PS:
身为一名 (20) 届学弟,面对考试无题解,题解少,出现了“千人看动动,万人颓吴迪”的现象。
至于 (skyh) 写了题解,但没有人看,具体原因,咱也不知道,咱也不敢问。
为了造福学弟,一定要多写题解,一定不会咕!!!

循环依赖
签到题,没什么可说的,除了读入字符串有点麻烦,建个图,判个环,就完了。
- 关于读入字符串,我是这么做的:由于 (scanf) 只能读入一个字符串,不会读多余的东西(如,空格, ),所以每读完一个字符串,可以再读一字符,根据这个字符是空格还是 来判断是否停止读入。
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
typedef unsigned long long ull;
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 50, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ull base = 233;
inline int read () {
register int x = 0, w = 1;
register char ch = getchar ();
for (; ch < '0' || ch > '9'; ch = getchar ()) if (ch == '-') w = -1;
for (; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar ()) x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
return x * w;
}
inline void write (register int x) {
if (x / 10) write (x / 10);
putchar (x % 10 + '0');
}
int T, n, nodecnt;
struct Edge {
int to, next;
} e[maxn * 3];
int tot, head[maxn];
inline void Add (register int u, register int v) {
e[++ tot].to = v;
e[tot].next = head[u];
head[u] = tot;
}
map <ull, int> mp;
inline ull HASH (register char * str) {
register int len = strlen (str + 1);
register ull hash = 0;
for (register int i = 1; i <= len; i ++) hash = hash * base + str[i] - '0';
return hash;
}
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], st[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int tic, top, sum;
inline void Init () {
memset (st, 0, sizeof st);
memset (vis, 0, sizeof vis);
memset (dfn, 0, sizeof dfn);
memset (low, 0, sizeof low);
memset (head, 0, sizeof head);
mp.clear (), tic = 0, top = 0, sum = 0, tot = 0, nodecnt = 0;
}
inline void Tarjan (register int u) {
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++ tic, st[++ top] = u, vis[u] = 1;
for (register int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
register int v = e[i].to;
if (! dfn[v]) {
Tarjan (v);
low[u] = min (low[u], low[v]);
} else if (vis[v]) {
low[u] = min (low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
if (dfn[u] == low[u]) {
sum ++;
while (st[top + 1] != u) {
register int v = st[top --];
vis[v] = 0;
}
}
}
int main () {
freopen ("dependency.in", "r", stdin);
freopen ("dependency.out", "w", stdout);
T = read();
while (T --) {
register bool kill = 0;
n = read(), nodecnt = 0, Init ();
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
register char str[11];
scanf ("%s", str + 1);
register ull uhash = HASH (str);
if (! mp[uhash]) mp[uhash] = ++ nodecnt;
register int u = mp[uhash];
while (scanf ("%s", str + 1)) {
register ull tmp = HASH (str);
if (! mp[tmp]) mp[tmp] = ++ nodecnt;
register int v = mp[tmp];
if (u == v) kill = 1;
Add (u, v);
register char flag;
scanf ("%c", &flag);
if (flag == '
') break;
}
}
if (kill) {
puts ("Yes");
goto end;
}
for (register int i = 1; i <= nodecnt; i ++) if (! dfn[i]) Tarjan (i);
if (sum == nodecnt) puts ("No");
else puts ("Yes");
end:;
}
return 0;
}
A
20 pts
应该很好拿吧,(define ;int ;long ;long),都能过。
20 pts + rp pts
可以发现,给出的二次函数,没有常数项,都是过原点的,将式子简单的化一下:
(x) 是给定的,可以分为两种情况:
-
