0.目录
1.KMP 子串查找算法
2.KMP 算法的应用
3.小结
1.KMP 子串查找算法
问题:
如何在目标字符串S中,查找是否存在子串P?
朴素解法:

朴素解法的一个优化线索:

示例:
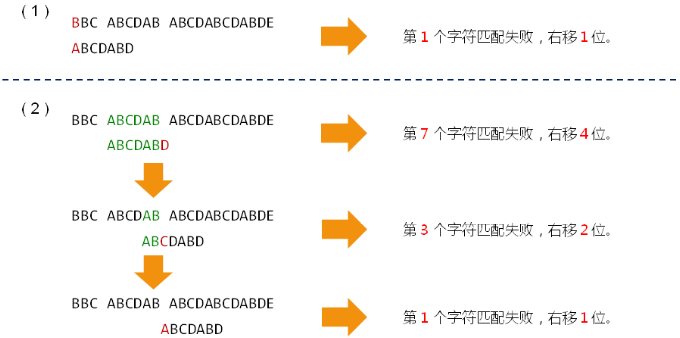
伟大的发现:
- 匹配失败时的右移位数与子串本身相关,与目标串无关
- 移动位数 = 已匹配的字符数 - 对应的部分匹配值
- 任意子串都存在一个唯一的部分匹配表
部分匹配表示例:
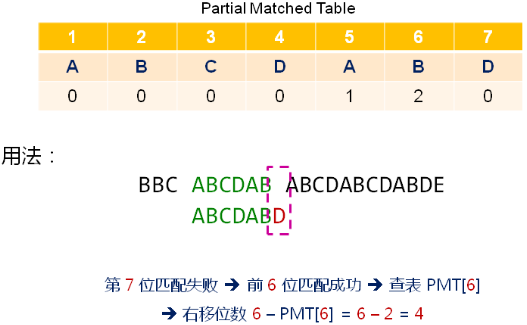
问题:
部分匹配表是怎么得到的?
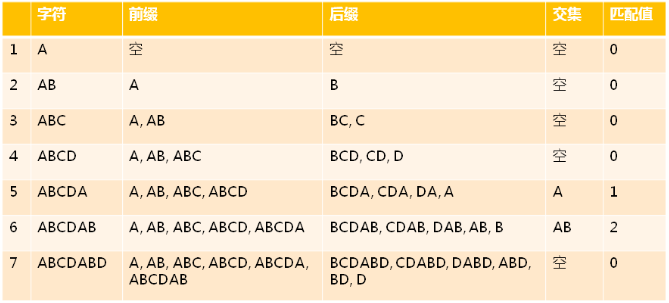
- 前缀
- 除了最后一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部头部组合
- 后缀
- 除了第一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部尾部组合
- 部分匹配值
- 前缀和后缀最长共有元素的长度
示例:ABCDABD
问题:
- 怎么编程产生部分匹配表?
