)
-
TooltoCount类里面的函数:
public String countCharacters(Set<String> file_paths)
public String countWords(Set<String> file_paths)
public String countLines(Set<String> file_paths)
public String countCodeLines(Set<String> file_paths)
public String countEmptyLines(Set<String> file_paths)
public String countNoteLines(Set<String> file_paths)
public Set<String> FilePaths(Set<String> names)
public static Set<String> DirectoryFilePaths(Filefile) -
它们之间的关系
5.代码说明
/** *统计字符数 *输入参数为文件路径 */ public String countCharacters(Set<String> file_paths) { int sum = 0,bytes = 0; byte[] t = new byte[30*2048];//存储字符数组 String count_result = ""; int length = t.length;//新建length避免循环调用t.length FileInputStream in = null; try { for (String file_path : file_paths) { in = new FileInputStream(file_path); while ((bytes = in.read(t,0,length))!=-1) { sum+=bytes;//统计字符数 } count_result += file_path + "-字符数:" + sum ;//存储输出的结果 sum = 0; } //如果输入有误 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {//抛出程序异常,退出程序 System.exit(0); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return count_result; }
/** *统计单词数 *输入参数为文件路径 */ public String countWords(Set<String> paths){ int Count = 0; String count_result = ""; StringBuffer SaveString = new StringBuffer(); String Tmp = ""; try { for (String Path : paths) { Tmp = SaveString.toString();//用split方法区分单词 Tmp = Tmp.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z\s+]", " "); Total = Tmp.split("[\s+,\. ]");//读取到的输入文件的数组 Count = Total.length; count_result += Path+"-单词数:"+Count;// 字符串数组长度就是单词个数 SaveString.setLength(0); Count = 0; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // 检查到文件不存在,结束程序 System.exit(0); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return count_result; }
/** *统计代码数 *输入参数为文件路径 */
public String countCodeLines(Set<String> paths) {
FileInputStream is = null; InputStreamReader ist = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { for (String filePath :paths) { is = new FileInputStream(filePath); ist = new InputStreamReader(is); br = new BufferedReader(ist); while((tmp = br.readLine())!=null) { // 去除读取的空格 tmp = tmp.replace(" ", ""); if (!"".equals(tmp)&&!tmp.startsWith("//")&&tmp.indexOf("//")!=1) { count++;// 改行不为空,则计数+1 } } // 拼接结果字符串 result+=filePath + "-代码行数:" + count; // 重置count count = 0; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { // 关闭输入流 is.close(); ist.close(); br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return result; }

public String countLines(Set<String> filePaths) { int count = 0; // foreach循环遍历数组 for (String filePath : filePaths) { bis = new BufferedReader(isr); // 实例化缓存输入流对象 while (bis.readLine()!=null) { count++; } // 结果字符 result += filePath+",行数:" + count;count = 0; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // 检查到文件不存在 // 结束程序 System.exit(0); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { // 关闭文件字符输入流 in.close(); // 关闭字节输入流 isr.close(); // 关闭缓存输入流 bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return result; }

public String countEmptyLines(Set<String> filePaths) { // 结果字符串 String result = ""; // 缓存变量 String tmp = ""; // 统计次数 int count = 0; // 得到输入流 FileInputStream is = null; InputStreamReader ist = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { for (String filePath : filePaths) { is = new FileInputStream(filePath); ist = new InputStreamReader(is); br = new BufferedReader(ist); while((tmp = br.readLine())!=null) { // 改行不为空,则计数+1 if ("".equals(tmp)) { count++; } } // 拼接结果字符串 result+=filePath+ ",空行数:" + count; // 重置count计数变量 count = 0; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { // 关闭输入流 is.close(); ist.close(); br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return result; }

