copy from : http://gityuan.com/2016/10/03/binder_linktodeath/
基于Android 6.0源码, 涉及相关源码
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Binder.java
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_Binder.cpp
frameworks/native/libs/binder/BpBinder.cpp
一. 概述
死亡通知是为了让Bp端(客户端进程)进能知晓Bn端(服务端进程)的生死情况,当Bn端进程死亡后能通知到Bp端。
- 定义:AppDeathRecipient是继承IBinder::DeathRecipient类,主要需要实现其binderDied()来进行死亡通告。
- 注册:binder->linkToDeath(AppDeathRecipient)是为了将AppDeathRecipient死亡通知注册到Binder上。
Bp端只需要覆写binderDied()方法,实现一些后尾清除类的工作,则在Bn端死掉后,会回调binderDied()进行相应处理。
1.1 实例说明
public final class ActivityManagerService {
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread, int pid) {
...
//创建IBinder.DeathRecipient子类对象
AppDeathRecipient adr = new AppDeathRecipient(app, pid, thread);
//建立binder死亡回调
thread.asBinder().linkToDeath(adr, 0);
app.deathRecipient = adr;
...
//取消binder死亡回调
app.unlinkDeathRecipient();
}
private final class AppDeathRecipient implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
...
public void binderDied() {
synchronized(ActivityManagerService.this) {
appDiedLocked(mApp, mPid, mAppThread, true);
}
}
}
}
前面涉及到linkToDeath和unlinkToDeath方法,实现如下:
[-> Binder.java]
public class Binder implements IBinder {
public void linkToDeath(DeathRecipient recipient, int flags) {
}
public boolean unlinkToDeath(DeathRecipient recipient, int flags) {
return true;
}
}
final class BinderProxy implements IBinder {
public native void linkToDeath(DeathRecipient recipient, int flags) throws RemoteException;
public native boolean unlinkToDeath(DeathRecipient recipient, int flags);
}
可见,以上两个方法:
- 当为Binder服务端,则相应的两个方法实现为空,没有实际功能;
- 当为BinderProxy代理端,则调用native方法来实现相应功能,这是真实的使用场景。
二. 上层注册死亡通知
BinderProxy调用linkToDeath()方法是一个native方法, 通过jni进入如下方法:
2.1 linkToDeath
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
static void android_os_BinderProxy_linkToDeath(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,
jobject recipient, jint flags)
{
if (recipient == NULL) {
jniThrowNullPointerException(env, NULL);
return;
}
//获取BinderProxy.mObject成员变量值, 即BpBinder对象
IBinder* target = (IBinder*)env->GetLongField(obj, gBinderProxyOffsets.mObject);
...
//只有Binder代理对象才会进入该分支
if (!target->localBinder()) {
DeathRecipientList* list = (DeathRecipientList*)
env->GetLongField(obj, gBinderProxyOffsets.mOrgue);
//创建JavaDeathRecipient对象[见小节2.1.1]
sp<JavaDeathRecipient> jdr = new JavaDeathRecipient(env, recipient, list);
//建立死亡通知[见小节2.2]
status_t err = target->linkToDeath(jdr, NULL, flags);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
//添加死亡通告失败, 则从list移除引用[见小节2.1.3]
jdr->clearReference();
signalExceptionForError(env, obj, err, true /*canThrowRemoteException*/);
}
}
}
过程说明:
- 获取DeathRecipientList: 其成员变量mList记录该BinderProxy的JavaDeathRecipient列表信息;
- 一个BpBinder可以注册多个死亡回调
- 创建JavaDeathRecipient: 继承于IBinder::DeathRecipient
2.1.1 JavaDeathRecipient
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
class JavaDeathRecipient : public IBinder::DeathRecipient
{
public:
JavaDeathRecipient(JNIEnv* env, jobject object, const sp<DeathRecipientList>& list)
: mVM(jnienv_to_javavm(env)), mObject(env->NewGlobalRef(object)),
mObjectWeak(NULL), mList(list)
{
//将当前对象sp添加到列表DeathRecipientList
list->add(this);
android_atomic_inc(&gNumDeathRefs);
incRefsCreated(env); //[见小节2.1.2]
}
}
该方法主要功能:
- 通过env->NewGlobalRef(object),为recipient创建相应的全局引用,并保存到mObject成员变量;
- 将当前对象JavaDeathRecipient的强指针sp添加到DeathRecipientList;
2.1.2 incRefsCreated
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp]
static void incRefsCreated(JNIEnv* env) {
int old = android_atomic_inc(&gNumRefsCreated);
if (old == 2000) {
android_atomic_and(0, &gNumRefsCreated);
//触发forceGc
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(gBinderInternalOffsets.mClass,
gBinderInternalOffsets.mForceGc);
}
}
该方法的主要是增加引用计数incRefsCreated,每计数增加2000则执行一次forceGc;
会触发调用incRefsCreated()的场景有:
- JavaBBinder对象创建过程
- JavaDeathRecipient对象创建过程;
- javaObjectForIBinder()方法:将native层BpBinder对象转换为Java层BinderProxy对象的过程;
2.1.3 clearReference
[-> android_util_Binder.cpp ::JavaDeathRecipient]
void clearReference() {
sp<DeathRecipientList> list = mList.promote();
if (list != NULL) {
list->remove(this); //从列表中移除引用
}
}
清除引用,将JavaDeathRecipient从DeathRecipientList列表中移除.
