可平面性算法——路径嵌入法
要判断一个图是否为平面图,在考虑路径嵌入法之前,先考虑其他的优化
1.根据欧拉定理:$n(点数)-e(边数)+f(面数)=w(连通块)+1$,而一个面最少由三个面组成,一个边属于两个面,得到$3f>=2e$,又$w>=1$得到$f<=2n-4$,$e<=3n-6$
所以如果边数超过了就直接判断False吧(面数不太好判断)
2.根据库拉托夫斯基定理:一个图的所有子图经过缩点(将所有度为2的点去掉并连接它的相邻两个点)后均不为K5(五个点的完全图)或K33(两边都是三个点的完全二分图),那么这个图就是可平面图
由此可以得到:对于两个可平面图A,B,任意连接小于等于两条从A到B的线段后得到的图仍然是一个平面图。(感性的理解,加入的这两条边并不能组成K5或者K33的任意一个部分)
这样理论上就可以把图分成一个个“边三联通分量”,当然我们只分成边双联通分量就可以了。
现在开始路径嵌入法吧!
路径嵌入法的算法流程是这样的:
pre:先把上面的1.2两点优化搞了
1.取出你的边双联通分量,记为G
2.在G中选出任意一个回路H,在G中去掉这个回路,将这个回路嵌入图中,并将G分成若干个连通块$B_1$~$B_n$,这些连通块以边为联通,以已经嵌入的点作为分隔,每个连通块的边界(即已经嵌入的点)称为这个连通块的附着点
3.对所有的联通块计算一个值$F(B_i)$,这个值是已经嵌入的面中能够包含$B_i$所有附着点的面的数量
4.如果有一个$F(B_i)=0$,那么就不能再嵌进去了,返回False,而对于$F=1$和$F>1$的连通块来说,先嵌入$F=1$的,再嵌入$F>1$的,证明详见论文
5.现在将一个连通块嵌入图中,首先在连通块中找出一条路径,这条路径的两个端点都是附着点,将这个路径嵌入图中,并将去掉这个路径的连通块又分为若干个连通块,返回第三步直到所有连通块都嵌入图中后结束
举个例子吧~
输入数据:
9 20 1 2 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 8 9 1 4 4 7 2 5 5 8 3 6 6 9 1 5 2 4 2 6 3 5 4 8 5 7 5 9 6 8
这张图长这样:
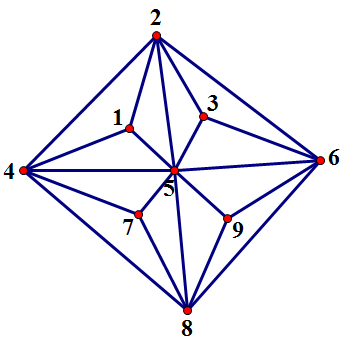
任意找一回路:
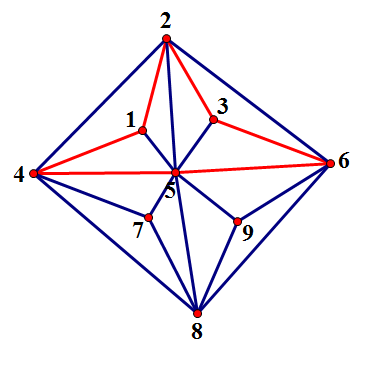
分成若干个连通块(注意连通块是边集):
$B_1={(1,5)},B_2={(3,5)},B_3={(2,5)},B_4={(4,2)},B_5={(6,2)},B_6={(5,7),(4,7),(7,8),(5,8),(4,8),(5,9),(9,8),(9,6),(6,8)}$
举个附着点的例子吧:当前$B_1$的附着点是${1,5},B_5$的附着点是${4,5,6}$
当前的面(有序点集)是:
$P_1={4,1,2,3,6,5},P_2={4,1,2,3,6,5}$(两个面一个是外面一个是里面,点集表示相同)
当前所有连通块的F值都是2,所以任意取一个连通块(例如$B_6$)
在其中取一条路径嵌入:
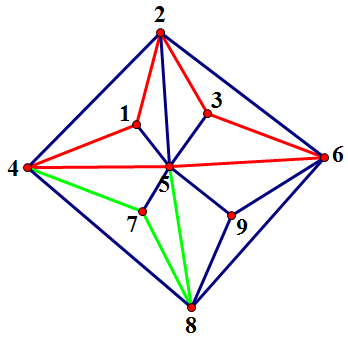
弹出$B_6$,生成$B_7={(5,7)},B_8={(4,8)},B_9={(6,8)},B_{10}={(5,9),(9,8),(9,6)}$
当前的面为$P_1={4,1,2,3,6,5,8,4},P_2={5,4,7,8},P_3={4,1,2,3,6,5}$
计算F值:$F(B_1)=2,F(B_2)=2,F(B_3)=2,F(B_4)=2,F(B_5)=2,F(B_7)=2,F(B_8)=2,F(B_9)=1,F(B_{10})=1$
所以要先嵌入$B_9$和$B_{10}$,$B_9$嵌完后就完了,$B_{10}$嵌一条路径又会分出一个小连通块...
