python3-列表-字典-集合
1.列表1作为key,列表2作为value,组成一个字典
1 #定义两个列表 2 list1 = ["a","b","c"] 3 list2 = ["红","绿","蓝"] 4 5 #合并为字典,调用dict(zip()) 6 dict_name = dict(zip(list1,list2)) 7 8 print(dict_name) 9 10 运行结果: 11 {"a": "红", "b": "绿","c": "蓝" }
2.list的set和反转
num = [2,2,1,5,4] num = list(set(num)) print(num) #结果为 [1,2,4,5] #list(set())可以重新排序,除去重复值
统计重复项的个数方法:
mylist = [1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4,4] myset = set(mylist) #myset是另外一个列表,里面的内容是mylist里面的无重复 项 for item in myset: print("the %d has found %d" %(item,mylist.count(item)))
num.reverse() print(num) #结果为 [5,4,2,1] #不能对其进行赋值,只能改原列表,翻转原列表中内容的顺序
python内置的数据类型
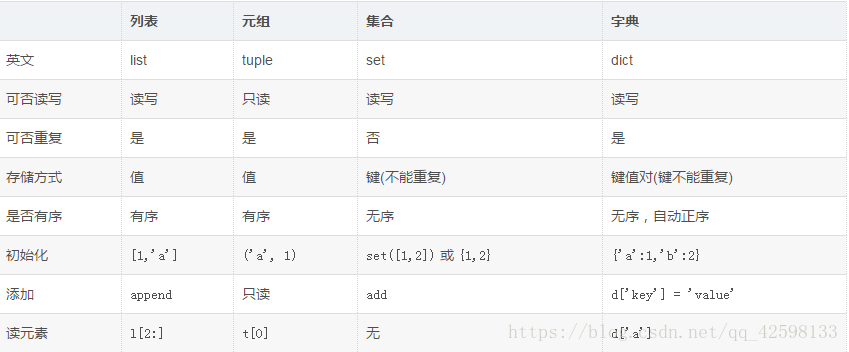
布尔(bool),整形(int),字符串(str),元组(tuple),列表(list),字典(dict)
其中元组,列表和字典的区别如下图
关于set()方法
对一个列表使用set()方法,可以去重并且重新排序,但操作之后获得的数据类型就会从列表变成集合,这点要注意一下
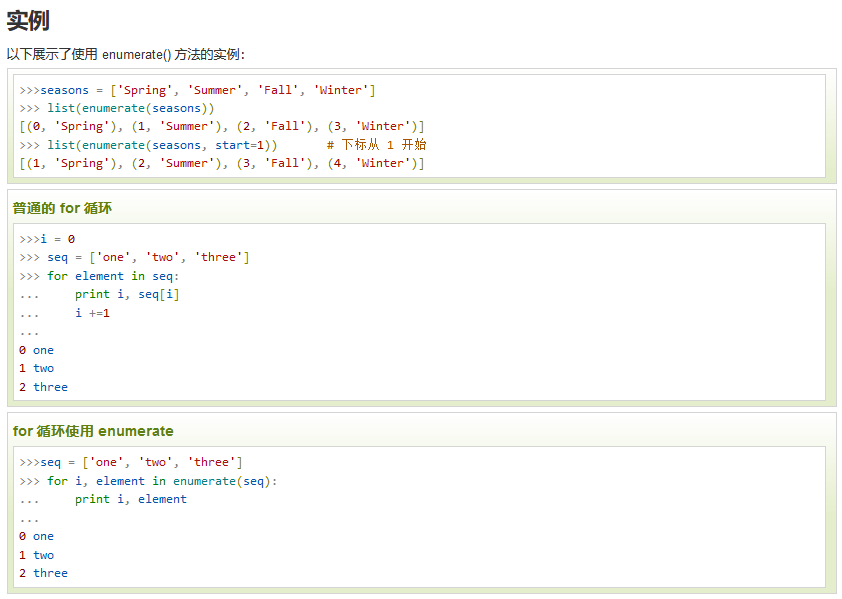
关于enumerate方法
把一个可遍历的数据对象组合为一个索引序列,同时出现数据和下标,一般用在for循环中
语法为enumerate(对象,[start=0])
start是下标起始位置
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42598133/article/details/81635795