2.2 linkToDeath
[-> BpBinder.cpp]
status_t BpBinder::linkToDeath(
const sp<DeathRecipient>& recipient, void* cookie, uint32_t flags)
{
Obituary ob;
ob.recipient = recipient; //该对象为JavaDeathRecipient
ob.cookie = cookie; // cookie=NULL
ob.flags = flags; // flags=0
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (!mObitsSent) { //没有执行过sendObituary,则进入该方法
if (!mObituaries) {
mObituaries = new Vector<Obituary>;
if (!mObituaries) {
return NO_MEMORY;
}
getWeakRefs()->incWeak(this);
IPCThreadState* self = IPCThreadState::self();
//[见小节2.3]
self->requestDeathNotification(mHandle, this);
//[见小节2.4]
self->flushCommands();
}
//将新创建的Obituary添加到mObituaries
ssize_t res = mObituaries->add(ob);
return res >= (ssize_t)NO_ERROR ? (status_t)NO_ERROR : res;
}
}
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
2.2.1 DeathRecipient关系图
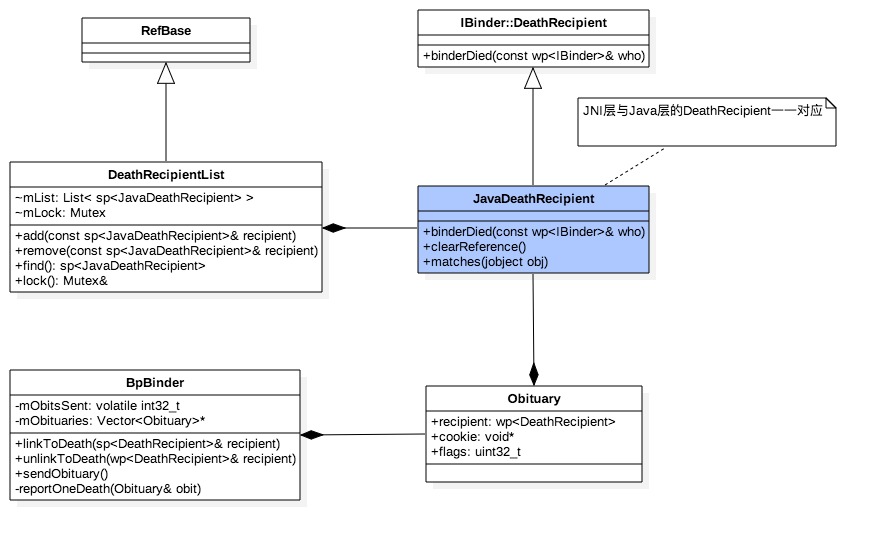
Java层的BinderProxy.mOrgue指向DeathRecipientList,而DeathRecipientList记录JavaDeathRecipient对象。
2.3 requestDeathNotification
[-> IPCThreadState.cpp]
status_t IPCThreadState::requestDeathNotification(int32_t handle, BpBinder* proxy)
{
mOut.writeInt32(BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION);
mOut.writeInt32((int32_t)handle);
mOut.writePointer((uintptr_t)proxy);
return NO_ERROR;
}
进入Binder driver后, 直接调用后进入binder_thread_write, 处理BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION命令
2.4 flushCommands
[-> IPCThreadState.cpp]
void IPCThreadState::flushCommands()
{
if (mProcess->mDriverFD <= 0)
return;
talkWithDriver(false);
}
flushCommands就是把命令向驱动发出,此处参数为false,则不会阻塞等待读。 向Kernel层的binder driver发送BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION命令,经过ioctl执行到 binder_ioctl_write_read()方法。
三. Kernel层注册通知
3.1 binder_ioctl_write_read
[-> kernel/drivers/android/binder.c]
static int binder_ioctl_write_read(struct file *filp,
unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg,
struct binder_thread *thread)
{
int ret = 0;
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
void __user *ubuf = (void __user *)arg;
struct binder_write_read bwr;
if (copy_from_user(&bwr, ubuf, sizeof(bwr))) { //把用户空间数据ubuf拷贝到bwr
ret = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
if (bwr.write_size > 0) { //此时写缓存有数据【见小节3.2】
ret = binder_thread_write(proc, thread,
bwr.write_buffer, bwr.write_size, &bwr.write_consumed);
...
