ASP.NET CORE 入门教程
第一课 基本概念
- 基本概念
- Asp.Net Core Mvc是.NET Core平台下的一种Web应用开发框架
- 符合Web应用特点
- .NET Core跨平台解决方案
- MVC设计模式的一种实现
- Asp.Net Core Mvc是.NET Core平台下的一种Web应用开发框架
- 环境准备
- 安装最新版Visual Studio 2017
- 安装最新版.NET Core Sdk
第二课 控制器的介绍
- 控制器定义方式:
- 命名以
Controller结尾 - 使用
ControllerAttribute标注
- 命名以
public class TestController : Controller
{
}
[Controller]
public class Test : Controller
{
}
-
默认路由规则
- 域名/控制器类/方法
{Domain}/{Controller}/{Action}
-
数据形式
QueryString: ?name=zhangsan&age=22FormCookieSessionHeader
-
HttpRequest
- HttpRequest 是用户请求对象
- 提供获取请求数据的属性
- Cookies,Headers,Query,QueryString,Form
public IActionResult Hello()
{
// Query
var name = Request.Query["name"];
// QueryString
var query = Request.QueryString.Value;
// Form
var username = Request.Form["username"];
// Cookies
var cookie = Request.Cookies["item"];
// Headers
var headers = Request.Headers["salt"];
return Content("Hello");
}
- HttpContext
- HttpContext是用户请求上下文
- 提供Session属性获取Session对象
- Session.Set 设置
- Session.Remove 移除
- Session.TryGetValue 获取数据
public IActionResult Hello()
{
// byte[]
HttpContext.Session.Set("byte", new byte[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 });
var bytes = HttpContext.Session.Get("byte");
// string
HttpContext.Session.SetString("name", "tom");
var name = HttpContext.Session.GetString("name");
// int
HttpContext.Session.SetInt32("id", 20);
var id = HttpContext.Session.GetInt32("id");
HttpContext.Session.Remove("name");
HttpContext.Session.Clear();
return Content("Hello");
}
- 数据绑定
- 把用户请求的数据绑定到控制器方法的参数上
- 支持简单类型与自定义类型
- 绑定规则是请求数据名称与参数名称一致
- 如查询字符串key名称跟参数一致
- Form表单名称跟参数一致
public IActionResult Hello(RequestModel request,int? age)
{
// 查询字符串
var test = Request.Query["test"];
// 简单类型
var userAge = age;
// 自定义类型
var name = request.Name;
return Content("Hello");
}
public class RequestModel
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
- 内容补充
- 如果以Controller结尾的都是控制器,那如果程序里面由一些业务命名的时候也是以Controller结尾,怎么办?
NonControllerAttribute
/// <summary>
/// 拍卖师控制类
/// </summary>
[NonController]
public class AuctionController
{
}
- 常用特性
| 特性 | 数据源 |
|---|---|
| FromHeaderAttribute | 请求头数据 |
| FromRouteAttribute | 路由数据 |
| FromBodyAttribute | 请求体 |
| FromFormAttribute | 表单数据 |
| FromQueryAttribute | 查询字符串 |
| FromServicesAttribute | 服务注册 |
public IActionResult Say(
[FromForm]string name,
[FromQuery]int age,
[FromHeader] string salt,
[FromBody] string content
)
{
return View();
}
-
特性参数
- 通过特性修饰参数来影响绑定逻辑
- 灵活扩展
-
IActionResult
- 动作结果接口
- 具体实现
- JsonResult:返回JSON结构数据
- RedirectResult:跳转到新地址
- FileResult:返回文件
- ViewResult:返回视图内容
- ContentResult:文本内容
第三课 视图与表单
- 数据传递
- ViewData
- ViewBag
- tempData
- Model
- Session
- Cache
| ViewData | ViewBag |
|---|---|
| 键值对 | 动态类型 |
| 索引器 | ViewData的封装 |
| 支持任意类型 | 动态属性 |
| TempData | Cache | Session |
|---|---|---|
| 视图级别 | 应用程序级别 | 会话级别 |
| 只允许消费一次 | 服务器端保存 | 服务器端保存 |
| 可多次赋值 | 可设置有效期 | 键值对形式 |
| 键值对形式 | 键值对形式 |
- Cache
- 与.NET Framework时代不同,一种全新实现
- IMemoryCache接口
- 依赖注入方式获取
- IMemoryCache.Get/Set操作数据
[Controller]
public class Test : Controller
{
private readonly IMemoryCache _cache;
public Test(IMemoryCache memoryCache)
{
this._cache = memoryCache;
}
public IActionResult ReadCache()
{
_cache.Set("name","tom");
_cache.Get("name");
_cache.Set("age",30);
_cache.Get("age");
User tom = new User(){ Name = "admin",Pwd = "123456"};
_cache.Set<User>("user",tom);
_cache.Get<User>("user");
return Content("ok");
}
}
public class User
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Pwd { get; set; }
}
- ViewStart
- 以_ViewStart.cshtml命名,固定名称,不能更换
- 一般放在视图所在目录的根目录下
- 自动执行,无需手工调用
- 不要再ViewStart中做大量的业务操作
- ViewImport
- 以_ViewImport.cshtml命名,固定名称,不能更换
- 只作引入操作
- 一般放在视图所在目录的根目录下
- 自动执行,无需手工调用
- 视图中可以使用@using关键字引入所需命名空间
- 通过ViewImport做全局性的命名空间引入,减少在每个页面中引入的工作量
第四课 数据验证
- 数据验证特性
ValidationAttribute
public abstract class ValidationAttribute : Attribute
{
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationAttribute"></see> class.</summary>
protected ValidationAttribute();
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationAttribute"></see> class by using the function that enables access to validation resources.</summary>
/// <param name="errorMessageAccessor">The function that enables access to validation resources.</param>
/// <exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException"><paramref name="errorMessageAccessor">errorMessageAccessor</paramref> is null.</exception>
protected ValidationAttribute(Func<string> errorMessageAccessor);
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationAttribute"></see> class by using the error message to associate with a validation control.</summary>
/// <param name="errorMessage">The error message to associate with a validation control.</param>
protected ValidationAttribute(string errorMessage);
/// <summary>Gets or sets an error message to associate with a validation control if validation fails.</summary>
/// <returns>The error message that is associated with the validation control.</returns>
public string ErrorMessage { get; set; }
/// <summary>Gets or sets the error message resource name to use in order to look up the <see cref="P:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationAttribute.ErrorMessageResourceType"></see> property value if validation fails.</summary>
/// <returns>The error message resource that is associated with a validation control.</returns>
public string ErrorMessageResourceName { get; set; }
/// <summary>Gets or sets the resource type to use for error-message lookup if validation fails.</summary>
/// <returns>The type of error message that is associated with a validation control.</returns>
public Type ErrorMessageResourceType { get; set; }
/// <summary>Gets the localized validation error message.</summary>
