决策树
原理
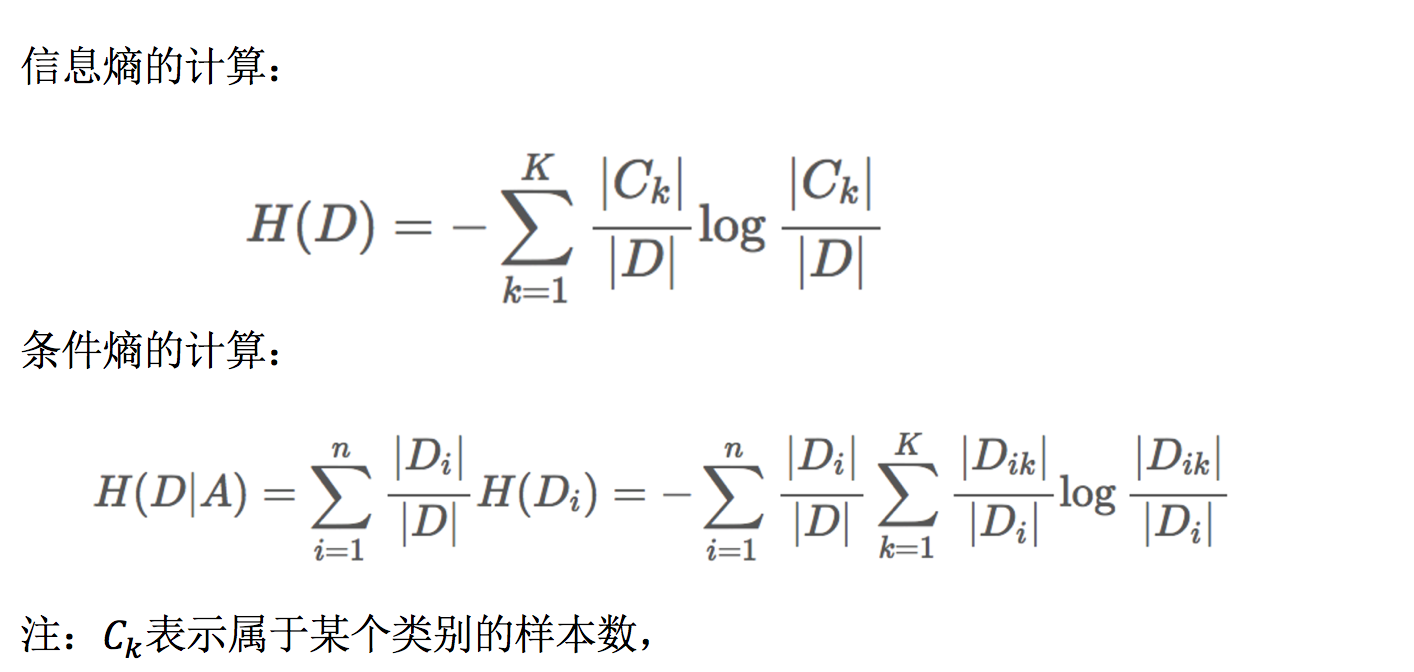
信息熵
定义:H的专业术语称之为信息熵,单位为比特。

总结:信息和消除不确定性是相联系的
信息增益:决策树的划分依据之一
定义与公式
特征A对训练数据集D的信息增益g(D,A),定义为集合D的信息熵H(D)与特征A给定条件下D的信息条件熵H(D|A)之差,即公式为:
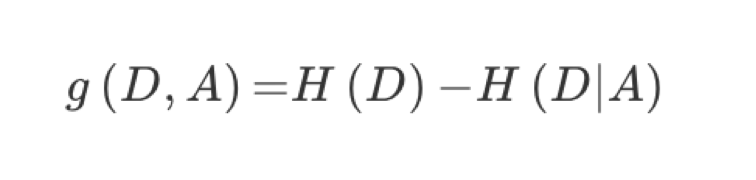
信息增益表示得知特征X的信息而息的不确定性减少的程度使得类Y的信息熵减少的程度
决策树API
class sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion=’gini’, max_depth=None,random_state=None)
- 决策树分类器
- criterion:默认是’gini’系数,也可以选择信息增益的熵’entropy’
- max_depth:树的深度大小
- random_state:随机数种子
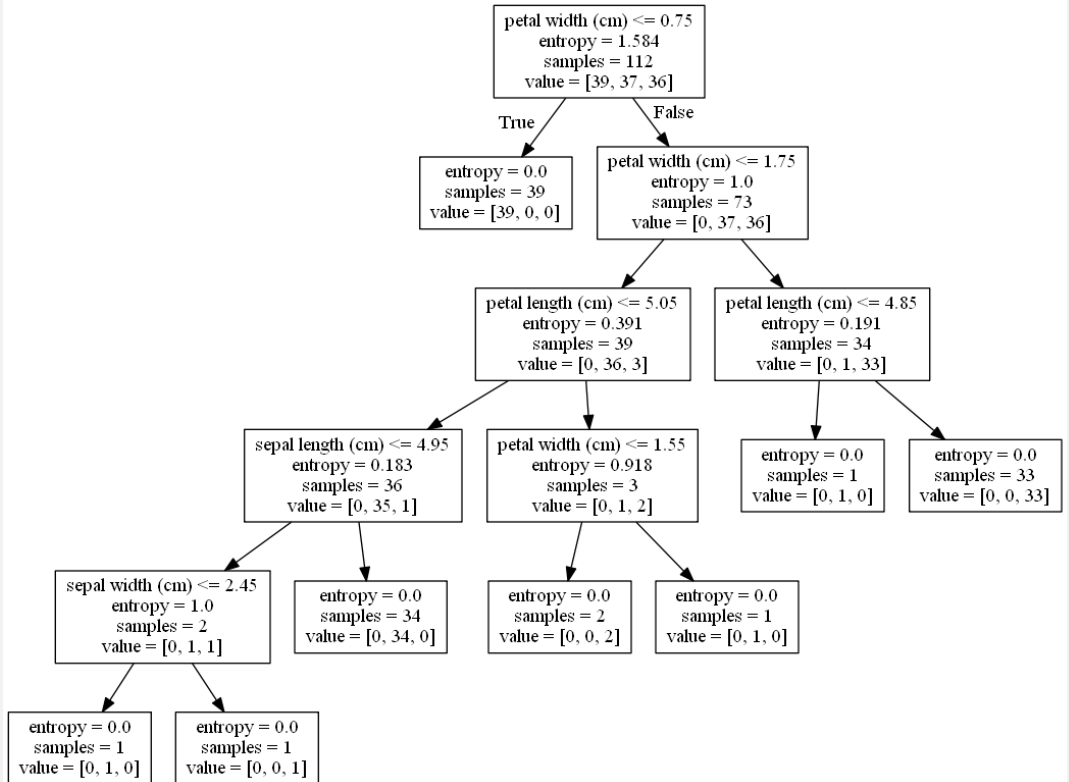
案例:用决策树对鸢尾花进行分类
代码
def decision_iris(): """ 用决策树对鸢尾花进行分类 :return: """ # 1)获取数据集 iris = load_iris() # 2)划分数据集 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, random_state=22) # 3)决策树预估器 estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy") estimator.fit(x_train, y_train) # 4)模型评估 # 方法1:直接比对真实值和预测值 y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test) print("y_predict: ", y_predict) print("直接比对真实值和预测值: ", y_test == y_predict) # 方法2:计算准确率 score = estimator.score(x_test, y_test) print("准确率为: ", score) # 可视化决策树 #export_graphviz(estimator, out_file="tree.dot", feature_names=iris.feature_names) dot_data = export_graphviz(estimator, out_file=None, feature_names=iris.feature_names) graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data) graph.write_pdf("iris.pdf") graph.write_png("tree.png") return None