}
if (bwr.read_size > 0) { //此时读缓存没有数据
...
}
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr))) { //将内核数据bwr拷贝到用户空间ubuf
ret = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
out:
return ret;
}
3.2 binder_thread_write
[-> kernel/drivers/android/binder.c]
static int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed)
{
uint32_t cmd;
//proc, thread都是指当前发起端进程的信息
struct binder_context *context = proc->context;
void __user *buffer = (void __user *)(uintptr_t)binder_buffer;
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error == BR_OK) {
get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr); //获取BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
switch (cmd) {
case BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION:{ //注册死亡通知
uint32_t target;
void __user *cookie;
struct binder_ref *ref;
struct binder_ref_death *death;
get_user(target, (uint32_t __user *)ptr); //获取target
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
get_user(cookie, (void __user * __user *)ptr); //获取BpBinder
ptr += sizeof(void *);
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, target); //拿到目标服务的binder_ref
if (cmd == BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
//native Bp可注册多个,但Kernel只允许注册一个死亡通知
if (ref->death) {
break;
}
death = kzalloc(sizeof(*death), GFP_KERNEL);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&death->work.entry);
death->cookie = cookie; //BpBinder指针
ref->death = death;
//当目标binder服务所在进程已死,则直接发送死亡通知。这是非常规情况
if (ref->node->proc == NULL) {
ref->death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER;
//当前线程为binder线程,则直接添加到当前线程的todo队列.
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) {
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &thread->todo);
} else {
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
}
} else {
...
}
} break;
case ...;
}
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
}
}
该方法在处理BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION过程,正好遇到对端目标binder服务所在进程已死的情况, 向todo队列增加BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER事务,直接发送死亡通知,但这属于非常规情况。
更常见的场景是binder服务所在进程死亡后,会调用binder_release方法, 然后调用binder_node_release.这个过程便会发出死亡通知的回调.
四. 触发死亡通知
当Binder服务所在进程死亡后,会释放进程相关的资源,Binder也是一种资源。 binder_open打开binder驱动/dev/binder,这是字符设备,获取文件描述符。在进程结束的时候会有一个关闭文件系统的过程中会调用驱动close方法,该方法相对应的是release()方法。当binder的fd被释放后,此处调用相应的方法是binder_release().
但并不是每个close系统调用都会触发调用release()方法. 只有真正释放设备数据结构才调用release(),内核维持一个文件结构被使用多少次的计数,即便是应用程序没有明显地关闭它打开的文件也适用: 内核在进程exit()时会释放所有内存和关闭相应的文件资源, 通过使用close系统调用最终也会release binder.
4.1 release
[-> binder.c]
static const struct file_operations binder_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.poll = binder_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = binder_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = binder_ioctl,
.mmap = binder_mmap,
.open = binder_open,
.flush = binder_flush,
.release = binder_release, //对应于release的方法
};
4.2 binder_release
static int binder_release(struct inode *nodp, struct file *filp)
{
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
debugfs_remove(proc->debugfs_entry);
//[见小节4.3]
binder_defer_work(proc, BINDER_DEFERRED_RELEASE);
return 0;
}
4.3 binder_defer_work
static void binder_defer_work(struct binder_proc *proc, enum binder_deferred_state defer) {
mutex_lock(&binder_deferred_lock); //获取锁
//添加BINDER_DEFERRED_RELEASE
proc->deferred_work |= defer;
if (hlist_unhashed(&proc->deferred_work_node)) {
hlist_add_head(&proc->deferred_work_node, &binder_deferred_list);
//向工作队列添加binder_deferred_work [见小节4.4]
queue_work(binder_deferred_workqueue, &binder_deferred_work);
}
mutex_unlock(&binder_deferred_lock); //释放锁
}
4.4 queue_work
//全局工作队列
static struct workqueue_struct *binder_deferred_workqueue;
static int __init binder_init(void)
{
int ret;
//创建了名叫“binder”的工作队列
binder_deferred_workqueue = create_singlethread_workqueue("binder");
if (!binder_deferred_workqueue)
return -ENOMEM;
...