实现关键:
- PMT[1] = 0 ( 下标为0的元素匹配值为0 )
- 从 2 个字符开始递推 ( 从下标为 1 的字符开始递推 )
- 假设 PMT[n] = PMT[n-1] + 1 ( 最长共有元素的长度 )
- 当假设不成立,PMT[n] 在 PMT[n-1] 的基础上减小
编程产生部分匹配表:
(ll代表longest length,即最长共有元素的长度。推导过程遵循下列原则:
(1). 当前欲求的ll值,通过历史ll值推导。
(2). 当可选ll值为0时,直接比对首尾元素。
在求ababax的最后一项ll值时,
前缀为aba b,
后缀为aba x。
重叠部分的长度就是当前的ll值,即:3;PMT(3)的含义是查找3个字符时的ll值,而3个字符时的ll值对应着下标为2的情形;编程实现时注意长度与下标的对应关系。)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int* make_pmt(const char* p)
{
int len = strlen(p);
int* ret = static_cast<int*>(malloc(sizeof(int) * len));
if( ret != NULL )
{
int ll = 0;
ret[0] = 0;
for(int i=1; i<len; i++)
{
while( (ll > 0) && (p[ll] != p[i]) )
{
ll = ret[ll-1];
}
if( p[ll] == p[i] )
{
ll++;
}
ret[i] = ll;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int* pmt_1 = make_pmt("ababax");
cout << "ababax:" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<strlen("ababax"); i++)
{
cout << i << " : " << pmt_1[i] << endl;
}
cout << endl;
int* pmt_2 = make_pmt("ABCDABD");
cout << "ABCDABD:" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<strlen("ABCDABD"); i++)
{
cout << i << " : " << pmt_2[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
ababax:
0 : 0
1 : 0
2 : 1
3 : 2
4 : 3
5 : 0
ABCDABD:
0 : 0
1 : 0
2 : 0
3 : 0
4 : 1
5 : 2
6 : 0
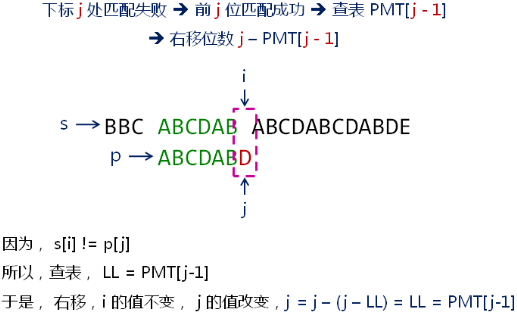
部分匹配表的使用 ( KMP 算法 ):
实现KMP算法:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int* make_pmt(const char* p)
{
int len = strlen(p);
int* ret = static_cast<int*>(malloc(sizeof(int) * len));
if( (ret != NULL) && (len > 0) )
{
int ll = 0;
ret[0] = 0;
for(int i=1; i<len; i++)
{
while( (ll > 0) && (p[ll] != p[i]) )
{
ll = ret[ll-1];
}
if( p[ll] == p[i] )
{
ll++;
}
ret[i] = ll;
}
}
return ret;
}
int kmp(const char* s, const char* p)
{
int ret = -1;
int sl = strlen(s);
int pl = strlen(p);
int* pmt = make_pmt(p);
if( (pmt != NULL) && (0 < pl) && (pl <= sl) )
{
for(int i=0, j=0; i<sl; i++)
{
while( (j > 0) && (s[i] != p[j]) )
{
j = pmt[j-1];
}
if( s[i] == p[j] )
{
j++;
}
if( j == pl )
{
ret = i + 1 - pl;
break;
}
}
}
free(pmt);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cout << kmp("abcde", "cde") << endl;
cout << kmp("ababax", "ba") << endl;
cout << kmp("ababax", "ax") << endl;
cout << kmp("ababax", "") << endl;
cout << kmp("ababax", "ababaxy") << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
2
1
4
-1
-1
2.KMP 算法的应用
思考:
- 如何在目标字符串中查找是否存在指定的子串?
