E. NN country
In the NN country, there are $ n $ cities, numbered from $ 1 $ to $ n $ ,ans $ n-1 $ roads, connecting them.
There is a roads path between any two cities.
There are $ m $ bidirectional bus routes between cities.
Buses drive between two cities taking the shortest path with stops in every city they drive through.
Travelling by bus, you can travel from any stop on the route to any other.
You can travel between cities only by bus.
You are interested in $ q $ questions:
is it possible to get from one city to another and what is the minimum number of buses you need to use for it?
Input
The first line contains a single integer $ n (2 le n le 2⋅10^5) $ — the number of cities.
The second line contains $ n-1 $ integers $ p_2,p_3,dots p_n (1 le p_i le i ) $ ,
where $ p_i $ means that cities $ p_i $ and $ i $ are connected by road.
The third line contains a single integer $ m(1 le m le 2⋅10^5) $ — the number of bus routes.
Each of the next $ m $ lines contains $ 2 $ integers $ a $ and $ b (1le a,b le n, quad a
ot= b ) $,
meaning that there is a bus route between cities $ a $and $ b $ .
It is possible that there is more than one route between two cities.
The next line contains a single integer $ q(1 le q le 2⋅10^5) $ — the number of questions you are interested in.
Each of the next $ q $ lines contains $ 2 $ integers $ v $ and $ u (1 le v,u le n,quad v
ot= u ) $,
meaning that you are interested if it is possible to get from city $ v $ to city $ v $ and
what is the minimum number of buses you need to use for it.
Output
Print the answer for each question on a separate line.
If there is no way to get from one city to another, print $ -1 $ .
Otherwise print the minimum number of buses you have to use.
Examples
input1
7
1 1 1 4 5 6
4
4 2
5 4
1 3
6 7
6
4 5
3 5
7 2
4 5
3 2
5 3
output1
1
3
-1
1
2
3
input2
7
1 1 2 3 4 1
4
4 7
3 5
7 6
7 6
6
4 6
3 1
3 2
2 7
6 3
5 3
output2
1
-1
-1
1
-1
1
Note
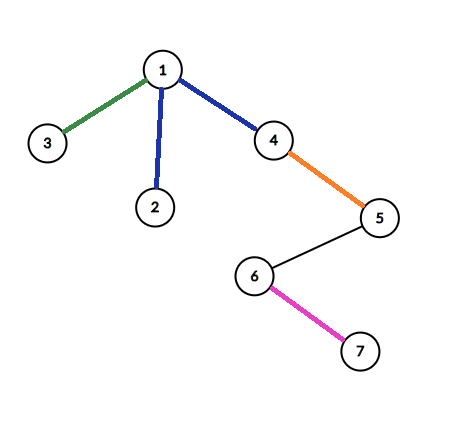
题目大意
-
给定一棵树和若干条路线,每条路线相当于$ x,y $ 之间的路径,途径路径上的每个点
-
给出若干个询问,每次询问从 $ u $ 到 $ v $ 至少需要利用几条路线
-
$ N,M,Q le 200000 $
题解
-
倍增对问题进行转化
-
对于每个点,求出只用一条路线向上能够到达的最高点 $ lowest[x] $
-
对 $ lowest $ 构造倍增数组
-
对于询问 $ (u,v) $ ,倍增到 $ u‘ , v’ $ 后,只需要检查 $ u‘ $ 到 $ v’ $ 是否有跨越 $ lca(u,v) $ 的直达路线
-
计算两点是否有直达路线
-
树状数组维护(DFS)序
-
(DFS)遍历整棵树,递归进入 (x) 时,扫描路线$ (x,y) $,把 $ y $ 在 (DFS) 序上的对应位置 (+1)
-
$ x,y $ 可直达,当且仅当 $ x $ 子树中的节点使 (DFS) 序上 $ y $ 对应的区间的和发生了变化
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 200010
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define PP pair<int,int>
#define mp(a,b) make_pair(a,b)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define debug cout<<1<<endl;
int n,m,Q,ans[maxn];
inline int read() {
register char ch;
while(!isdigit(ch=getchar()));
register int x=ch^'0';
while(isdigit(ch=getchar())) x=(((x<<2)+x)<<1)+(ch^'0');
return x;
}
namespace BIT{
int c[maxn];
inline void add(int x,int val){
for(;x<=n;x+=x&-x) c[x]+=val;
}
inline int qry(int x){
int res=0;
for(;x;x-=x&-x) res+=c[x];
return res;
}
}
namespace Union{
int f[maxn];
inline void init(int n){
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) f[i]=i;