}
device_initcall(binder_init);
关于binder_deferred_work的定义:
static DECLARE_WORK(binder_deferred_work, binder_deferred_func);
#define DECLARE_WORK(n, f)
struct work_struct n = __WORK_INITIALIZER(n, f)
#define __WORK_INITIALIZER(n, f) {
.data = WORK_DATA_STATIC_INIT(),
.entry = { &(n).entry, &(n).entry },
.func = (f),
__WORK_INIT_LOCKDEP_MAP(#n, &(n))
}
在Binder设备驱动初始化的过程执行binder_init()方法中,调用 create_singlethread_workqueue(“binder”),创建了名叫“binder”的工作队列(workqueue)。 workqueue是kernel提供的一种实现简单而有效的内核线程机制,可延迟执行任务。
此处binder_deferred_work的func为binder_deferred_func,接下来看该方法。
4.5 binder_deferred_func
static void binder_deferred_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct binder_proc *proc;
struct files_struct *files;
int defer;
do {
mutex_lock(&binder_main_lock); //获取binder_main_lock
mutex_lock(&binder_deferred_lock);
preempt_disable(); //禁止CPU抢占
if (!hlist_empty(&binder_deferred_list)) {
proc = hlist_entry(binder_deferred_list.first,
struct binder_proc, deferred_work_node);
hlist_del_init(&proc->deferred_work_node);
defer = proc->deferred_work;
proc->deferred_work = 0;
} else {
proc = NULL;
defer = 0;
}
mutex_unlock(&binder_deferred_lock);
files = NULL;
if (defer & BINDER_DEFERRED_PUT_FILES) {
files = proc->files;
if (files)
proc->files = NULL;
}
if (defer & BINDER_DEFERRED_FLUSH)
binder_deferred_flush(proc);
if (defer & BINDER_DEFERRED_RELEASE)
binder_deferred_release(proc); //[见小节4.6]
mutex_unlock(&binder_main_lock); //释放锁
preempt_enable_no_resched();
if (files)
put_files_struct(files);
} while (proc);
}
可见,binder_release最终调用的是binder_deferred_release; 同理,binder_flush最终调用的是binder_deferred_flush。
4.6 binder_deferred_release
static void binder_deferred_release(struct binder_proc *proc)
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct rb_node *n;
int threads, nodes, incoming_refs, outgoing_refs, buffers,
active_transactions, page_count;
hlist_del(&proc->proc_node); //删除proc_node节点
if (binder_context_mgr_node && binder_context_mgr_node->proc == proc) {
binder_context_mgr_node = NULL;
}
//释放binder_thread[见小节4.6.1]
threads = 0;
active_transactions = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->threads))) {
struct binder_thread *thread;
thread = rb_entry(n, struct binder_thread, rb_node);
threads++;
active_transactions += binder_free_thread(proc, thread);
}
//释放binder_node [见小节4.6.2]
nodes = 0;
incoming_refs = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->nodes))) {
struct binder_node *node;
node = rb_entry(n, struct binder_node, rb_node);
nodes++;
rb_erase(&node->rb_node, &proc->nodes);
incoming_refs = binder_node_release(node, incoming_refs);
}
//释放binder_ref [见小节4.6.3]
outgoing_refs = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->refs_by_desc))) {
struct binder_ref *ref;
ref = rb_entry(n, struct binder_ref, rb_node_desc);
outgoing_refs++;
binder_delete_ref(ref);
}
//释放binder_work [见小节4.6.4]
binder_release_work(&proc->todo);
binder_release_work(&proc->delivered_death);
buffers = 0;
while ((n = rb_first(&proc->allocated_buffers))) {
struct binder_buffer *buffer;
buffer = rb_entry(n, struct binder_buffer, rb_node);
t = buffer->transaction;
if (t) {
t->buffer = NULL;
buffer->transaction = NULL;
}
//释放binder_buf [见小节4.6.5]
binder_free_buf(proc, buffer);
buffers++;
}
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_PROC);
page_count = 0;
if (proc->pages) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < proc->buffer_size / PAGE_SIZE; i++) {
void *page_addr;
if (!proc->pages[i])
continue;
page_addr = proc->buffer + i * PAGE_SIZE;
unmap_kernel_range((unsigned long)page_addr, PAGE_SIZE);
__free_page(proc->pages[i]);
page_count++;
}
kfree(proc->pages);
vfree(proc->buffer);
}
put_task_struct(proc->tsk);
kfree(proc);
}
此处proc是来自Bn端的binder_proc
4.6.1 binder_free_thread
static int binder_free_thread(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread)
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct binder_transaction *send_reply = NULL;
int active_transactions = 0;
rb_erase(&thread->rb_node, &proc->threads);
t = thread->transaction_stack;
if (t && t->to_thread == thread)
send_reply = t; //服务端
while (t) {
active_transactions++;
if (t->to_thread == thread) {
t->to_proc = NULL;
t->to_thread = NULL;
if (t->buffer) {
t->buffer->transaction = NULL;
t->buffer = NULL;
}
t = t->to_parent;
} else if (t->from == thread) {
t->from = NULL;
t = t->from_parent;
}
}
//将发起方线程的return_error值设置为BR_DEAD_REPLY【见小节4.6.4.1】
if (send_reply)
binder_send_failed_reply(send_reply, BR_DEAD_REPLY);
//[见小节4.6.4]
binder_release_work(&thread->todo);
kfree(thread);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_THREAD);
return active_transactions;
}
4.6.2 binder_node_release
static int binder_node_release(struct binder_node *node, int refs)
{
struct binder_ref *ref;
int death = 0;
list_del_init(&node->work.entry);
//[见小节4.6.4]
binder_release_work(&node->async_todo);
if (hlist_empty(&node->refs)) {
kfree(node); //引用为空,则直接删除节点
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_NODE);
return refs;
}
node->proc = NULL;
node->local_strong_refs = 0;
node->local_weak_refs = 0;