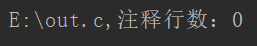
public String countNoteLines(Set<String> filePaths) { // 结果字符串 String result = ""; // 缓存变量 String tmp = ""; // 统计次数 int count = 0; // 得到输入流 FileInputStream is = null; InputStreamReader ist = null; BufferedReader br = null; try { for (String filePath : filePaths) { is = new FileInputStream(filePath); ist = new InputStreamReader(is); br = new BufferedReader(ist); while((tmp = br.readLine())!=null) { // 去除读取的空格,方便识别内容类型 tmp = tmp.replace(" ", ""); // 改行不为空,则计数+1 if (!"".equals(tmp)&&tmp.startsWith("//")||tmp.indexOf("//")==1) { count++; } } // 拼接结果字符串 result+=filePath + ",注释行数:" + count; // 重置count计数变量 count = 0; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { // 关闭输入流 is.close(); ist.close(); br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return result; }
/** *主函数main *调用程序入口参数 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String choose = null ;//判断输入变量 //新建WordCountDemo类,用以控制函数调用 WordCountDemo wordCountDemo = new WordCountDemo(); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("校验是否执行如下命令行:"); //循环输出命令行 for (int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){ System.out.println(args[i]); } System.out.println("输入Y确定并执行程序,输入N退出程序"); choose = scanner.nextLine(); if (choose.charAt(0) == 'Y') { wordCountDemo.judge(args);//如果命令行没错就执行判断方法 }else { System.exit(0); } }
/** *judge函数,用于判断入口参数命令行,判断调用那些统计方法 *入口参数为args */ public String judge(String[] args){ String count_result = ""; //取得文件输入流 paths = tooltoCount.getAllFilePaths(paths); for (int i = 0;i < args.length;i++){ //循环判断输入命令是否为功能 if(!args[i].startsWith("-") || args[i].endsWith("-s")){ if (args[i].startsWith("-s")){ paths.add(args[i+1]);//如果为-s,收集查询条件 } paths.add(args[i]);// } } for (int j = 0;j < args.length;j++){ if (args[j].startsWith("-") == true){ switch (args[j]){ case "-c": //-c指令 count_result += tooltoCount.countCharacters(paths) + " "; break; case "-w": //-w指令 count_result += tooltoCount.countWords(paths) + " "; break; case "-l": //-l指令 count_result += tooltoCount.countLines(paths) + " "; break; case "-s": //-s指令 if (!args[j+1].startsWith("-")){ paths = tooltoCount.getAllFilePaths(paths); } break; case "-a": //-a指令 count_result += tooltoCount.countCodeLines(paths) + " "; count_result += tooltoCount.countEmptyLines(paths) + " "; count_result += tooltoCount.countNoteLines(paths) + " "; break; case "-x": //-c指令,还未实现 break; default: System.out.println("输入错误!"); break; } } } System.out.println(count_result); return count_result; }
6.测试运行
单元测试:
//junit单元测试 @org.junit.Test public void testcountCharacters() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "E:\test.java"; String File2 = "E:\WordCount"; filePaths.add(File2); filePaths.add(File1); filePaths =new TooltoCount().getAllFilePaths(filePaths); String Result = new TooltoCount().countCharacters(filePaths); System.out.println(Result); } @org.junit.Test public void testcountWords() { Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "E:\test.java"; String File2 = "E:\WordCount"; String stopList = ""; filePaths.add(File2); filePaths.add(File1); filePaths =new TooltoCount().getAllFilePaths(filePaths); System.out.println(new TooltoCount().countWords(filePaths)); } @org.junit.Test public void testcountLines(){ Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String File1 = "E:\test.java"; String File2 = "E:\WordCount"; filePaths.add(File2); filePaths.add(File1); filePaths =new TooltoCount().getAllFilePaths(filePaths); System.out.println(new TooltoCount().countLines(filePaths)); } @org.junit.Test public void testcountCodeLines(){ Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String result = new TooltoCount().countCodeLines(filePaths); System.out.println(result); } @org.junit.Test public void testcountEmptyLines(){ Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String result = new TooltoCount().countEmptyLines(filePaths); System.out.println(result); } @org.junit.Test public void countNoteLines(){ Set<String> filePaths = new HashSet<String>(); String result = new TooltoCount().countNoteLines(filePaths); System.out.println(result); }
- 采用junit进行单元测试十分方便高效
- 先在E盘新建一个Word Count文件夹和一个test.java