字符串类中的新功能:

将kmp算法的代码集成到自定义字符串类中去:
protected:
static int* make_pmt(const char* p);
static int kmp(const char* s, const char* p);
具体实现:
int* String::make_pmt(const char* p)
{
int len = strlen(p);
int* ret = static_cast<int*>(malloc(sizeof(int) * len));
if( (ret != NULL) && (len > 0) )
{
int ll = 0;
ret[0] = 0;
for(int i=1; i<len; i++)
{
while( (ll > 0) && (p[ll] != p[i]) )
{
ll = ret[ll-1];
}
if( p[ll] == p[i] )
{
ll++;
}
ret[i] = ll;
}
}
return ret;
}
int String::kmp(const char* s, const char* p)
{
int ret = -1;
int sl = strlen(s);
int pl = strlen(p);
int* pmt = make_pmt(p);
if( (pmt != NULL) && (0 < pl) && (pl <= sl) )
{
for(int i=0, j=0; i<sl; i++)
{
while( (j > 0) && (s[i] != p[j]) )
{
j = pmt[j-1];
}
if( s[i] == p[j] )
{
j++;
}
if( j == pl )
{
ret = i + 1 - pl;
break;
}
}
}
free(pmt);
return ret;
}
子串查找 ( KMP 算法的直接运用 ):
- int indexOf(const char* s) const
- int indexOf(const String& s) const
子串查找:
public:
int indexOf(const char* s) const;
int indexOf(const String& s) const;
具体实现:
int String::indexOf(const char* s) const
{
return kmp(m_str, s ? s : "");
}
int String::indexOf(const String& s) const
{
return kmp(m_str, s.m_str);
}
在字符串中将指定的子串删除:
- String& remove(const char* s)
- String& remove(const String& s)

在字符串中将指定的子串删除:
public:
String& remove(int i, int len);
String& remove(const char* s);
String& remove(const String& s);
具体实现:
String& String::remove(int i, int len)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
int n = i;
int m = i + len;
while( (n < m) && (m < m_length) )
{
m_str[n++] = m_str[m++];
}
m_str[n] = '�';
m_length = n;
}
return *this;
}
String& String::remove(const char* s)
{
return remove(indexOf(s), s ? strlen(s) : 0);
}
String& String::remove(const String& s)
{
return remove(indexOf(s), s.length());
}
字符串的减法操作定义 ( operator - ):
- 使用 remove 实现字符串间的减法操作
- 字符串自身不被修改
- 返回产生的新串

字符串的减法操作定义:
public:
String operator - (const String& s) const;
String operator - (const char* s) const;
String& operator -= (const String& s);
String& operator -= (const char* s);
具体实现:
String String::operator - (const String& s) const
{
return String(*this).remove(s);
}
String String::operator - (const char* s) const
{
return String(*this).remove(s);
}
String& String::operator -= (const String& s)
{
return remove(s);
}
String& String::operator -= (const char* s)
{
return remove(s);
}
字符串中的子串替换:
- String& replace(const char* t, const char* s)
- String& replace(const String& t, const char* s)
- String& replace(const char* t, const String& s)
- String& replace(const String& t, const String& s)
字符串中的子串替换:
public:
String& replace(const char* t, const char* s);
String& replace(const String& t, const char* s);
String& replace(const char* t, const String& s);
String& replace(const String& t, const String& s);
具体实现:
String& String::replace(const char* t, const char* s)
{
int index = indexOf(t);
if( index >= 0 )
{
remove(t);
insert(index, s);
}
return *this;
}
String& String::replace(const String& t, const char* s)
{
return replace(t.m_str, s);
}
String& String::replace(const char* t, const String& s)
{
return replace(t, s.m_str);
}
String& String::replace(const String& t, const String& s)
{
return replace(t.m_str, s.m_str);
}
从字符串中创建子串:
- String sub(int i, int len) const
- 以 i 为起点提取长度为 len 的子串
- 子串提取不会改变字符串本身的状态

从字符串中创建子串:
public:
String sub(int i, int len) const;
具体实现:
String String::sub(int i, int len) const
{
String ret;
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
if( len < 0 ) len = 0;
if( len + i > m_length ) len = m_length - i;
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(len + 1));
strncpy(str, m_str + i, len);
str[len] = '�';
ret = str;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
return ret;
}
3.小结
- 部分匹配表是提高子串查找效率的关键
- 部分匹配值定义为前缀和后缀最长共有元素的长度
- 可以用递推的方法产生部分匹配表
- KMP 利用部分匹配值与子串移动位数的关系提高查找效率
- 字符串类是工程开发中必不可少的组件
- 字符串中应该包含常用字符串操作函数
- 增 : insert , operator + , ...
- 删 : remove , operator - , ...
- 查 : indexOf , ...
- 改 : replace , ...