hlist_add_head(&node->dead_node, &binder_dead_nodes);
hlist_for_each_entry(ref, &node->refs, node_entry) {
refs++;
if (!ref->death)
continue;
death++;
if (list_empty(&ref->death->work.entry)) {
//添加BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER事务到todo队列 [见小节5.1]
ref->death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER;
list_add_tail(&ref->death->work.entry, &ref->proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&ref->proc->wait);
}
}
return refs;
}
该方法会遍历该binder_node所有的binder_ref, 当存在binder死亡通知,则向相应的binder_ref 所在进程的todo队列添加BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER事务并唤醒处于proc->wait的binder线程,下一步行动见[见小节5.1]。
4.6.3 binder_delete_ref
static void binder_delete_ref(struct binder_ref *ref)
{
rb_erase(&ref->rb_node_desc, &ref->proc->refs_by_desc);
rb_erase(&ref->rb_node_node, &ref->proc->refs_by_node);
if (ref->strong)
binder_dec_node(ref->node, 1, 1);
hlist_del(&ref->node_entry);
binder_dec_node(ref->node, 0, 1);
if (ref->death) {
list_del(&ref->death->work.entry);
kfree(ref->death);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_DEATH);
}
kfree(ref);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_REF);
}
4.6.4 binder_release_work
static void binder_release_work(struct list_head *list)
{
struct binder_work *w;
while (!list_empty(list)) {
w = list_first_entry(list, struct binder_work, entry);
list_del_init(&w->entry); //删除binder_work
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION: {
struct binder_transaction *t;
t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);
if (t->buffer->target_node &&
!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
//发送failed回复【见小节4.6.4.1】
binder_send_failed_reply(t, BR_DEAD_REPLY);
} else {
t->buffer->transaction = NULL;
kfree(t);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
}
} break;
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE: {
kfree(w);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
} break;
case BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR:
case BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION: {
struct binder_ref_death *death;
death = container_of(w, struct binder_ref_death, work);
kfree(death);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_DEATH);
} break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
4.6.4.1 binder_send_failed_reply
static void binder_send_failed_reply(struct binder_transaction *t,
uint32_t error_code)
{
struct binder_thread *target_thread;
struct binder_transaction *next;
while (1) {
target_thread = t->from;
if (target_thread) {
if (target_thread->return_error != BR_OK &&
target_thread->return_error2 == BR_OK) {
target_thread->return_error2 =
target_thread->return_error;
target_thread->return_error = BR_OK;
}
if (target_thread->return_error == BR_OK) {
binder_pop_transaction(target_thread, t);
//设置错误的返回码,并唤醒等待线程
target_thread->return_error = error_code;
wake_up_interruptible(&target_thread->wait);
}
return;
}
next = t->from_parent;
binder_pop_transaction(target_thread, t);
if (next == NULL) {
return;
}
t = next;
}
}
4.6.5 binder_free_buf
static void binder_free_buf(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_buffer *buffer)
{
size_t size, buffer_size;
buffer_size = binder_buffer_size(proc, buffer);
size = ALIGN(buffer->data_size, sizeof(void *)) +
ALIGN(buffer->offsets_size, sizeof(void *));
if (buffer->async_transaction) {
proc->free_async_space += size + sizeof(struct binder_buffer);
}
binder_update_page_range(proc, 0,
(void *)PAGE_ALIGN((uintptr_t)buffer->data),
(void *)(((uintptr_t)buffer->data + buffer_size) & PAGE_MASK),
NULL);
rb_erase(&buffer->rb_node, &proc->allocated_buffers);
buffer->free = 1;
if (!list_is_last(&buffer->entry, &proc->buffers)) {
struct binder_buffer *next = list_entry(buffer->entry.next,
struct binder_buffer, entry);
if (next->free) {
rb_erase(&next->rb_node, &proc->free_buffers);
binder_delete_free_buffer(proc, next);
}
}
if (proc->buffers.next != &buffer->entry) {
struct binder_buffer *prev = list_entry(buffer->entry.prev,
struct binder_buffer, entry);
if (prev->free) {
binder_delete_free_buffer(proc, buffer);
rb_erase(&prev->rb_node, &proc->free_buffers);
buffer = prev;
}
}
binder_insert_free_buffer(proc, buffer);
}
4.6.6 小结
binder_deferred_release的主要工作有:
- binder_free_thread: proc->threads所有线程
- binder_send_failed_reply(send_reply, BR_DEAD_REPLY):将发起方线程的return_error值设置为BR_DEAD_REPLY,让其直接返回;
- binder_node_release: proc->nodes所有节点
- binder_release_work(&node->async_todo)
- node->refs的所有死亡回调
- binder_delete_ref: proc->refs_by_desc所有引用
- 清除引用
- binder_release_work: proc->todo, proc->delivered_death
- binder_send_failed_reply(t, BR_DEAD_REPLY)
- binder_free_buf: proc->allocated_buffers所有已分配buffer
- 释放已分配的buffer
- __free_page: proc->pages所有物理内存页
不论是binder线程正在处理的事务,还是位于进程todo队列的事务,当进程被杀后,则会立马通知请求发起方来结束请求。
五. 处理死亡通知
前面[小节4.6.2] binder_node_release的过程会向BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER事务并唤醒处于proc->wait的binder线程。
5.1 binder_thread_read
static int binder_thread_read(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed, int non_block)
...
