在循环神经网络的基础上进行了 RNN 的改进,我将介绍四种进化版的循环神经网络
- GRU
- LSTM
- 深度循环神经网络
- 双向循环神经网络
循环神经网络初识:https://blog.csdn.net/RokoBasilisk/article/details/104307813
RNN 出现的梯度爆炸和梯度衰减问题解决梯度爆炸的裁剪梯度方法:https://blog.csdn.net/RokoBasilisk/article/details/104307813
解决梯度衰减问题
GRU RNN
称为 [ 门控循环神经网络 ] :通过捕捉时间序列中时间步较大的依赖关系
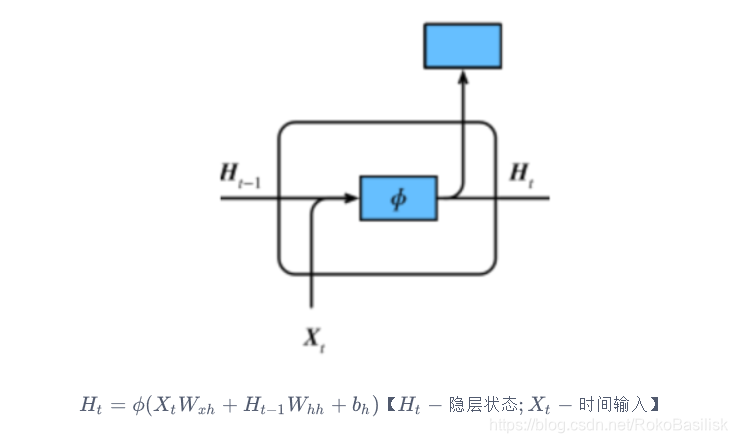
对比 普通神经网络 与 GRU
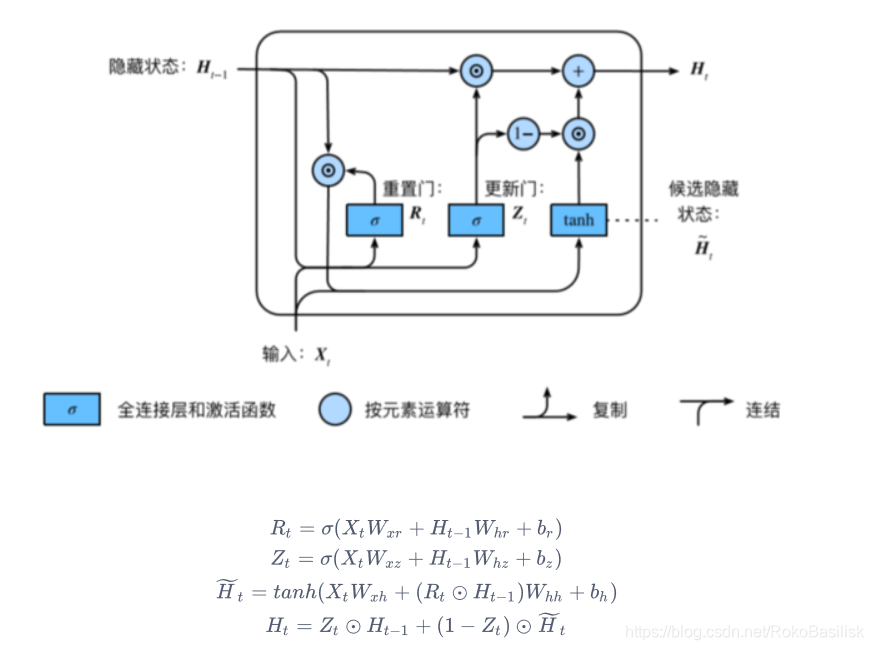
• 重置⻔ : 有助于捕捉时间序列⾥短期的依赖关系;
• 更新⻔ : 有助于捕捉时间序列⾥⻓期的依赖关系。
参数详释
根据参数理解需要初始化的参数,首先表达式中的权重和偏置,6个W和3个b,是更新门、重置门和候选隐藏状态的初始化,紧接着作为下一个 GRU 的 ,此阶段输出时需要初始化输出层参数。
那么假如是第一层这样没有再上一层的输入,就需要初始化最初的状态
实践中理解设计
尽管一个 nn.GRU 包揽全盘,但是为了理解 GRU 的设计…
初始化参数
num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_outputs = vocab_size, 256, vocab_size
# print('will use', device)
def get_params():
def _one(shape):
ts = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=shape), device=device, dtype=torch.float32) #正态分布
return torch.nn.Parameter(ts, requires_grad=True)
def _three():
return (_one((num_inputs, num_hiddens)),
_one((num_hiddens, num_hiddens)),
torch.nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_hiddens, device=device, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=True))
W_xz, W_hz, b_z = _three() # 更新门参数
W_xr, W_hr, b_r = _three() # 重置门参数
W_xh, W_hh, b_h = _three() # 候选隐藏状态参数
# 输出层参数
W_hq = _one((num_hiddens, num_outputs))
b_q = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_outputs, device=device, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=True)
return nn.ParameterList([W_xz, W_hz, b_z, W_xr, W_hr, b_r, W_xh, W_hh, b_h, W_hq, b_q])
def init_gru_state(batch_size, num_hiddens, device): #隐藏状态初始化
return (torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device), )