最终的自定义字符串类代码:
StString.h
#ifndef STSTRING_H
#define STSTRING_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace StLib
{
class String : public Object
{
protected:
char* m_str;
int m_length;
void init(const char* s);
bool equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const;
static int* make_pmt(const char* p);
static int kmp(const char* s, const char* p);
public:
String();
String(char c);
String(const char* s);
String(const String& s);
int length() const;
const char* str() const;
bool startWith(const char* s) const;
bool startWith(const String& s) const;
bool endOf(const char* s) const;
bool endOf(const String& s) const;
String& insert(int i, const char* s);
String& insert(int i, const String& s);
String& trim();
int indexOf(const char* s) const;
int indexOf(const String& s) const;
String& remove(int i, int len);
String& remove(const char* s);
String& remove(const String& s);
String& replace(const char* t, const char* s);
String& replace(const String& t, const char* s);
String& replace(const char* t, const String& s);
String& replace(const String& t, const String& s);
String sub(int i, int len) const;
char& operator [] (int i);
char operator [] (int i) const;
bool operator == (const String& s) const;
bool operator == (const char* s) const;
bool operator != (const String& s) const;
bool operator != (const char* s) const;
bool operator > (const String& s) const;
bool operator > (const char* s) const;
bool operator < (const String& s) const;
bool operator < (const char* s) const;
bool operator >= (const String& s) const;
bool operator >= (const char* s) const;
bool operator <= (const String& s) const;
bool operator <= (const char* s) const;
String operator + (const String& s) const;
String operator + (const char* s) const;
String& operator += (const String& s);
String& operator += (const char* s);
String operator - (const String& s) const;
String operator - (const char* s) const;
String& operator -= (const String& s);
String& operator -= (const char* s);
String& operator = (const String& s);
String& operator = (const char* s);
String& operator = (char c);
~String();
};
}
#endif // STSTRING_H
StString.cpp
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "StString.h"
#include "Exception.h"
using namespace std;
namespace StLib
{
int* String::make_pmt(const char* p)
{
int len = strlen(p);
int* ret = static_cast<int*>(malloc(sizeof(int) * len));
if( (ret != NULL) && (len > 0) )
{
int ll = 0;
ret[0] = 0;
for(int i=1; i<len; i++)
{
while( (ll > 0) && (p[ll] != p[i]) )
{
ll = ret[ll-1];
}
if( p[ll] == p[i] )
{
ll++;
}
ret[i] = ll;
}
}
return ret;
}
int String::kmp(const char* s, const char* p)
{
int ret = -1;
int sl = strlen(s);
int pl = strlen(p);
int* pmt = make_pmt(p);
if( (pmt != NULL) && (0 < pl) && (pl <= sl) )
{
for(int i=0, j=0; i<sl; i++)
{
while( (j > 0) && (s[i] != p[j]) )
{
j = pmt[j-1];
}
if( s[i] == p[j] )
{
j++;
}
if( j == pl )
{
ret = i + 1 - pl;
break;
}
}
}
free(pmt);
return ret;
}
void String::init(const char *s)
{
m_str = strdup(s);
if( m_str )
{
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to create String object ...");
}
}
String::String()
{
init("");
}
String::String(char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '�'};
init(s);
}
String::String(const char *s)
{
init(s ? s : "");
}
String::String(const String &s)
{
init(s.m_str);
}
int String::length() const
{
return m_length;
}
const char* String::str() const
{
return m_str;
}
bool String::equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const
{
bool ret = true;
for(int i=0; i<len && ret; i++)
{
ret = ret && (l[i] == r[i]);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::startWith(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = (s != NULL);
if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s);
ret = (len < m_length) && equal(m_str, s, len);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::startWith(const String& s) const
{
return startWith(s.m_str);
}
bool String::endOf(const char* s) const
{
bool ret = (s != NULL);
if( ret )
{
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = m_str + (m_length - len);
ret = (len < m_length) && equal(str, s, len);
}
return ret;
}
bool String::endOf(const String& s) const
{
return endOf(s.m_str);
}
String& String::insert(int i, const char* s)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i <= m_length) )
{
if( (s != NULL) && (s[0] != '�') )
{
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(m_length + len + 1));
if( str != NULL )
{
strncpy(str, m_str, i);
strncpy(str + i, s, len);
strncpy(str + i + len, m_str + i, m_length - i);
str[m_length + len] = '�';
free(m_str);