//唤醒等待中的binder线程
wait_event_freezable_exclusive(proc->wait, binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread));
binder_lock(__func__); //加锁
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads--; //空闲的binder线程减1
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
while (1) {
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
//从todo队列拿出前面放入的binder_work, 此时type为BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER
if (!list_empty(&thread->todo)) {
w = list_first_entry(&thread->todo, struct binder_work,
entry);
} else if (!list_empty(&proc->todo) && wait_for_proc_work) {
w = list_first_entry(&proc->todo, struct binder_work,
entry);
}
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER: {
struct binder_ref_death *death;
uint32_t cmd;
death = container_of(w, struct binder_ref_death, work);
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION)
...
else
cmd = BR_DEAD_BINDER; //进入此分支
put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr);//拷贝到用户空间[见小节5.2]
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
//此处的cookie是前面传递的BpBinder
put_user(death->cookie, (binder_uintptr_t __user *)ptr);
ptr += sizeof(binder_uintptr_t);
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
...
} else
//把该work加入到delivered_death队列
list_move(&w->entry, &proc->delivered_death);
if (cmd == BR_DEAD_BINDER)
goto done;
} break;
}
}
...
return 0;
}
将命令BR_DEAD_BINDER写到用户空间,此时用户空间执行过程:
5.2 IPC.getAndExecuteCommand
status_t IPCThreadState::getAndExecuteCommand()
{
status_t result;
int32_t cmd;
result = talkWithDriver(); //该Binder Driver进行交互
if (result >= NO_ERROR) {
size_t IN = mIn.dataAvail();
if (IN < sizeof(int32_t)) return result;
cmd = mIn.readInt32(); //读取命令
pthread_mutex_lock(&mProcess->mThreadCountLock);
mProcess->mExecutingThreadsCount++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mProcess->mThreadCountLock);
result = executeCommand(cmd); //【见小节5.3】
pthread_mutex_lock(&mProcess->mThreadCountLock);
mProcess->mExecutingThreadsCount--;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&mProcess->mThreadCountDecrement);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mProcess->mThreadCountLock);
set_sched_policy(mMyThreadId, SP_FOREGROUND);
}
return result;
}
5.3 IPC.executeCommand
status_t IPCThreadState::executeCommand(int32_t cmd)
{
BBinder* obj;
RefBase::weakref_type* refs;
status_t result = NO_ERROR;
switch ((uint32_t)cmd) {
case BR_DEAD_BINDER:
{
BpBinder *proxy = (BpBinder*)mIn.readPointer();
proxy->sendObituary(); //[见小节5.4]
mOut.writeInt32(BC_DEAD_BINDER_DONE);
mOut.writePointer((uintptr_t)proxy);
} break;
...
}
...
return result;
}
同一个bp端即便注册多次死亡通知,但只会发送一次死亡回调。
5.4 Bp.sendObituary
void BpBinder::sendObituary()
{
mAlive = 0;
if (mObitsSent) return;
mLock.lock();
Vector<Obituary>* obits = mObituaries;
if(obits != NULL) {
IPCThreadState* self = IPCThreadState::self();
//清空死亡通知[见小节6.2]
self->clearDeathNotification(mHandle, this);
self->flushCommands();
mObituaries = NULL;
}
mObitsSent = 1;
mLock.unlock();
if (obits != NULL) {
const size_t N = obits->size();
for (size_t i=0; i<N; i++) {
//发送死亡通知 [见小节5.5]
reportOneDeath(obits->itemAt(i));
}
delete obits;
}
}
5.5 reportOneDeath
void BpBinder::reportOneDeath(const Obituary& obit)
{
//将弱引用提升到sp
sp<DeathRecipient> recipient = obit.recipient.promote();
if (recipient == NULL) return;
//回调死亡通知的方法
recipient->binderDied(this);
}
本文开头的实例传递的是AppDeathRecipient,那么回调如下方法。
5.6 binderDied
private final class AppDeathRecipient implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
...
