Description
While creating a customer logo, ACM uses graphical utilities to draw a picture that can later be cut into special fluorescent materials. To ensure proper processing, the shapes in the picture cannot intersect. However, some logos contain such intersecting shapes. It is necessary to detect them and decide how to change the picture.
Given a set of geometric shapes, you are to determine all of their intersections. Only outlines are considered, if a shape is completely inside another one, it is not counted as an intersection.
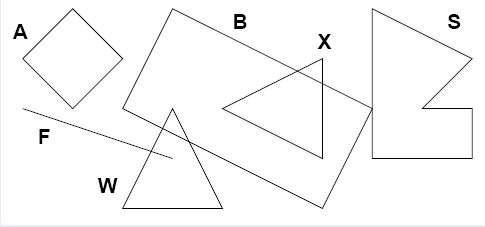
Input
Input contains several pictures. Each picture describes at most 26 shapes, each specified on a separate line. The line begins with an uppercase letter that uniquely identifies the shape inside the corresponding picture. Then there is a kind of the shape and two or more points, everything separated by at least one space. Possible shape kinds are:
• square: Followed by two distinct points giving the opposite corners of the square.
• rectangle: Three points are given, there will always be a right angle between the lines connecting the first point with the second and the second with the third.
• line: Specifies a line segment, two distinct end points are given.
• triangle: Three points are given, they are guaranteed not to be co-linear.
• polygon: Followed by an integer number N (3 ≤ N ≤ 20) and N points specifying vertices of the polygon in either clockwise or anti-clockwise order. The polygon will never intersect itself and its sides will have non-zero length.
All points are always given as two integer coordinates X and Y separated with a comma and enclosed in parentheses. You may assume that |X|, |Y | ≤ 10000.
The picture description is terminated by a line containing a single dash (“-”). After the last picture, there is a line with one dot (“.”).
Output
For each picture, output one line for each of the shapes, sorted alphabetically by its identifier (X). The line must be one of the following:
• “X has no intersections”, if X does not intersect with any other shapes.
• “X intersects with A”, if X intersects with exactly 1 other shape.