m_str = str;
m_length = m_length + len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert string value ...");
}
}
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
return *this;
}
String& String::insert(int i, const String& s)
{
return insert(i, s.m_str);
}
String& String::trim()
{
int b = 0;
int e = m_length - 1;
while( m_str[b] == ' ' ) b++;
while( m_str[e] == ' ' ) e--;
if( b == 0 )
{
m_str[e + 1] = '�';
m_length = e + 1;
}
else
{
for(int i=0, j=b; j<=e; i++, j++)
{
m_str[i] = m_str[j];
}
m_str[e - b + 1] = '�';
m_length = e - b + 1;
}
return *this;
}
int String::indexOf(const char* s) const
{
return kmp(m_str, s ? s : "");
}
int String::indexOf(const String& s) const
{
return kmp(m_str, s.m_str);
}
String& String::remove(int i, int len)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
int n = i;
int m = i + len;
while( (n < m) && (m < m_length) )
{
m_str[n++] = m_str[m++];
}
m_str[n] = '�';
m_length = n;
}
return *this;
}
String& String::remove(const char* s)
{
return remove(indexOf(s), s ? strlen(s) : 0);
}
String& String::remove(const String& s)
{
return remove(indexOf(s), s.length());
}
String& String::replace(const char* t, const char* s)
{
int index = indexOf(t);
if( index >= 0 )
{
remove(t);
insert(index, s);
}
return *this;
}
String& String::replace(const String& t, const char* s)
{
return replace(t.m_str, s);
}
String& String::replace(const char* t, const String& s)
{
return replace(t, s.m_str);
}
String& String::replace(const String& t, const String& s)
{
return replace(t.m_str, s.m_str);
}
String String::sub(int i, int len) const
{
String ret;
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
if( len < 0 ) len = 0;
if( len + i > m_length ) len = m_length - i;
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(len + 1));
strncpy(str, m_str + i, len);
str[len] = '�';
ret = str;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
return ret;
}
char& String::operator [] (int i)
{
if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) )
{
return m_str[i];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
}
char String::operator [] (int i) const
{
return (const_cast<String&>(*this))[i];
}
bool String::operator == (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) == 0);
}
bool String::operator == (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") == 0);
}
bool String::operator != (const String& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator != (const char* s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator > (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) > 0);
}
bool String::operator > (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") > 0);
}
bool String::operator < (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) < 0);
}
bool String::operator < (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") < 0);
}
bool String::operator >= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) >= 0);
}
bool String::operator >= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") >= 0);
}
bool String::operator <= (const String& s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) <= 0);
}
bool String::operator <= (const char* s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") <= 0);
}
String String::operator + (const String& s) const
{
return (*this + s.m_str);
}
String String::operator + (const char* s) const
{
String ret;
int len = m_length + strlen(s ? s : "");
char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(len + 1));
if( str )
{
strcpy(str, m_str);
strcat(str, s ? s : "");
free(ret.m_str);
ret.m_str = str;
ret.m_length = len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to add String values ...");
}
return ret;
}
String& String::operator += (const String& s)
{
return (*this = *this + s.m_str);
}
String& String::operator += (const char* s)
{
return (*this = *this + s);
}
String String::operator - (const String& s) const
{
return String(*this).remove(s);
}
String String::operator - (const char* s) const
{
return String(*this).remove(s);
}
String& String::operator -= (const String& s)
{
return remove(s);
}
String& String::operator -= (const char* s)
{
return remove(s);
}
String& String::operator = (const String& s)
{
return (*this = s.m_str);
}
String& String::operator = (const char* s)
{
if( m_str != s )
{
char* str = strdup(s ? s : "");
if( str )
{
free(m_str);
m_str = str;
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to assign new String value ...");
}
}
return *this;
}
String& String::operator = (char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '�'};
return (*this = s);
}
String::~String()
{
free(m_str);
}
}