public void binderDied() {
synchronized(ActivityManagerService.this) {
appDiedLocked(mApp, mPid, mAppThread, true);
}
}
}
六. unlinkToDeath
6.1 unlinkToDeath
status_t BpBinder::unlinkToDeath(
const wp<DeathRecipient>& recipient, void* cookie, uint32_t flags,
wp<DeathRecipient>* outRecipient)
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (mObitsSent) {
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
const size_t N = mObituaries ? mObituaries->size() : 0;
for (size_t i=0; i<N; i++) {
const Obituary& obit = mObituaries->itemAt(i);
if ((obit.recipient == recipient
|| (recipient == NULL && obit.cookie == cookie))
&& obit.flags == flags) {
if (outRecipient != NULL) {
*outRecipient = mObituaries->itemAt(i).recipient;
}
mObituaries->removeAt(i); //移除死亡通知
if (mObituaries->size() == 0) {
//清理死亡通知
self->clearDeathNotification(mHandle, this);
self->flushCommands();
delete mObituaries;
mObituaries = NULL;
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
}
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
6.2 clearDeathNotification
status_t IPCThreadState::clearDeathNotification(int32_t handle, BpBinder* proxy)
{
mOut.writeInt32(BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION);
mOut.writeInt32((int32_t)handle);
mOut.writePointer((uintptr_t)proxy);
return NO_ERROR;
}
写入BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION命令,再经过flushCommands(),则进入Kernel层。
6.3 Kernel层取消死亡通知
6.3.1 binder_thread_write
static int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed)
{
uint32_t cmd;
//proc, thread都是指当前发起端进程的信息
struct binder_context *context = proc->context;
void __user *buffer = (void __user *)(uintptr_t)binder_buffer;
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error == BR_OK) {
get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr); //获取BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
switch (cmd) {
case BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION:
case BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION: { //清除死亡通知
uint32_t target;
void __user *cookie;
struct binder_ref *ref;
struct binder_ref_death *death;
get_user(target, (uint32_t __user *)ptr); //获取target
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
get_user(cookie, (void __user * __user *)ptr);
ptr += sizeof(void *);
ref = binder_get_ref(proc, target); //拿到目标服务的binder_ref
if (cmd == BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
...
} else {
if (ref->death == NULL) {
break;
}
death = ref->death;
if (death->cookie != cookie) {
break; //比较是否同一个BpBinder
}
ref->death = NULL; //设置死亡通知为NULL
if (list_empty(&death->work.entry)) {
//添加BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION事务
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION;
if (thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED | BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &thread->todo);
} else {
list_add_tail(&death->work.entry, &proc->todo);
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
}
} else {
death->work.type = BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR;
}
}
} break;
case ...;
}
}
}
添加BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION事务
6.3.2 binder_thread_read
static int binder_thread_read(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size,
binder_size_t *consumed, int non_block)
...
//唤醒等待中的binder线程
wait_event_freezable_exclusive(proc->wait, binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread));
binder_lock(__func__); //加锁
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads--; //空闲的binder线程减1
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
while (1) {
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
//从todo队列拿出前面放入的binder_work, 此时type为BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER
if (!list_empty(&thread->todo)) {
w = list_first_entry(&thread->todo, struct binder_work,
entry);
} else if (!list_empty(&proc->todo) && wait_for_proc_work) {
w = list_first_entry(&proc->todo, struct binder_work,
entry);
}
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER:
case BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER_AND_CLEAR:
case BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION: {
struct binder_ref_death *death;
uint32_t cmd;
death = container_of(w, struct binder_ref_death, work);
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION)
cmd = BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE; //清除完成
...
if (w->type == BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION) {
list_del(&w->entry); //清除死亡通知的work队列
kfree(death);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_DEATH);
}
...
if (cmd == BR_DEAD_BINDER)
goto done;
} break;
}
}
...
return 0;
}
需要再回到用户空间,查看BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE处理过程
6.4 IPC.executeCommand
status_t IPCThreadState::executeCommand(int32_t cmd)
{
BBinder* obj;
RefBase::weakref_type* refs;
status_t result = NO_ERROR;
switch ((uint32_t)cmd) {
case BR_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION_DONE:
{
BpBinder *proxy = (BpBinder*)mIn.readPointer();
//减少弱引用
proxy->getWeakRefs()->decWeak(proxy);
} break;
...