最终按照程序嵌入下去直到连通块数量为0,判断这个图——是平面图!
算法复杂度分析:这个算法的复杂度和实现有着密不可分的关系,但由于代码实在过于复杂(或者说找不到合适的数据结构来维护?),大致分析复杂度在$O(n^2)$到$O(n^3)$之间,但实际运行时由于优化很多(这些优化大多都是能够明显加快速度但理论分析却省不了时间),尤其是随机数据的表现极其良好,几乎可以当做$O(n^2)$来看待
最后的最后,给出大常数+冗长+STL依赖症患者+诡异的实现方式代码
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <list> using namespace std; inline long long read(){ long long ans = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while(!isdigit(ch)) f *= (ch == '-') ? -1 : 1, ch = getchar(); do ans = (ans << 1) + (ans << 3) + (ch ^ 48), ch = getchar(); while(isdigit(ch)); return ans * f; } const int MAXN = 205; int sta[MAXN], dfn[MAXN], low[MAXN], vis[MAXN], isEmbed[MAXN]; vector<int> Plane[MAXN<<1], book[MAXN<<1]; int PlaneNum = 1; struct Graph{ map<int, int> head; vector<int> next, last, val, att; int atp, atpPos; void clear(){ head.clear(), next.clear(), last.clear(), val.clear(), att.clear(), atp = atpPos = 0; next.push_back(0), last.push_back(0), val.push_back(0); next.push_back(0), last.push_back(0), val.push_back(0); } Graph(){clear();} void add(int x,int y){ next.push_back(head[x]), last.push_back(y), val.push_back(1), head[x] = next.size() - 1; } const bool operator < (const Graph &temp) const{ return atp < temp.atp; } }Tot; void getAtp(Graph &G){ sort(G.att.begin(), G.att.end()), G.atp = 0; for(int i=1; i<=PlaneNum; i++){ if(book[i].size() < G.att.size()) continue; int now = 0; for(int j=0; j<G.att.size(); j++){ while(now < book[i].size() - 1 && book[i][now] < G.att[j]) now++; if(book[i][now] != G.att[j]) break; else if(j == G.att.size() - 1) G.atp++, G.atpPos = i; } } } void embed(int pos){ for(int i=1; i<=sta[0]; i++) isEmbed[sta[i]] = true; int l = 0, r = Plane[pos].size() - 1; while(Plane[pos][l] != sta[1] && Plane[pos][l] != sta[sta[0]]) l++; while(Plane[pos][r] != sta[1] && Plane[pos][r] != sta[sta[0]]) r--; vector<int> temp1, temp2; for(int i=0; i<l; i++) temp1.push_back(Plane[pos][i]); if(Plane[pos][l] == sta[1]) for(int i=1; i<=sta[0]; i++) temp1.push_back(sta[i]); else for(int i=sta[0]; i>=1; i--) temp1.push_back(sta[i]); for(int i=r+1; i<Plane[pos].size(); i++) temp1.push_back(Plane[pos][i]); for(int i=r-1; i>l; i--) temp2.push_back(Plane[pos][i]); if(Plane[pos][l] == sta[1]) for(int i=1; i<=sta[0]; i++) temp2.push_back(sta[i]); else for(int i=sta[0]; i>=1; i--) temp2.push_back(sta[i]); Plane[pos] = book[pos] = temp1, ++PlaneNum; Plane[PlaneNum] = book[PlaneNum] = temp2; sort(book[pos].begin(), book[pos].end()), sort(book[PlaneNum].begin(), book[PlaneNum].end()); } bool match(int x,int goal,Graph &G){ vis[x] = true; for(int l=G.head[x]; l; l=G.next[l]){ int y = G.last[l]; if(vis[y]) continue; if(y == goal || (!isEmbed[y] && match(y, goal, G))){ G.val[l] = G.val[l^1] = 0; if(y == goal) sta[++sta[0]] = y; sta[++sta[0]] = x; return true; } } return false; } void findGraph(Graph &G,int l,Graph &ret){ int x = G.last[l], fa = G.last[l^1]; ret.add(x, fa), ret.add(fa, x), G.val[l] = G.val[l^1] = 0; if(!isEmbed[x]) for(int lk=G.head[x]; lk; lk=G.next[lk]){ if(G.val[lk]) findGraph(G, lk, ret); }else if(!vis[x]) ret.att.push_back(x), vis[x] = true; } bool