- 各项结果




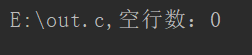
程序输入方法:
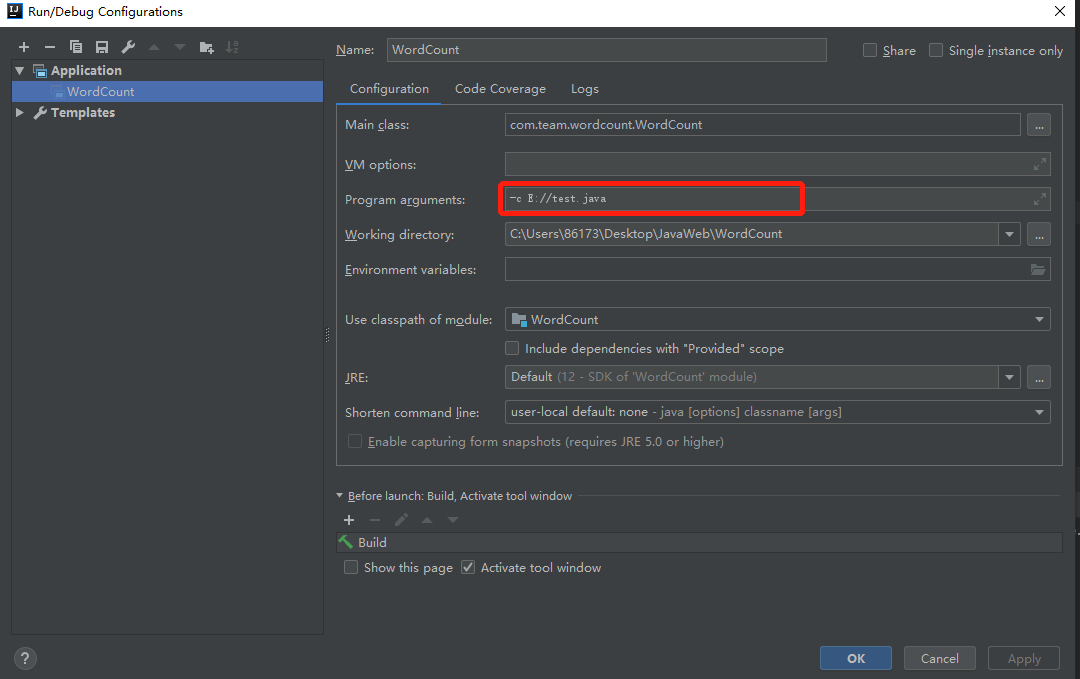
因为程序使用args传入参数,所以在控制台使用程序参数进行输入
输入用例:以下两文件为E盘的文件夹

以及一个实际上的Java源文件,它是放于E盘目录下的
![]()

-x结果:


7.个人PSP
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
15 |
|
·Estimate |
·估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
30 |
|
Development |
开发 |
1200 |
200 |
|
·Analysis |
·需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
150 |
|
·Design Spec |
·生成设计文档 |
20 |
30 |
|
·Design Review |
·设计复审(和同事审核设计文档) |
0 |
0 |
|
·Coding Standard |
·代码规范(为目前的开发指定合适的规范) |
30 |
60 |
|
·Design |
·具体设计 |
20 |
40 |
|
·Coding |
·具体编码 |
150 |
2160 |
|
·Code Review |
·代码复审 |
30 |
990 |
|
·Test |
·测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
185 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
60 |
60 |
|
·Test Report |
·测试报告 |
30 |
30 |
|
·Size Measurement |
·计算工作量 |
10 |
10 |
|
·Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 |
15 |
500 |
|
Total |
合计 |
2765 |
3308 |
8.个人总结
第一次撰写博客有很多迷茫之处,但是过程中我发现这其实是对整个项目过程的一次回顾与反思。在以前的作业中,通常都是写完代码测试完后就不再关注,也不会反在完成项目的途中犯过什么样的错误。每当下次遇到同样的问题还是会被困扰住,所以我觉得写博客是真的有必要的。我们的目的就在于回顾过程,反思过程中的错误,让项目的过程在我们脑海里留下更深的印象。总的来说,这个项目还没有到完备的阶段。最后,这次的作业的量还是算比较大的,但是却真的能感觉到有很多的收获。很多东西都是词不达意的,真的用心体会过就能明白。也是希望这不完备的代码可以使自己更加完善,更加明白做工一定要做细!