Splay
还是前面那个模板。注意所有操作以后都要splay一次,避免被卡掉。
splay的复杂度证明可看论文(知乎的相关问题中有链接),大体思想是定义树的势函数,进行势能分析,可证得splay一次的时间复杂度是(O(logn))。由于被splay的点就是被查询的点,并且查询一个点A的路径和splay点A的路径是同一个,因此只要每次操作查询一个点以后都splay一下,可以保证时间复杂度一定控制在均摊(O(logn))内。然而实测洛谷模板题上,atrank操作,pre和next操作的第二个find不用splay反而跑的更快0.0(不过也没快多少)。
补充一下具体的东西。一个点势函数的定义是(rank(x)=klog_2size(x))
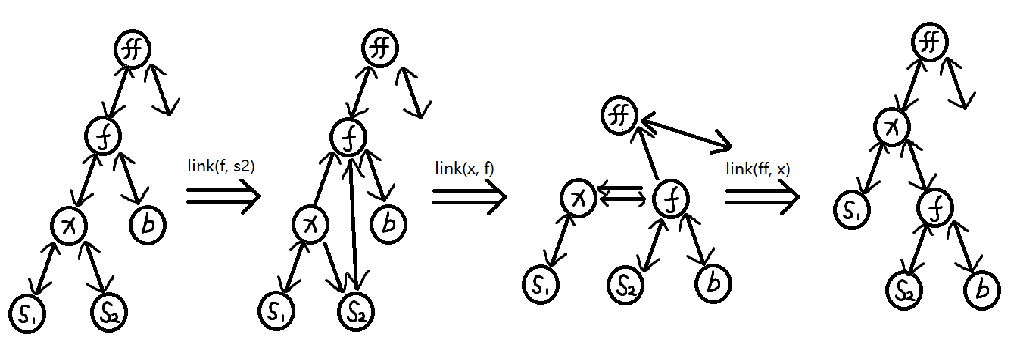
再插一句,维护区间翻转的splay和这个splay不一样。在这个splay中,每个点的大小序号和中序遍历排名是一样的。但是在区间翻转的splay中,它们就不一样了。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+5, INF=1e9;
int n, m;
//不能像写treap那样写旋转,因为splay是一个单独的操作
struct Splay{
int root, tot, siz[maxn], v[maxn], s[maxn][2], cnt[maxn], fa[maxn];
inline void up(int x){ siz[x]=siz[s[x][0]]+siz[s[x][1]]+cnt[x]; }
inline void clear(int x){ siz[x]=v[x]=s[x][0]=s[x][1]=cnt[x]=fa[x]=0; }
inline int which(int x){ return s[fa[x]][0]==x?0:1; }
inline void link(int f, int x, int p){
s[f][p]=x; fa[x]=f; }
inline void spin(int x){ //旋转x
int f=fa[x], ff=fa[f];
int p=which(x), fp=which(f);
link(f, s[x][!p], p); link(x, f, !p); link(ff, x, fp);
up(f); up(x);
}
void splay(int x, int dst){
int limit=fa[dst];
for (int f; (f=fa[x])!=limit; spin(x))
if (fa[f]) spin((which(x)==which(f))?f:x); //如果有父亲的父亲,同侧先转父亲,否则先转儿子(为了避免势能分析失效)
root=x;
}
//如果flag=0,若找不到,会找到前驱或后继
//如果=1,若找不到,会创造一个点
int find(int x, int c, int flag){
int f=0, p;
while (true){
siz[x]+=flag; f=x;
if (c==v[x]){ cnt[x]+=flag; return x; }
p=(c<v[x]?0:1); if (!s[x][p]) break;
x=s[x][p];
}
if (flag==1){
x=++tot; siz[x]=cnt[x]=flag; v[x]=c;
fa[x]=f, s[f][p]=x; }
return x;
}
void ins(int c){ int t=find(root, c, 1); splay(t, root); }
int rank(int c){ //询问c的最小排名
int t=find(root, c, 0); splay(t, root);
return siz[s[t][0]];
}
int atrank(int c){ //询问第c个数
int x=root; ++c;
while (x){
int t=c-siz[s[x][0]]; //t:除了左子树中的点,还需要多少点
if (t>0&&t<=cnt[x]) break;
if (t<=0) x=s[x][0];
else c=t-cnt[x], x=s[x][1];
}
return v[x];
}
int pre(int x){ //小于根的第一个点位置
int t=find(root, x, 0); splay(t, root);
if (v[t]>=x) t=find(s[t][0], INF, 0);
return v[t];
}
int nxt(int x){ //大于根的第一个点位置
int t=find(root, x, 0); splay(t, root);
if (v[t]<=x) t=find(s[t][1], -INF, 0);
return v[t];
}
void del(int c){ //删除c 若cnt用完必须回收点,避免pre和nxt出错
int t=find(root, c, -1); splay(t, root);
if (cnt[t]) return;
splay(find(s[t][0], INF, 0), root);
fa[s[t][1]]=root; s[root][1]=s[t][1];
clear(t); up(root);
}
Splay(){ root=++tot; siz[1]=cnt[1]=1; v[1]=-INF; ins(INF); } //这里有点稍稍不优美
}splay;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n); int op, x;
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i){
scanf("%d%d", &op, &x);
if (op==1) splay.ins(x);
if (op==2) splay.del(x);
if (op==3) printf("%d
", splay.rank(x));
if (op==4) printf("%d
", splay.atrank(x));
if (op==5) printf("%d
", splay.pre(x));
if (op==6) printf("%d
", splay.nxt(x));
}
return 0;
}