}
...
return result;
}
七. 结论
对于Binder IPC进程都会打开/dev/binder文件,当进程异常退出时,Binder驱动会保证释放将要退出的进程中没有正常关闭的/dev/binder文件,实现机制是binder驱动通过调用/dev/binder文件所对应的release回调函数,执行清理工作,并且检查BBinder是否有注册死亡通知,当发现存在死亡通知时,那么就向其对应的BpBinder端发送死亡通知消息。
死亡回调DeathRecipient只有Bp才能正确使用,因为DeathRecipient用于监控Bn端挂掉的情况, 如果Bn建立跟自己的死亡通知,自己进程都挂了,也就无法通知。
每个BpBinder都有一个记录DeathRecipient列表的对象DeathRecipientList。
7.1 流程图
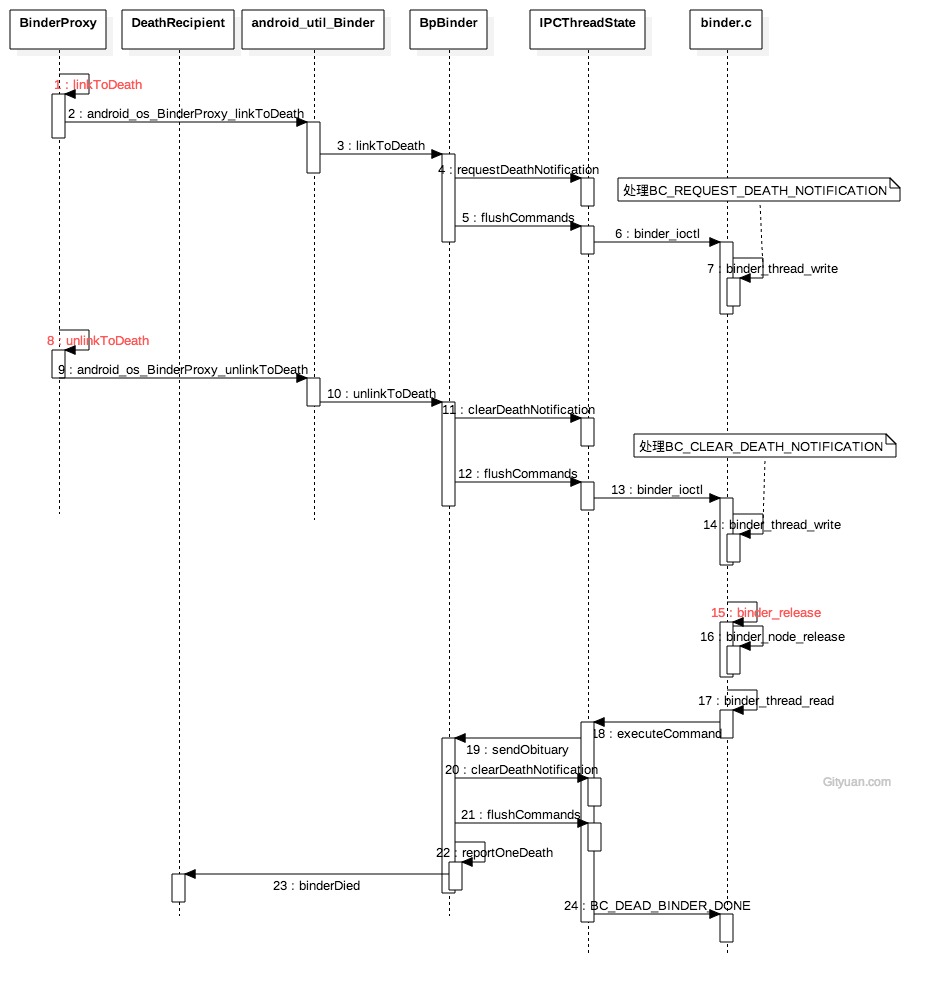
图解:点击查看大图
linkToDeath过程
- requestDeathNotification过程向驱动传递的命令BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION,参数有mHandle和BpBinder对象;
- binder_thread_write()过程,同一个BpBinder可以注册多个死亡回调,但Kernel只允许注册一次死亡通知。
- 注册死亡回调的过程,实质就是向binder_ref结构体添加binder_ref_death指针, binder_ref_death的cookie记录BpBinder指针。
unlinkToDeath过程
- unlinkToDeath只有当该BpBinder的所有mObituaries都被移除,才会向驱动层执行清除死亡通知的动作, 否则只是从native层移除某个recipient。
- clearDeathNotification过程向驱动传递BC_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION,参数有mHandle和BpBinder对象;
- binder_thread_write()过程,将BINDER_WORK_CLEAR_DEATH_NOTIFICATION事务添加当前当前进程/线程的todo队列
触发死亡回调
- 服务实体进程:binder_release过程会执行binder_node_release(),loop该binder_node下所有的ref->death对象。 当存在,则将BINDER_WORK_DEAD_BINDER事务添加ref->proc->todo(即ref所在进程的todo队列)
- 引用所在进程:执行binder_thread_read()过程,向用户空间写入BR_DEAD_BINDER,并触发死亡回调。
- 发送死亡通知sendObituary