变量,表达式与顺序语句 | 01
这次主要讲解的是C++在算法中常用的语法,不会设计C++在工程中语法. 例如<<C++ Primer>>这本书就是介绍了许多了C++在工程上的语法. 这个C++的语法基础其实是为了后面的算法做铺垫.
其实只要学习了语法基础课和算法基础课,基本都可以应付大多数的笔试面试了.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "Hello World" << endl;
return 0;
}
首先是最简单的一个C++程序, 运行结果打印输出Hello World.
头文件
这里先介绍两个有关于输入输出的头文件
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>包含了printf和scanf
#include<iostream>包含了cin和cout,endl
#include<bits/stdc++.h> 万能头文件,基本包含了全部的头文件
#include<cmath>基本所有和数学头文件都在#include<cmath>
#include<string> 使用字符串
命名空间
using namespace std;
std是个命名空间,类似于cout这些都是定义在std中的.
命名空间的主要用途就是用来防止命名冲突的.
如果没有书写上using namespace std;使用cout的话,就会爆出错误.
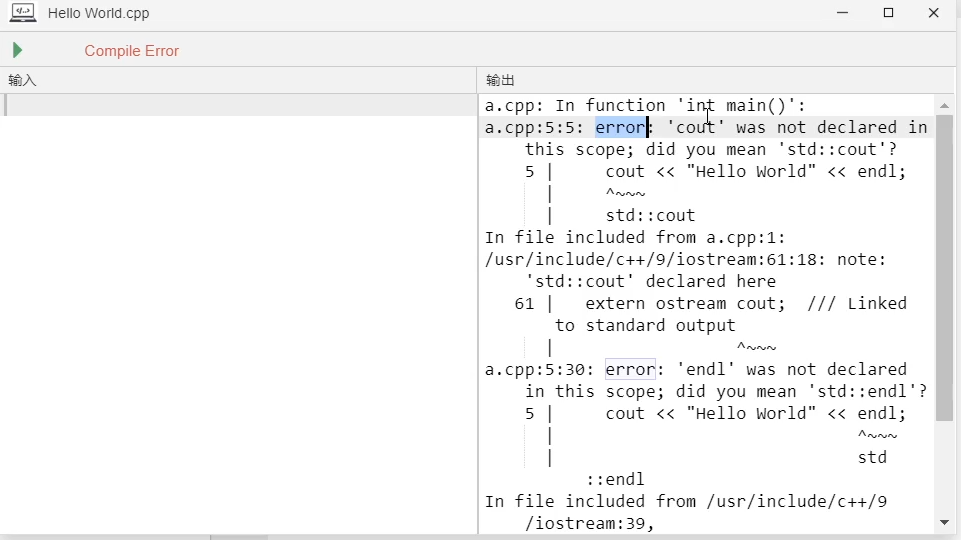
解决方法:
一个就是加上命名空间using namespace std;,一般都是推荐这么做
还有就是使用std::cout, 一般是不会这么写的
主函数
int main(){
// 逻辑代码
return 0;
}
变量的定义
变量必须先定义才能使用,不能重名.
变量的定义方式:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 5;
int b,c = a,d = 10 / 2; // 这里定义按照 类型 __,__,__
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << " " << d << endl;
// 逗号表达式是输出逗号的最后一个
cout << (5,4,3,2) << endl;
return 0;
}
常用变量类型

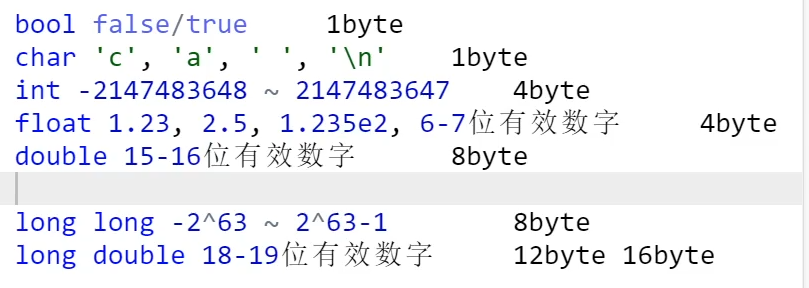
变量的定义方式
类型 __ , __ , __ ;
下划线部分可以填入变量,或者变量直接赋值
#include<iostrream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
int a,b=2,c=4; // 注意按照逗号分开看
float d=1.5,e=1,f=1.235e4; // int也是特殊的float
bool g=false,h=false;
char j='k',k='b'; // 注意要有单引号
long long l = 12321LL;
long double m = 123.154;
return 0;
}
注意: long long在存常数的时候结尾要加上LL,否则就还是按照int来存放
整数的输入输出
首先展示cin/cout的输入输出
// 下面都是一样的
cin >> a >> b;
cin >> a;
cin >> b;
cout << a+b << " " << a*b << endl
cout << a+b;
cout << " ";
cout << endl;
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b; // 定义两个变量
cin >> a >> b; // 输入
cout << a+b << endl; // 输出
return 0;
}
展示scanf/printf的输入输出
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
int main(){
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); // 输入a,b 整数
print("a+b=%d
a*b=%d",a+b,a*b);
// 浮点数的输入输出
// 注意怎么输出保留的小数点
float c,d;
scanf("%f%f",&c,&d); // 输入a,b 整数
print("c+d=%.2f
c*d=%.3f",c+d,c*d);
char e,f;
scanf("%c %c",&e,&f); // 输入a,b 整数
print("%c %c
",e,f);
return 0;
double a,b;
scanf("%lf %lf",&a,&b);
printf("a+b=%.2lf
a*b=%.2lf",a+b,a*b);
long long a,b;
scanf("%lld %lld",&a,&b);
printf("a+b=%lld
a*b=%lld",a+b,a*b);
}
注意: %c是会读入空格的,所以需要把空格过滤一下,但是%d是不会读入空格的
在c++中,bool被当作int来处理
cout保留几位小数这个是比较难写的,不建议大家去看. 需要使用到格式化输出就是使用printf