(x) 为正数,((ax+b)) 取最大值。
-
(x) 为负数,((ax+b)) 取最小值。
这样问题就转化成了求 ((ax+b)) 的极值,排一下序,乱搞一下,就有 (60;pts) 了。
如果你像 (skyh) 一样,(rp = INF),你就可以将本题 (A) 掉。
100 pts
考场上距离正解就差那么亿点点,就直接原路返回了。
现在问题不是转化成了求 ((ax+b)) 的极值了吗,可以用单调栈维护一下上凸包和下凸包,来求出多个一次函数的极值。
以 维护最小值,上凸包 为例
将若干个一次函数的斜率 (a) 从大到小排序,以此推入栈中,分为两种情况:
- 插入后与之前的形成一个凸包,(i) 与 (top) 的交点的横坐标大于 (i) 与 (top-1) 的交点的横坐标,不用 (pop)。
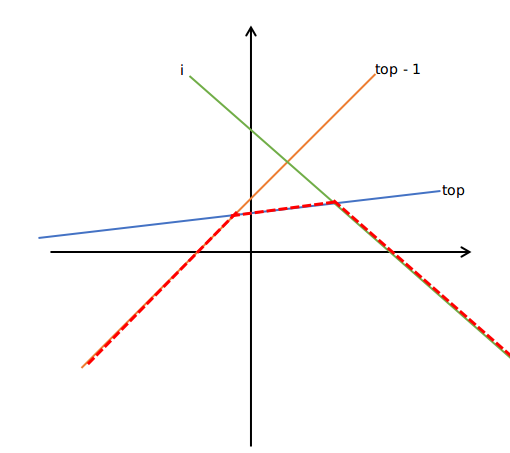
- 插入后与之前的形成一个新的凸包,(i) 与 (top) 的交点的横坐标小于 (i) 与 (top-1) 的交点的横坐标,需要 (pop)。
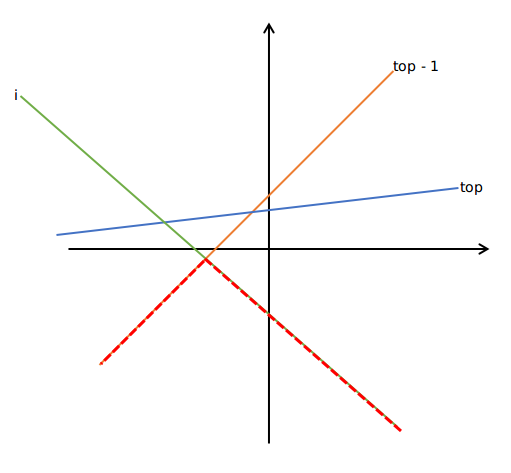
其他情况建议直接手摸,用 (sir) 的话来说:“就挺板子的”。
我们会发现,最后停留在栈中的每个函数片段就是我们所求的凸包,根据不同情况判断,跳一下即可。
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5e5 + 50, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
inline ll read () {
register ll x = 0, w = 1;
register char ch = getchar ();
for (; ch < '0' || ch > '9'; ch = getchar ()) if (ch == '-') w = -1;
for (; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar ()) x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
return x * w;
}
inline void write (register int x) {
if (x / 10) write (x / 10);
putchar (x % 10 + '0');
}
int n, q, top, tmp;
int st[maxn];
ll ans1[maxn], ans2[maxn];
struct Node {
ll a, b;
} a[maxn];
inline bool cmp1 (register Node x, register Node y) {
return x.a > y.a;
}
inline bool cmp2 (register Node x, register Node y) {
return x.a < y.a;
}
inline double Link (register int x, register int y) {
return (double) (a[y].b - a[x].b) / (a[x].a - a[y].a);
}
inline ll Calc (register int i, register ll x) {
return 1ll * a[i].a * x + 1ll * a[i].b;
}
int main () {
freopen ("A.in", "r", stdin);
freopen ("A.out", "w", stdout);
n = read(), q = read();
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) a[i].a = read(), a[i].b = read();
top = 0, tmp = 1, sort (a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp1); // 最小值斜率从大到小
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { // 维护最小值,上凸包
if (top && a[st[top]].a == a[i].a && a[st[top]].b <= a[i].b) continue;
while (top && a[st[top]].a == a[i].a && a[st[top]].b > a[i].b) top --;
while (top > 1 && Link (i, st[top - 1]) >= Link (i, st[top])) top --;
st[++ top] = i;
}
for (register ll x = 32323; x >= 1; x --) {
while (tmp < top && Calc (st[tmp], -x) >= Calc (st[tmp + 1], -x)) tmp ++;
ans2[x] = Calc (st[tmp], -x);
}
top = 0, tmp = 1, sort (a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp2); // 最大值斜率从小到大
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) { // 维护最大值,下凸包
if (top && a[st[top]].a == a[i].a && a[st[top]].b >= a[i].b) continue;
while (top && a[st[top]].a == a[i].a && a[st[top]].b < a[i].b) top --;
while (top > 1 && Link (i, st[top - 1]) >= Link (i, st[top])) top --;
st[++ top] = i;
}
for (register ll x = 1; x <= 32323; x ++) {
while (tmp < top && Calc (st[tmp], x) <= Calc (st[tmp + 1], x)) tmp ++;
ans1[x] = Calc (st[tmp], x);
}
while (q --) {
register ll x = read();
if (x >= 0) printf ("%lld
", 1ll * x * ans1[x]);
else printf ("%lld
", 1ll * x * ans2[-x]);
}
return 0;
}
B
因为考场上撤硕,(skyh) 改题面没听到,考完我也没读懂题,向 ghosh 图草。
某人:哦,改题面了,忘了跟你说...