GRU 模型
def gru(inputs, state, params):
W_xz, W_hz, b_z, W_xr, W_hr, b_r, W_xh, W_hh, b_h, W_hq, b_q = params
H, = state
outputs = []
for X in inputs:
Z = torch.sigmoid(torch.matmul(X, W_xz) + torch.matmul(H, W_hz) + b_z)
R = torch.sigmoid(torch.matmul(X, W_xr) + torch.matmul(H, W_hr) + b_r)
H_tilda = torch.tanh(torch.matmul(X, W_xh) + R * torch.matmul(H, W_hh) + b_h)
H = Z * H + (1 - Z) * H_tilda
Y = torch.matmul(H, W_hq) + b_q
outputs.append(Y)
return outputs, (H,)
LSTM
较 GRUB,LSTM 多了记忆功能,也就是结构上多了个记忆细胞
包含三个门,引入了记忆细胞,和隐藏状态相似,用来记忆额外的信息
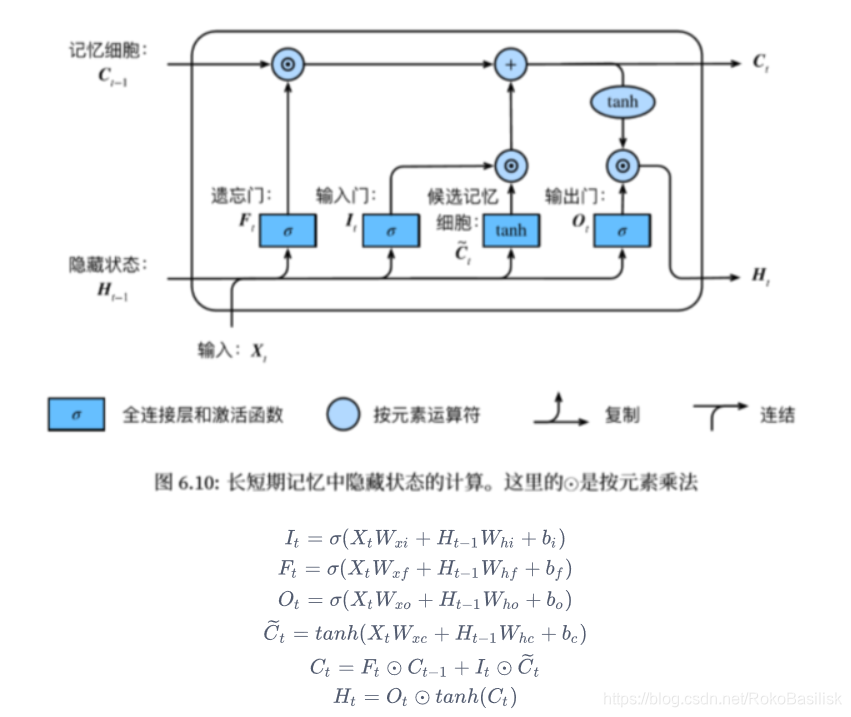
- 遗忘门:控制上一时间步的记忆细胞
- 输入门:控制当前时间步的输入
- 输出门:控制从记忆细胞到隐藏状态
- 记忆细胞:⼀种特殊的隐藏状态的信息的流动
实践中理解设计
初始化参数
num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_outputs = vocab_size, 256, vocab_size
print('will use', device)
def get_params():
def _one(shape):
ts = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=shape), device=device, dtype=torch.float32)
return torch.nn.Parameter(ts, requires_grad=True)
def _three():
return (_one((num_inputs, num_hiddens)),
_one((num_hiddens, num_hiddens)),
torch.nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_hiddens, device=device, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=True))
W_xi, W_hi, b_i = _three() # 输入门参数
W_xf, W_hf, b_f = _three() # 遗忘门参数
W_xo, W_ho, b_o = _three() # 输出门参数
W_xc, W_hc, b_c = _three() # 候选记忆细胞参数
# 输出层参数
W_hq = _one((num_hiddens, num_outputs))
b_q = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_outputs, device=device, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=True)
return nn.ParameterList([W_xi, W_hi, b_i, W_xf, W_hf, b_f, W_xo, W_ho, b_o, W_xc, W_hc, b_c, W_hq, b_q])