cin/cout和printf/scanf的不同在于前者是不需要判断变量的类型的,而后者是需要判断变量的类型的.
还有一个就是效率的问题,cin/cout就是使用起来比较方便,但是效率的话scanf/printf会高很多, 特别是大数据读取的时候,推荐使用scanf/printf
取模运算
在C++中的取模运算和数学上的取模还不太一样,数学上要求两个数大于等于0,并且被除数严格小于除数. 但是在c++中,可以支持负数的模运算,取决于除数的符号.
5 % 2 ==> 1
-5 % 2 ==> -1
-5 % -2 ==> -1
自增和自减
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=6;
int b=6;
cout << a++ << endl; // 6
cout << ++a << endl; // 8
cout << ++b << endl; // 7
return 0;
}
a++是先用a的值,然后再进行+1,++a是先进行+1操作.
变量的强制转换
不同的变量类型之间是可以相互赋值的.
float单精度向double双精度变化是没有任何问题的,如果是double向float转的话会损失一些精度.
int变成(float,double)是直接就行变化的,如果是(float,double)转为int,则是进行下取整
int和char的转换就依赖于ASCII码表, 其实char本质上就是一个整数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 5;
float b = (float)a; // 强制转换为浮点类型
printf("%f",b) // 5.000000
float a = 5.23;
float b = (int)a; // 强制转换为int类型
printf("%d",b) // 输出5
int a = 97;
char c = (char)a;
print("%c",c) // 输出a
char a = 'a';
char c = (int)a;
print("%c",c) // 输出97
return 0;
}
char是可以直接和int进行运算的,运算结果就是int.
char a = 'A';
cout << a + 32 << endl; // 97
cout << (char)(a+32) << endl; // 'a'
习题一
A+B
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << a + b << endl;
return 0;
}
差

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b,c,d;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
cout << "DIFERENCA = " << (a*b - c*d) << endl; // 这里还输出了字符串类型
return 0;
}
这种输入的话, 如果是整数,c++输入的时候会过滤空格和回车,这个比Java方便很多
圆的面积

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double pi = 3.14159,r;
cin >> r;
printf("A=%.4lf", r * r * pi);
return 0;
}
在做算法题的时候,能用double尽量使用double,不要使用float
平均数1

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double a,b;
scanf("%lf %lf",&a,&b);
printf("MEDIA = %.5lf",(3.5*a + 7.5*b)/11);
return 0;
}
工资
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,t;
double m;
cin >> n >> t >> m; // cin是可以不区分数据类型直接输入的
printf("NUMBER = %d
SALARY = U$ %.2lf",n,m*t);
return 0;
}
油耗

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double X,Y;
cin >> X >> Y;
printf("%.3lf km/l",X/Y);
return 0;
}
两点的距离

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double x1,x2,y1,y2;
cin >> x1 >> y1;
cin >> x2 >> y2;
printf("%.4lf",sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2)));
return 0;
}
钞票