决策树总结
- 优点:
- 简单的理解和解释,树木可视化。
- 缺点:
- 决策树学习者可以创建不能很好地推广数据的过于复杂的树,这被称为过拟合。
- 改进:
- 减枝cart算法(决策树API当中已经实现,随机森林参数调优有相关介绍)
- 随机森林
随机森林
定义
随机森林是一个包含多个决策树的分类器,并且其输出的类别是由个别树输出的类别的众数而定。
原理
用N来表示训练用例(样本)的个数,M表示特征数目。
- 1、一次随机选出一个样本,重复N次, (有可能出现重复的样本)
- 2、随机去选出m个特征, m <<M,建立决策树
API
-
class sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=10, criterion=’gini’, max_depth=None, bootstrap=True, random_state=None, min_samples_split=2)
- 随机森林分类器
- n_estimators:integer,optional(default = 10)森林里的树木数量120,200,300,500,800,1200
- criteria:string,可选(default =“gini”)分割特征的测量方法
- max_depth:integer或None,可选(默认=无)树的最大深度 5,8,15,25,30
- max_features="auto”,每个决策树的最大特征数量
- If "auto", then
max_features=sqrt(n_features). - If "sqrt", then
max_features=sqrt(n_features)(same as "auto"). - If "log2", then
max_features=log2(n_features). - If None, then
max_features=n_features.
- If "auto", then
- bootstrap:boolean,optional(default = True)是否在构建树时使用放回抽样
- min_samples_split:节点划分最少样本数
- min_samples_leaf:叶子节点的最小样本数
- 超参数:n_estimator, max_depth, min_samples_split,min_samples_leaf
总结
- 在当前所有算法中,具有极好的准确率
- 能够有效地运行在大数据集上,处理具有高维特征的输入样本,而且不需要降维
- 能够评估各个特征在分类问题上的重要性