}
int find(int x){
return x==f[x] ? x : f[x]=find(f[x]);
}
inline void merge(int u,int v){
f[u]=v;
}
}
struct edge{ int v,nxt; }e[maxn<<1];
int heade[maxn],tote=1;
void adde(int u,int v){
e[++tote].v=v; e[tote].nxt=heade[u]; heade[u]=tote;
}
struct buss{ int v,nxt; }b[maxn<<1];
int headb[maxn],totb=1,LCA_b[maxn<<1];
void addb(int u,int v){
b[++totb].v=v; b[totb].nxt=headb[u]; headb[u]=totb;
}
struct querys{ int u,v,nxt; }q[maxn<<1];
int headq[maxn],totq=1,LCA_q[maxn<<1];
void addq(int u,int v){
q[++totq].v=v; q[totq].u=u; q[totq].nxt=headq[u]; headq[u]=totq;
}
struct Querys{ int v,nxt; }Qs[maxn<<1];
int headQ[maxn],totQ=1,LCA_Q[maxn<<1];
void addQ(int u,int v){
Qs[++totQ].v=v; Qs[totQ].nxt=headQ[u]; headQ[u]=totQ;
}
PP dfslen[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int dep[maxn],dfn;
void dfs(int u,int pre){
vis[u]=1;
dfslen[u].fi=++dfn;
for(int i=heade[u];i;i=e[i].nxt)
if(!vis[e[i].v]){
int v=e[i].v;
dep[v]=dep[u]+1;
dfs(v,u);
Union::merge(v,u);
}
dfslen[u].se=dfn;
for(int i=headb[u];i;i=b[i].nxt)
if(vis[b[i].v]) LCA_b[i]=LCA_b[i^1]=Union::find(b[i].v);
for(int i=headq[u];i;i=q[i].nxt)
if(vis[q[i].v]) LCA_q[i]=LCA_q[i^1]=Union::find(q[i].v);
}
int lowest[maxn][21];
void getlowest(int u){
vis[u]=1; lowest[u][0]=u;
for(int i=headb[u];i;i=b[i].nxt)
if(dep[LCA_b[i]]<dep[lowest[u][0]] || lowest[u][0]==0)
lowest[u][0]=LCA_b[i];
for(int i=heade[u];i;i=e[i].nxt)
if(!vis[e[i].v]){
int v=e[i].v;
getlowest(v);
if(dep[lowest[v][0]]<dep[lowest[u][0]])
lowest[u][0]=lowest[v][0];
}
}
void dfs2(int u){
vis[u]=1; vector<PP>Qtmp;
for(int i=headQ[u];i;i=Qs[i].nxt){
int v=Qs[i].v;
if(dfslen[v].fi>dfslen[u].fi && ans[i>>1]!=-1)
Qtmp.pb(mp(i,BIT::qry(dfslen[v].se)-BIT::qry(dfslen[v].fi-1)));
}
for(int i=heade[u];i;i=e[i].nxt)
if(!vis[e[i].v]) dfs2(e[i].v);
for(int i=headb[u];i;i=b[i].nxt){
BIT::add(dfslen[b[i].v].fi,1);
BIT::add(dfslen[u ].fi,1);
}
for(int i=0;i<Qtmp.size();++i){
int tmp=BIT::qry(dfslen[Qs[Qtmp[i].fi].v].se)-BIT::qry(dfslen[Qs[Qtmp[i].fi].v].fi-1);
ans[Qtmp[i].fi>>1]+=(Qtmp[i].se!=tmp ? 1 : 2);
}
}
int main(){
n=read();
for(int i=2;i<=n;++i){
int v; v=read();
adde(i,v); adde(v,i);
}
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){
int u,v; u=read(); v=read();
addb(u,v); addb(v,u);
}
scanf("%d",&Q);
for(int i=1;i<=Q;++i){
int u,v; u=read(); v=read();
addq(u,v); addq(v,u);
}
Union::init(n);
dfs(1,0);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(bool)*(n+1));
getlowest(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=20;++j)
lowest[i][j]=lowest[lowest[i][j-1]][j-1];
for(int i=2;i<=totq;i+=2){
int u=q[i].u,v=q[i].v;
int tmp=0;
for(int j=20;~j;--j)
if(dep[lowest[u][j]]>dep[LCA_q[i]]){
u=lowest[u][j];
tmp+=(1<<j);
}
for(int j=20;~j;--j)
if(dep[lowest[v][j]]>dep[LCA_q[i]]){
v=lowest[v][j];
tmp+=(1<<j);
}
addQ(u,v); LCA_Q[totQ]=LCA_q[i];
addQ(v,u); LCA_Q[totQ]=LCA_q[i];
if(dep[lowest[u][0]]<=dep[LCA_Q[i]] && dep[lowest[v][0]]<=dep[LCA_Q[i]])
ans[i>>1]=tmp;
else ans[i>>1]=-1;
}
memset(vis,0,sizeof(bool)*(n+1));
dfs2(1);
for(int i=1;i<=Q;++i) printf("%d
",ans[i]);
return 0;
}