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[7] = {100,50,20,10,5,2,1},n;
cin >> n;
cout << n << endl;
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
printf("%d nota(s) de R$ %d,00
",n/a[i],a[i]);
n %= a[i]; // %相当于把这个数剔除,不能再和这个数进行整除
}
return 0;
}
时间转换
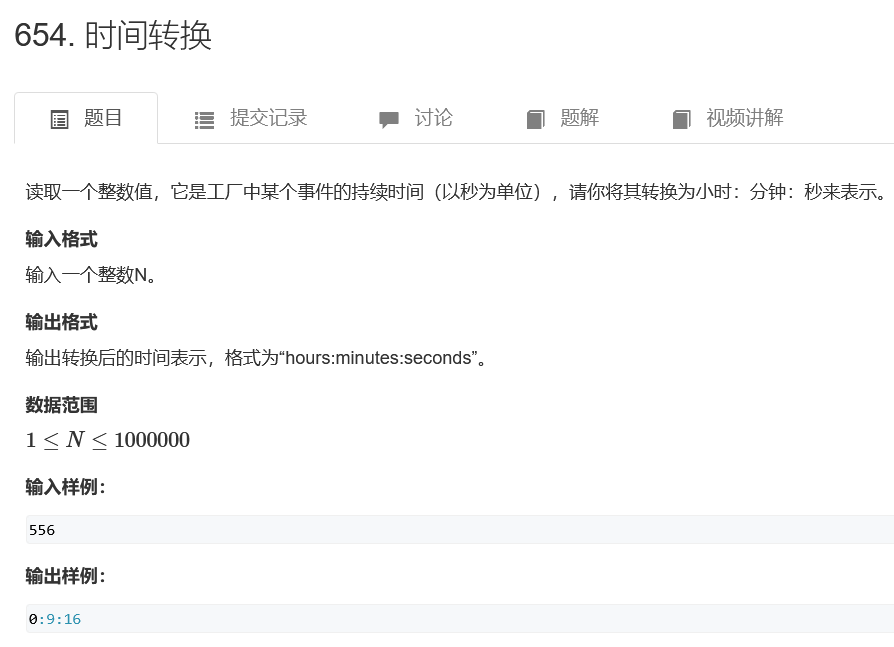
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
printf("%d:%d:%d",n/3600,n%3600/60,n%3600%60);
return 0;
}
注意: %相当于把可以被整除得数给剔除了,而/相当于求出可以被整除的个数
简单乘积

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
printf("PROD = %d",a*b);
return 0;
}
简单计算

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a0,a1,b0,b1;
double a2,b2;
cin >> a0 >> a1 >> a2;
cin >> b0 >> b1 >> b2;
printf("VALOR A PAGAR: R$ %.2lf",a1*a2+b1*b2);
return 0;
}
球的体积

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int r;
cin >> r;
double pi = 3.14159;
printf("VOLUME = %.3lf",4/3. * pi * r * r * r);
return 0 ;
}
面积

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double pi = 3.14159;
double a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
printf("TRIANGULO: %.3lf
",a*c/2);
printf("CIRCULO: %.3lf
",c*c*pi);
printf("TRAPEZIO: %.3lf
",(a+b)*c/2);
printf("QUADRADO: %.3lf
",b*b);
printf("RETANGULO: %.3lf
",a*b);
return 0;
}
平均数2

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
printf("MEDIA = %.1lf",(2*a+3*b+5*c)/10);
return 0;
}
工资和奖金
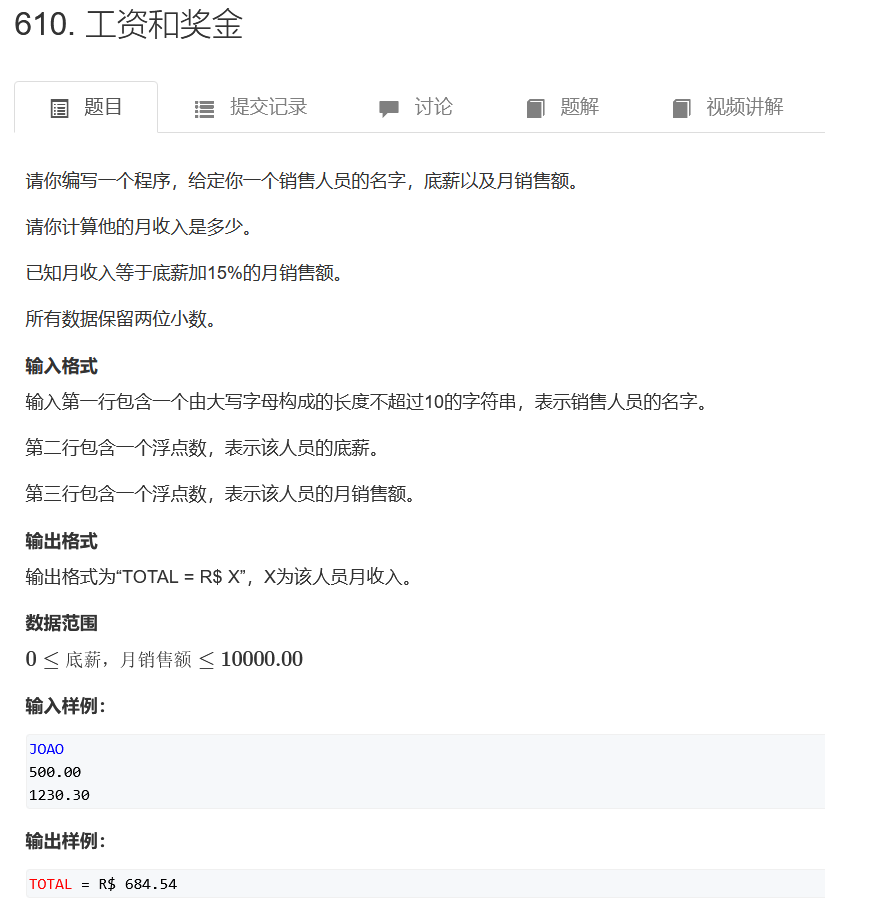
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string name;
cin >> name;
double a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
printf("TOTAL = R$ %.2lf
",a+b*0.15);
return 0;
}
最大值