def init_lstm_state(batch_size, num_hiddens, device):
return (torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device),
torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device))
LSTM 模型
num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_outputs = vocab_size, 256, vocab_size
print('will use', device)
def get_params():
def _one(shape):
ts = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=shape), device=device, dtype=torch.float32)
return torch.nn.Parameter(ts, requires_grad=True)
def _three():
return (_one((num_inputs, num_hiddens)),
_one((num_hiddens, num_hiddens)),
torch.nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_hiddens, device=device, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=True))
W_xi, W_hi, b_i = _three() # 输入门参数
W_xf, W_hf, b_f = _three() # 遗忘门参数
W_xo, W_ho, b_o = _three() # 输出门参数
W_xc, W_hc, b_c = _three() # 候选记忆细胞参数
# 输出层参数
W_hq = _one((num_hiddens, num_outputs))
b_q = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(num_outputs, device=device, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=True)
return nn.ParameterList([W_xi, W_hi, b_i, W_xf, W_hf, b_f, W_xo, W_ho, b_o, W_xc, W_hc, b_c, W_hq, b_q])
def init_lstm_state(batch_size, num_hiddens, device):
return (torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device),
torch.zeros((batch_size, num_hiddens), device=device))
深度循环神经网络
深度代表高度,对于神经网络隐藏层来说,并非如此,层数的加深会导致收敛困难
对比循环神经网络:https://blog.csdn.net/RokoBasilisk/article/details/104307813
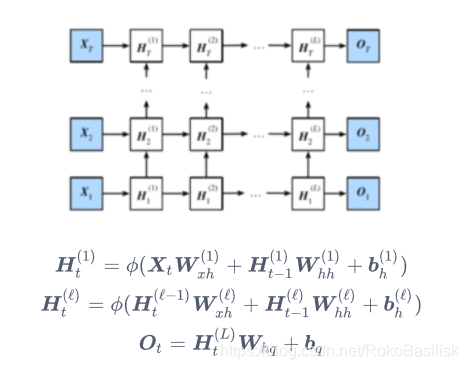
实现方式相同,改变的是 num_layer
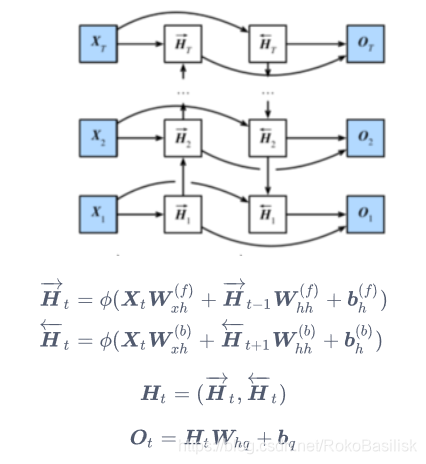
双向循环神经网络
常用于 NLP
特点:预测不再仅依赖于前面的元素,而是同时结合了前后元素,一个词:content
两层隐藏层之间的连接采用了concat的方式