10 pts
显然 (5 imes 5 = 25) 的超强数据,直接暴搜显然会 (T),发现好多状态被访问了多次,记忆化一下好了。
20 pts
会发现 (a_i=1) 时,有规律,(frac {num[1] + 1}{2}),很好找到吧~~
60 pts
当只有两个数的时候,可以分情况讨论:
- 在 (a[1]) 取完后,(a[2]) 没取完。
考虑 (a[2]) 在 (a[1]) 取完前取了 (i) 个,如果我们将每次取数的操作打成一个序列,当前情况如下:

最后一个取的必定是 (a[1]),答案是:
意义:
一共选了 (a[1] + i) 个,步数就是 (a[1] + i),由于选这段序列的时候 (a[1]) 和 (a[2]) 都未选完,所以要乘上每一位所需的概率 (frac{1}{2})。
再乘上前面那个线段里的 (a[1]) 和 (a[2]) 选择的顺序是任意的,所以乘上一个组合数。
- 在 (a[2]) 取完后,(a[1]) 没取完。
考虑 (a[2]) 取完后 (a[1]) 剩了 (i;(igeq 1)) (最后一个取的一定是 (a[1]),所以至少剩一个) 个,打成序列如下:
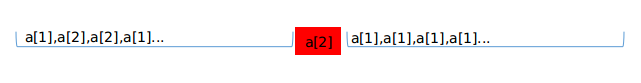
标红的是最后一个 (a[2]),显然后面取得只能全是 (a[1]),答案是:
意义:
如果你理解了上面那个,这个不用我说,你应该就能理解。
显然这已经将 (a[1]) 和 (a[2]) 全选完了,所以步数就是 (a[1] + a[2]) 。
在取完最后一个 (a[2]) 之前,(a[1]) 和 (a[2]) 都还有,所以要乘上概率 (frac{1}{2}),但是取完最后一个 (a[2]),就只剩下 (i) 个 (a[1]) 了,概率就是 (1) 。
再乘上前面那个线段 (a[1]) 和 (a[2]) 任意选的组合数。
100 pts
如果你将 (60;pts) 轻易的打出来了,下面的可能需要你重新整理一下思路,正解与上面的说有关系,也没关系(啊巴啊巴啊巴)
首先引进一个函数 (f[i]) 表示 (a[i]) 被取的期望值,也就是选 (a[i]) 的期望次数。
由期望的线性性((E_{a + b} = E_a + E_b))得出:
很好理解吧~~
容易发现:
我们 (60;pts) 的做法,求的就是这个,但是,如果我们对每个 (a[i]) 都求一边,复杂度是 (Theta(n^2)),难以接受。
但是我们漏了一个很重要的条件 (a[i]leq 5 imes 10^5),不妨求出每个值的期望次数,对于每个 (a[i]),在根据 (a[i]) 的值得到相应的概率。
由此,我们可以得到我们的 (f[a[i]]) 的式子:
会发现,式子跟之前那个出现了一点小差别,前半部分应该没问题,仍就是“在 (a[1]) 取完后,(a[2]) 没取完”的情况。
后面的式子我们用了一个 (1) 减去什么东东,很好理解,因为除了上面的情况,剩下的就是这样的情况了,所以直接用 (1) 减是正确的。
然后 (for) 循环直接求即可。
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define int long long // 小朋友不要学坏
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5e5 + 50, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 323232323;
inline int read () {
register int x = 0, w = 1;
register char ch = getchar ();
for (; ch < '0' || ch > '9'; ch = getchar ()) if (ch == '-') w = -1;
for (; ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'; ch = getchar ()) x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
return x * w;
}
inline void write (register int x) {
if (x / 10) write (x / 10);
putchar (x % 10 + '0');
}
int n, ans, inv2, maxval;
int a[maxn], f[maxn], g[maxn];
int fac[maxn], facinv[maxn];
inline int qpow (register int a, register int b) {
register int ans = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) ans = ans * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
inline void Init () {
fac[0] = 1;
for (register int i = 1; i <= 5e5; i ++) fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % mod;
facinv[500000] = qpow (fac[500000], mod - 2);
for (register int i = 5e5; i >= 1; i --) facinv[i - 1] = facinv[i] * i % mod;
}
inline int C (register int a, register int b) {
if (a == b || a == 0 || b == 0) return 1;
if (a < b) return 0;
return fac[a] * facinv[b] % mod * facinv[a - b] % mod;
}
signed main () {
freopen ("B.in", "r", stdin);
freopen ("B.out", "w", stdout);
n = read(), Init (), inv2 = facinv[2];
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
a[i] = read();
if (i >= 2) maxval = max (a[i], maxval);
}
g[0] = C (a[1] - 1, 0) * qpow (inv2, a[1]) % mod;
for (register int i = 1; i <= maxval; i ++) {
g[i] = (g[i - 1] + C (a[1] + i - 1, i) * qpow (inv2, a[1] + i) % mod) % mod;
f[i] = (f[i - 1] + i * C (a[1] + i - 1, i) % mod * qpow (inv2, a[1] + i) % mod) % mod;
}
for (register int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) {
ans = (ans + (f[a[i]] + a[i] * (1 - g[a[i]] + mod) % mod) % mod) % mod;
}
printf ("%lld
", (ans + a[1]) % mod);
return 0;
}
C
暂时只会一个一个跳...