• “X intersects with A and B”, if X intersects with exactly 2 other shapes.
• “X intersects with A, B, . . ., and Z”, if X intersects with more than 2 other shapes.
Please note that there is an additional comma for more than two intersections. A, B, etc. are all intersecting shapes, sorted alphabetically.
Print one empty line after each picture, including the last one.
Sample Input
A square (1,2) (3,2) F line (1,3) (4,4) W triangle (3,5) (5,5) (4,3) X triangle (7,2) (7,4) (5,3) S polygon 6 (9,3) (10,3) (10,4) (8,4) (8,1) (10,2) B rectangle (3,3) (7,5) (8,3) - B square (1,1) (2,2) A square (3,3) (4,4) - .
Sample Output
A has no intersections B intersects with S, W, and X F intersects with W S intersects with B W intersects with B and F X intersects with B A has no intersections B has no intersections
题意:给你一些多边形的点,判断每个多边形和那些多边形相交,编号按照字典序输出
关于对一个样例的解释:
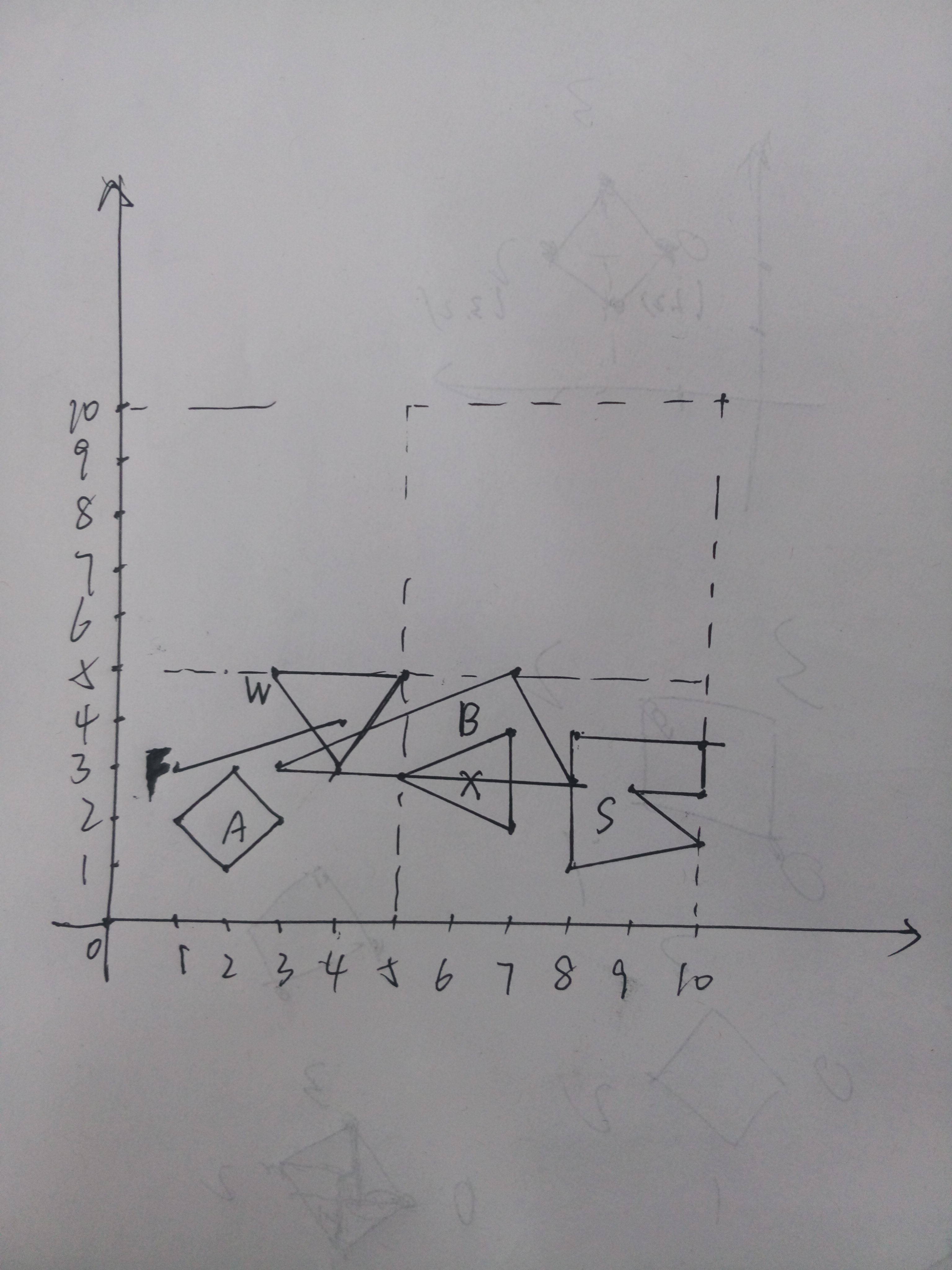
题解:枚举每个多边形的每条边看是否相交,这里的相交是包括端点的,
关键是给你正方形不相邻两个点求另外两个点怎么求,长方形给你3个点求第四个点怎么求?

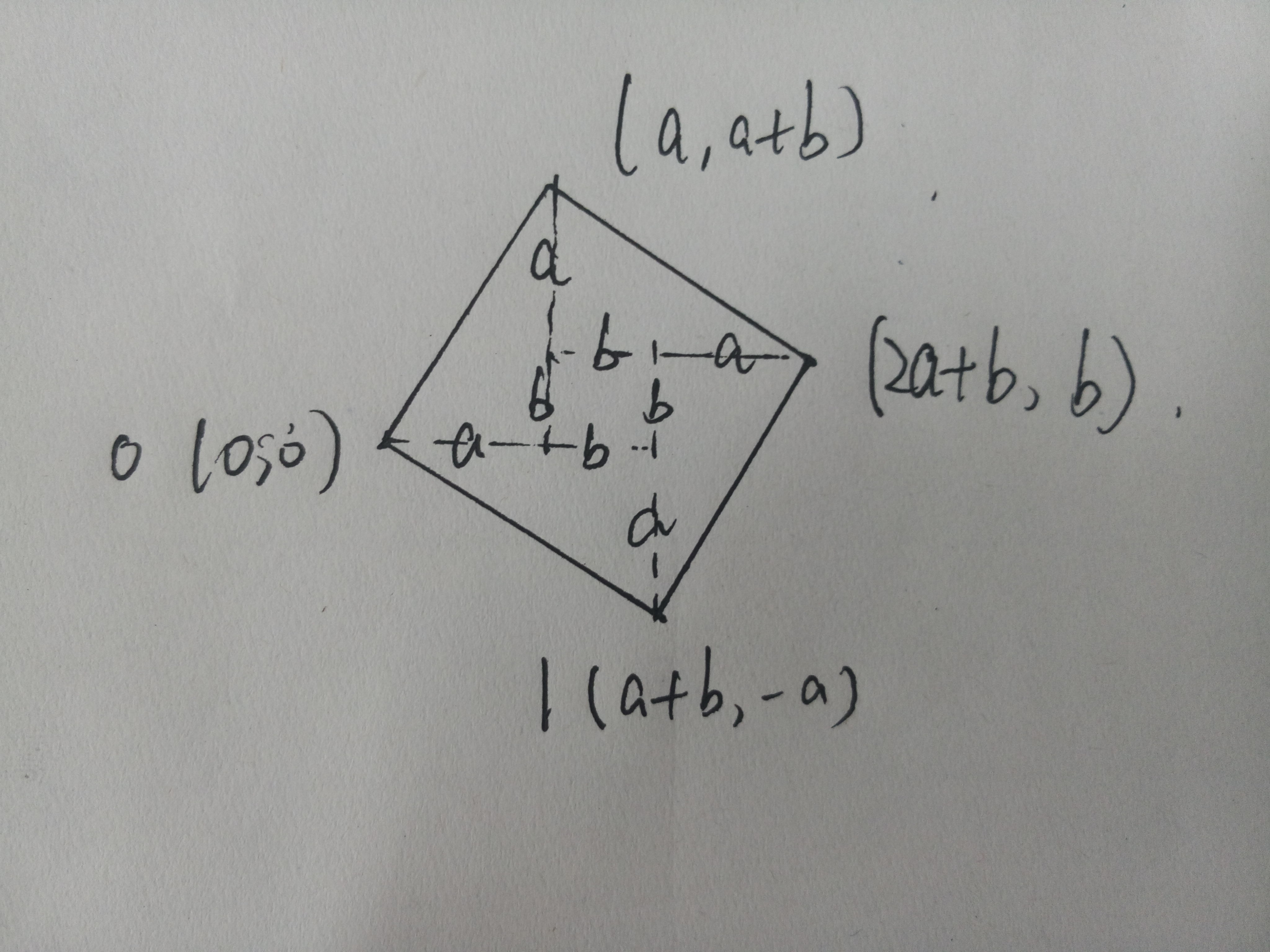
因为对角线的交点为两条对角线的中点,所以
x0 + x2 = x1 + x3
y0 + y2 = y1 + y3
可以证明分割的这几个小三角形是全等的所以有
x1 - x3 = y2 - y0
y1 - y3 = x2 - x0
根据这几个式子可以推出 另外两个点的坐标
求得另一对不相邻的顶点(x1,y1),(x3,y3)。
x1 = (x0 + x2 + y2 - y0) / 2
x3 = (x0 + x2 + y0 - y2) / 2
y1 = (y0 + y2 + x0 - x2) / 2
y3 = (y0 + y2 - x0 + x2) / 2
长方形也是给定三个点求第四个点,很好求,推一下就出来了。
解决了上面的问题之后,把点放到集合中暴力判断线段就行了。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> using namespace std; struct Point { double x,y; Point(double x = 0,double y = 0):x(x),y(y){} }; typedef Point Vector; typedef Point point; Vector operator + (Vector a, Vector b) { return Vector(a.x+b.x,a.y+b.y) ;} Vector operator - (Vector a, Vector b) { return Vector(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y) ;} Vector operator * (Vector a,double p) { return Vector(a.x*p,a.y*p) ;} Vector operator / (Vector a,double p) { return Vector(a.x/p,a.y/p) ;} double Dot(Vector a,Vector b) { return a.x*b.x + a.y*b.y ;} double Length(Vector a) { return sqrt(Dot(a,a)) ;} double Cross(Vector a, Vector b) { return a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x ;} const double eps = 1e-8; int dcmp(double x) { if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0; else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1; } bool operator == (Point a,Point b) { return dcmp(a.x-b.x) == 0&& dcmp(a.y-b.y) == 0; } bool operator < (Point a,Point b) { return a.x < b.x || (a.x == b.x && a.y < b.y); } //下面注释掉的这个是判断直线相交的 本题中全都是线段 /*double Across(point a,point b,point c,point d) //非规范相交也包含在内 { double tmp=Cross(c-a,b-a)*Cross(d-a,b-a); if(tmp<0||fabs(tmp)<eps) return true; return false; }*/ bool Onsegment(Point p,Point a,Point b) //p在ab上 { return dcmp(Cross(b-a,p-a)) == 0 && dcmp(Dot(b-p,a-p)) < 0 || (p == a) || (p == b); } //相交就算 非规范相交也算 bool Segmentsection(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d) { double d1 = Cross(b-a,c-a),d2 = Cross(b-a,d-a),d3 = Cross(d-c,a-c),d4 = Cross(d-c,b-c); if(dcmp(d1)*dcmp(d2) < 0 && dcmp(d3)*dcmp(d4) < 0) return true; else if(dcmp(d1) == 0 && Onsegment(c,a,b) ) return true; else if(dcmp(d2) == 0 && Onsegment(d,a,b) ) return true; else if(dcmp(d3) == 0 && Onsegment(a,c,d) ) return true; else if(dcmp(d4) == 0 && Onsegment(b,c,d) ) return true; else return false; } struct Line { Point s,e; Line(Point s = 0,Point e = 0) :s(s),e(e){} }; struct polygon { Point p[30]; int num; }poly[50]; bool Ispoly(polygon a,polygon b) { if(a.num != 0 && b.num != 0) { for(int i = 0; i < a.num; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < b.num; j++) { if( Segmentsection(a.p[i],a.p[(i+1)%a.num],b.p[j],b.p[(j+1)%b.num]) ) //有一个交点就可以返回了 return true; } } } return false; } int main() { char str[10],strr[20]; memset(poly,0,sizeof(poly)); while(scanf("%s",str) != EOF) //str表示前面的大写字母 { if(strcmp(str,".") == 0) break; if(strcmp(str,"-") == 0) { char c[30]; int k,j; for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) { if(poly[i].num==0) //输入中没有该图形 continue; k = 0; for(j = 0; j < 26; j++) { if(poly[i].num==0||i==j) //输入中没有该图形或者遍历到自己的时候 continue; if(Ispoly(poly[i],poly[j])) //如果有交点 { c[k++] = j + 'A'; } } if(k == 0) //i与其他图形全都没有交点 { printf("%c has no intersections ",i+'A'); } else { printf("%c intersects with %c",i+'A',c[0]); if(k == 2) { printf(" and %c",c[1]); } else if(k > 2) { for(int m = 1; m < k-1; m++) { printf(", %c",c[m]); } printf(", and %c",c[k-1]); //输出格式问题 } printf(" "); } } printf(" "); memset(poly,0,sizeof(poly)); //输出以后清空 continue; } scanf("%s",strr); int temp = str[0]-'A'; //用这个式子把字母转化成数字temp(0~25)排序 因为输出要按照字典序输出 double x,y; if(strcmp(strr,"square") == 0) { poly[temp].num = 4; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[0].x = x, poly[temp].p[0].y = y; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[2].x = x, poly[temp].p[2].y = y; poly[temp].p[1].x = (poly[temp].p[0].x+poly[temp].p[2].x +poly[temp].p[2].y-poly[temp].p[0].y)/2; poly[temp].p[1].y = (poly[temp].p[0].y+poly[temp].p[2].y+poly[temp].p[0].x-poly[temp].p[2].x)/2; poly[temp].p[3].x = (poly[temp].p[0].x+poly[temp].p[2].x +poly[temp].p[0].y-poly[temp].p[2].y)/2; poly[temp].p[3].y = (poly[temp].p[0].y+poly[temp].p[2].y+poly[temp].p[2].x-poly[temp].p[0].x)/2; } else if(strcmp(strr,"rectangle") == 0) { poly[temp].num = 4; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[0].x = x, poly[temp].p[0].y = y; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[1].x = x, poly[temp].p[1].y = y; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[2].x = x, poly[temp].p[2].y = y; poly[temp].p[3].x = (poly[temp].p[0].x + poly[temp].p[2].x - poly[temp].p[1].x); poly[temp].p[3].y = ( poly[temp].p[2].y - poly[temp].p[1].y + poly[temp].p[0].y); } else if(strcmp(strr,"line") == 0) { poly[temp].num = 2; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[0].x = x, poly[temp].p[0].y = y; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[1].x = x, poly[temp].p[1].y = y; } else if(strcmp(strr,"polygon") == 0) { int n; scanf("%d",&n); poly[temp].num = n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[i].x = x, poly[temp].p[i].y = y; } } else { poly[temp].num = 3; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[0].x = x, poly[temp].p[0].y = y; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[1].x = x, poly[temp].p[1].y = y; scanf(" (%lf,%lf)",&x,&y); poly[temp].p[2].x = x, poly[temp].p[2].y = y; } } return 0; }