Solve(list<Graph> &Lis){ if(!Lis.size()) return true; list<Graph>::iterator it = Lis.begin(); int cnt = Lis.size() - 1; while(!Lis.empty()){ Graph &Now = *it; getAtp(Now), cnt++; if(!Now.atp) return false; if(cnt == Lis.size() || Now.atp == 1){ memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); sta[0] = 0, match(Now.att[0], Now.att[1], Now); embed(Now.atpPos), memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); for(int j=2; j<sta[0]; j++) for(int l=Now.head[sta[j]]; l; l=Now.next[l]) if(Now.val[l]){ Graph temp; findGraph(Now, l, temp); if(!vis[sta[j]]) temp.att.push_back(sta[j]); for(int k=0; k<temp.att.size(); k++) vis[temp.att[k]] = 0; Lis.push_back(temp); } list<Graph>::iterator temp = it++; Lis.erase(temp), cnt = 0, it--; } it++; if(it == Lis.end()) it = Lis.begin(); } return true; } void Tarjan(int x,int fa,vector<Graph> &ret){ dfn[x] = low[x] = ++dfn[0]; for(int l=Tot.head[x]; l; l=Tot.next[l]){ int y = Tot.last[l]; if(y == fa) continue; if(!dfn[y]) Tarjan(y, x, ret), low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]); else low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]); } if(dfn[x] <= low[x]){ Graph temp; for(int l=Tot.head[x]; l; l=Tot.next[l]) if(Tot.val[l] && dfn[Tot.last[l]] > dfn[x]) findGraph(Tot, l, temp); ret.push_back(temp); } } void findCircle(Graph &G){ int x = G.last[2]; while(!vis[x]){ vis[x] = true; for(int l=G.head[x]; l; l=G.next[l]) if((l ^ 1) != sta[sta[0]]){ x = G.last[l], sta[++sta[0]] = l; break; } } int l = 1, r = sta[0]; while(G.last[sta[l] ^ 1] != x) l++; sta[0] = 0; for(int i=l; i<=r; i++) G.val[sta[i]] = G.val[sta[i] ^ 1] = 0, sta[++sta[0]] = G.last[sta[i] ^ 1]; } int main(){ int T = read(); while(T--){ int n = read(), m = read(); vector<Graph> Div; Tot.clear(); for(int i=1; i<=m; i++){ int x = read(), y = read(); if(x == y) continue; Tot.add(x, y), Tot.add(y, x); } for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) read(); if(m > 3 * n - 6 && m > 1){ printf("NO "); continue; } memset(dfn, 0, sizeof(dfn)); memset(low, 0, sizeof(low)); memset(isEmbed, 0, sizeof(isEmbed)); memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(!dfn[i]) Tarjan(i, -1, Div); bool flag = true; for(int i=0; i<Div.size(); i++){ if(!Div[i].head.size()) continue; sta[0] = 0, findCircle(Div[i]); Plane[1].push_back(sta[1]), Plane[1].push_back(sta[sta[0]]); embed(1); list<Graph> ret; memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); for(int j=1; j<=sta[0]; j++) for(int l=Div[i].head[sta[j]]; l; l=Div[i].next[l]) if(Div[i].val[l]){ Graph temp; findGraph(Div[i], l, temp); if(!vis[sta[j]]) temp.att.push_back(sta[j]); for(int k=0; k<temp.att.size(); k++) vis[temp.att[k]] = 0; ret.push_back(temp); } flag &= Solve(ret); for(int j=1; j<=PlaneNum; j++) Plane[j].clear(), book[j].clear(); PlaneNum = 1; if(!flag) break; } if(flag) printf("YES "); else printf("NO "); } return 0; }
题目是HNOI2010d的Planar,只不过没有读入哈密顿回路
洛谷连接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3209
哈密顿回路做法的时间:

路径嵌入法的时间

总感觉时间多了不少啊。。。。。。不过想想直接寻找哈密顿回路的时间复杂度——
如果要判断一般图的平面性,还是选择路径嵌入法吧