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b,c,max;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
a > b ? max = a : max = b;
max > c ? max = max : max = c;
printf("%d eh o maior",max);
return 0;
}
距离

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int L;
cin >> L;
printf("%d minutos",L*2);
return 0;
}
燃料消耗
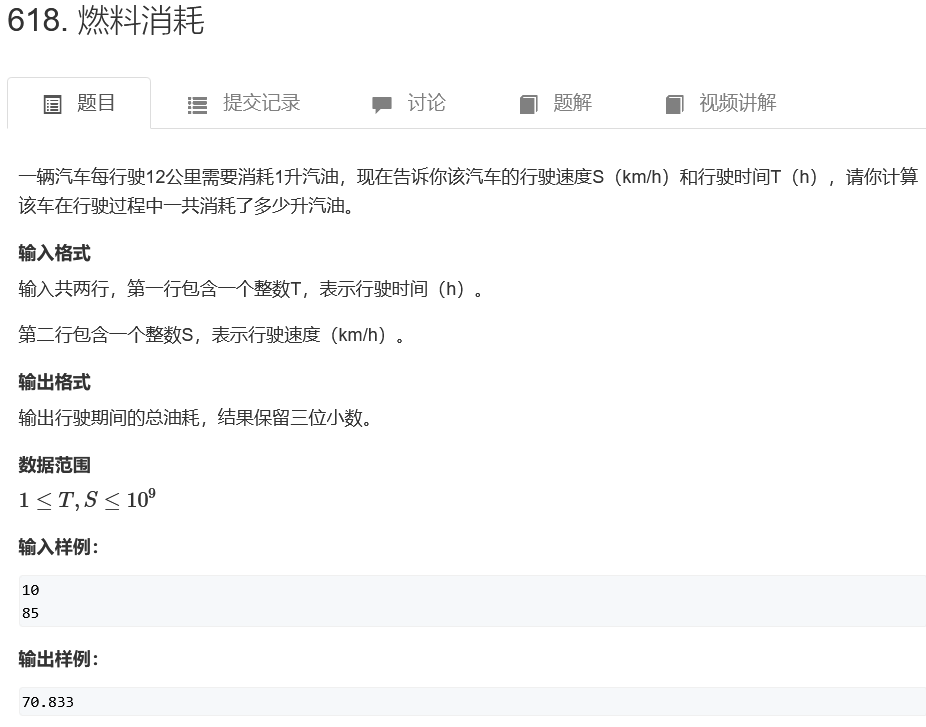
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
double s,t;
cin >> s >> t;
printf("%.3lf",s*t/12);
return 0;
}
钞票和硬币

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "NOTAS:" << endl;
// 扩大100倍数处理
double n;
cin >> n;
n *= 100;
int m = (int)n;
int a[12]={10000,5000,2000,1000,500,200,100,50,25,10,5,1};
int ans[12]; // 存放答案
for(int i=0;i<12;i++){
ans[i] = m/a[i];
m %= a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<12;i++){
if(i>5){
if(i==6)cout << "MOEDAS:" << endl;
printf("%d moeda(s) de R$ %.2lf
",ans[i],a[i]/100.);
}else{
printf("%d nota(s) de R$ %.2lf
",ans[i],a[i]/100.);
}
}
return 0;
}
这个可以把整数和小数分开处理.
强制转int就可以实现向下取整,还有就是需要注意的是浮点数是没有取余数的运算的.
所以最好的做法就是先把这个数扩大100倍.
天数转换

#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
printf("%d ano(s)
",n/365);
printf("%d mes(es)
",n%365/30);
printf("%d dia(s)
",n%365%30/1);
return 0;
}