Logistic回归
算法优缺点:
1.计算代价不高,易于理解和实现
2.容易欠拟合,分类精度可能不高
3.适用数据类型:数值型和标称型
算法思想:
- 其实就我的理解来说,logistic回归实际上就是加了个sigmoid函数的线性回归,这个sigmoid函数的好处就在于,将结果归到了0到1这个区间里面了,并且sigmoid(0)=0.5,也就是说里面的线性部分的结果大于零小于零就可以直接计算到了。这里的求解方式是梯度上升法,具体我就不扯了,最推荐的资料还是Ng的视频,那里面的梯度下降就是啦,只不过一个是梯度上升的方向一个是下降的方向,做法什么的都一样。
- 而梯度上升(准确的说叫做“批梯度上升”)的一个缺点就是计算量太大了,每一次迭代都需要把所有的数据算一遍,这样一旦训练集大了之后,那么计算量将非常大,所以这里后面还提出了随机梯度下降,思想就是每次只是根据一个data进行修正。这样得到的最终的结果可能会有所偏差但是速度却提高了很多,而且优化之后的偏差还是很小的。随机梯度上升的另一个好处是这是一个在线算法,可以根据新数据的到来不断处理
函数:
loadDataSet()
创建数据集,这里的数据集就是在一个文件中,这里面有三行,分别是两个特征和一个标签,但是我们在读出的时候还加了X0这个属性sigmoid(inX)
sigmoid函数的计算,这个函数长这样的,基本坐标大点就和阶跃函数很像了

gradAscend(dataMatIn, classLabels)
梯度上升算法的实现,里面用到了numpy的数组,并且设定了迭代次数500次,然后为了计算速度都采取了矩阵计算,计算的过程中的公式大概是:w= w+alpha*(y-h)x[i](一直懒得写公式,见谅。。。)gradAscendWithDraw(dataMatIn, classLabels)
上面的函数加强版,增加了一个weight跟着迭代次数的变化曲线stocGradAscent0(dataMatrix, classLabels)
这里为了加快速度用来随机梯度上升,即每次根据一组数据调整(额,好吧,这个际没有随机因为那是线面那个函数)stocGradAscentWithDraw0(dataMatrix, classLabels)
上面的函数加强版,增加了一个weight跟着迭代次数的变化曲线stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150)
这就真的开始随机了,随机的主要好处是减少了周期性的波动了。另外这里还加入了alpha的值随迭代变化,这样可以让alpha的值不断的变化,但是都不会减小到0。stocGradAscentWithDraw1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150)
上面的函数加强版,增加了一个weight跟着迭代次数的变化曲线plotBestFit(wei)
根据计算的weight值画出拟合的线,直观观察效果
迭代变化趋势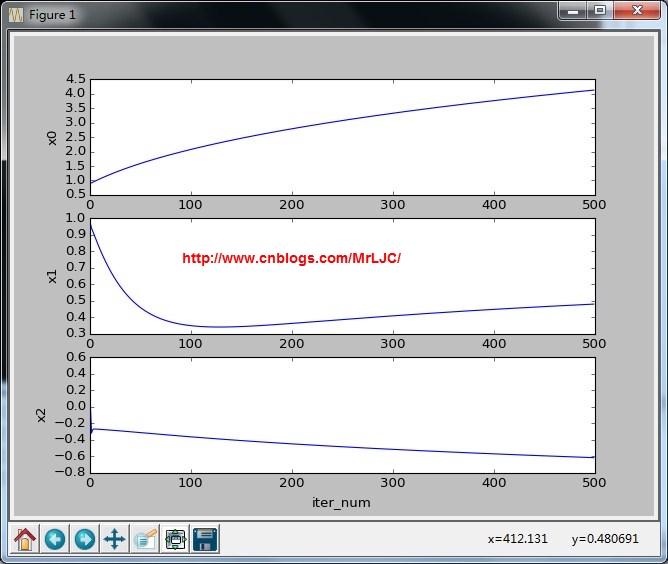 分类结果:
分类结果:
迭代变化趋势分类结果:这个速度虽然快了很多但是效果不太理想啊。不过这个计算量那么少,我们如果把这个迭代200次肯定不一样了,效果如下果然好多了
迭代变化趋势分类结果:恩,就是这样啦,效果还是不错的啦。代码的画图部分写的有点烂,见谅啦
-
1 #coding=utf-8 2 from numpy import * 3 4 def loadDataSet(): 5 dataMat = [] 6 labelMat = [] 7 fr = open('testSet.txt') 8 for line in fr.readlines(): 9 lineArr = line.strip().split() 10 dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])]) 11 labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2])) 12 return dataMat, labelMat 13 14 def sigmoid(inX): 15 return 1.0/(1+exp(-inX)) 16 17 def gradAscend(dataMatIn, classLabels): 18 dataMatrix = mat(dataMatIn) 19 labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose() 20 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 21 alpha = 0.001 22 maxCycle = 500 23 weight = ones((n,1)) 24 for k in range(maxCycle): 25 h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weight) 26 error = labelMat - h 27 weight += alpha * dataMatrix.transpose() * error 28 #plotBestFit(weight) 29 return weight 30 31 def gradAscendWithDraw(dataMatIn, classLabels): 32 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 33 fig = plt.figure() 34 ax = fig.add_subplot(311,ylabel='x0') 35 bx = fig.add_subplot(312,ylabel='x1') 36 cx = fig.add_subplot(313,ylabel='x2') 37 dataMatrix = mat(dataMatIn) 38 labelMat = mat(classLabels).transpose() 39 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 40 alpha = 0.001 41 maxCycle = 500 42 weight = ones((n,1)) 43 wei1 = [] 44 wei2 = [] 45 wei3 = [] 46 for k in range(maxCycle): 47 h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weight) 48 error = labelMat - h 49 weight += alpha * dataMatrix.transpose() * error 50 wei1.extend(weight[0]) 51 wei2.extend(weight[1]) 52 wei3.extend(weight[2]) 53 ax.plot(range(maxCycle), wei1) 54 bx.plot(range(maxCycle), wei2) 55 cx.plot(range(maxCycle), wei3) 56 plt.xlabel('iter_num') 57 plt.show() 58 return weight 59 60 def stocGradAscent0(dataMatrix, classLabels): 61 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 62 63 alpha = 0.001 64 weight = ones(n) 65 for i in range(m): 66 h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[i]*weight)) 67 error = classLabels[i] - h 68 weight = weight + alpha * error * dataMatrix[i] 69 return weight 70 71 def stocGradAscentWithDraw0(dataMatrix, classLabels): 72 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 73 fig = plt.figure() 74 ax = fig.add_subplot(311,ylabel='x0') 75 bx = fig.add_subplot(312,ylabel='x1') 76 cx = fig.add_subplot(313,ylabel='x2') 77 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 78 79 alpha = 0.001 80 weight = ones(n) 81 wei1 = array([]) 82 wei2 = array([]) 83 wei3 = array([]) 84 numIter = 200 85 for j in range(numIter): 86 for i in range(m): 87 h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[i]*weight)) 88 error = classLabels[i] - h 89 weight = weight + alpha * error * dataMatrix[i] 90 wei1 =append(wei1, weight[0]) 91 wei2 =append(wei2, weight[1]) 92 wei3 =append(wei3, weight[2]) 93 ax.plot(array(range(m*numIter)), wei1) 94 bx.plot(array(range(m*numIter)), wei2) 95 cx.plot(array(range(m*numIter)), wei3) 96 plt.xlabel('iter_num') 97 plt.show() 98 return weight 99 100 def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150): 101 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 102 103 #alpha = 0.001 104 weight = ones(n) 105 for j in range(numIter): 106 dataIndex = range(m) 107 for i in range(m): 108 alpha = 4/ (1.0+j+i) +0.01 109 randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex))) 110 h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weight)) 111 error = classLabels[randIndex] - h 112 weight = weight + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex] 113 del(dataIndex[randIndex]) 114 return weight 115 116 def stocGradAscentWithDraw1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150): 117 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 118 fig = plt.figure() 119 ax = fig.add_subplot(311,ylabel='x0') 120 bx = fig.add_subplot(312,ylabel='x1') 121 cx = fig.add_subplot(313,ylabel='x2') 122 m,n = shape(dataMatrix) 123 124 #alpha = 0.001 125 weight = ones(n) 126 wei1 = array([]) 127 wei2 = array([]) 128 wei3 = array([]) 129 for j in range(numIter): 130 dataIndex = range(m) 131 for i in range(m): 132 alpha = 4/ (1.0+j+i) +0.01 133 randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex))) 134 h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weight)) 135 error = classLabels[randIndex] - h 136 weight = weight + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex] 137 del(dataIndex[randIndex]) 138 wei1 =append(wei1, weight[0]) 139 wei2 =append(wei2, weight[1]) 140 wei3 =append(wei3, weight[2]) 141 ax.plot(array(range(len(wei1))), wei1) 142 bx.plot(array(range(len(wei2))), wei2) 143 cx.plot(array(range(len(wei2))), wei3) 144 plt.xlabel('iter_num') 145 plt.show() 146 return weight 147 148 def plotBestFit(wei): 149 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 150 weight = wei 151 dataMat,labelMat = loadDataSet() 152 dataArr = array(dataMat) 153 n = shape(dataArr)[0] 154 xcord1 = [] 155 ycord1 = [] 156 xcord2 = [] 157 ycord2 = [] 158 for i in range(n): 159 if int(labelMat[i]) == 1: 160 xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1]) 161 ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2]) 162 else: 163 xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1]) 164 ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2]) 165 fig = plt.figure() 166 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 167 ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c='red', marker='s') 168 ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c='green') 169 x = arange(-3.0, 3.0, 0.1) 170 y = (-weight[0] - weight[1]*x)/weight[2] 171 ax.plot(x,y) 172 plt.xlabel('X1') 173 plt.ylabel('X2') 174 plt.show() 175 176 def main(): 177 dataArr,labelMat = loadDataSet() 178 #w = gradAscendWithDraw(dataArr,labelMat) 179 w = stocGradAscentWithDraw0(array(dataArr),labelMat) 180 plotBestFit(w) 181 182 if __name__ == '__main__': 183 main()
机器学习笔记索引