/// <returns>The localized validation error message.</returns>
protected string ErrorMessageString { get; }
/// <summary>Gets a value that indicates whether the attribute requires validation context.</summary>
/// <returns>true if the attribute requires validation context; otherwise, false.</returns>
public virtual bool RequiresValidationContext { get; }
/// <summary>Applies formatting to an error message, based on the data field where the error occurred.</summary>
/// <param name="name">The name to include in the formatted message.</param>
/// <returns>An instance of the formatted error message.</returns>
public virtual string FormatErrorMessage(string name);
/// <summary>Checks whether the specified value is valid with respect to the current validation attribute.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The value to validate.</param>
/// <param name="validationContext">The context information about the validation operation.</param>
/// <returns>An instance of the <see cref="System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationResult"></see> class.</returns>
public ValidationResult GetValidationResult(
object value,
ValidationContext validationContext);
/// <summary>Determines whether the specified value of the object is valid.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The value of the object to validate.</param>
/// <returns>true if the specified value is valid; otherwise, false.</returns>
public virtual bool IsValid(object value);
/// <summary>Validates the specified value with respect to the current validation attribute.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The value to validate.</param>
/// <param name="validationContext">The context information about the validation operation.</param>
/// <returns>An instance of the <see cref="System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationResult"></see> class.</returns>
protected virtual ValidationResult IsValid(
object value,
ValidationContext validationContext);
/// <summary>Validates the specified object.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The object to validate.</param>
/// <param name="validationContext">The <see cref="T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationContext"></see> object that describes the context where the validation checks are performed. This parameter cannot be null.</param>
/// <exception cref="T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationException">Validation failed.</exception>
public void Validate(object value, ValidationContext validationContext);
/// <summary>Validates the specified object.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The value of the object to validate.</param>
/// <param name="name">The name to include in the error message.</param>
/// <exception cref="T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationException"><paramref name="value">value</paramref> is not valid.</exception>
public void Validate(object value, string name);
}
-
常用数据验证
- RequiredAttribute
- RegularExpressionAttribute
- CompareAttribute
- RangeAttribute
- MaxAttribute
- MinAttribute
- StringLengthAttribute
- DataTypeAttribute
-
服务器端使用
- 使用包含验证规则的类接收数据
- 使用ModelState.IsValid判断是否符合要求
-
前端使用
- 定义强类型视图并传递包含验证规则的业务数据模型
- 使用HtmlHelper.ValidationFor初始前端验证规则
- 使用HtmlHelper.ValidationMessageFor生成提示文字
public class UserLogin
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "用户名不能为空")]
[StringLength(10,ErrorMessage = "用户名长度不能超过10位")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
//[Required(ErrorMessage = "密码不能为空")]
[StringLength(6,ErrorMessage = "密码长度不能超过6位")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
public class FormController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View(new UserLogin());
}
public IActionResult PostData(UserLogin login)
{
return Content(ModelState.IsValid?"数据有效":"数据无效");
}
}
@model Lesson2.Models.UserLogin
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Index</title>
<script src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/lib/jquery-validation/dist/jquery.validate.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/lib/jquery-validation-unobtrusive/jquery.validate.unobtrusive.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<form asp-action="PostData" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名</td>
<td>@Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.UserName)</td>
<td>@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.UserName)</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>密码</td>
<td>@Html.PasswordFor(m => m.Password)</td>
<td>@Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.Password)</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><input type="submit" value="登录" /></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
第五课 路由规则
-
路由
- 定义用户请求与控制器方法之前的映射关系
-
路由配置
- IRouteBuilder
- 通过MapRoute方法配置路由模板
- IRouteBuilder
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
routes.MapRoute(
name: "admin_default",
template: "admin/{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
- RouteAttribute
- 应用在控制器及方法上
- 通过Template属性配置路由模板
[Route("admin/form")]
public class FormController : Controller
{
[Route("index")]
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View(new UserLogin());
}
public IActionResult PostData(UserLogin login)
{
return Content(ModelState.IsValid?"数据有效":"数据无效");
}
}
- 路由约束
- 对路由数据进行约束
- 只有约束满足条件才能匹配成功
| 约束 | 示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| required | "Product/{ProductName:required}" | 参数必选 |
| alpha | "Product/{ProductName:alpha}" | 匹配字母,大小写不限 |
| int | "Product/{ProductId:int}" | 匹配int类型 |
| ··· | ··· | ··· |
| composite | "Product/{ProductId:composite}" | 匹配composite类型 |
| length | "Product/{ProductName:length(5)}" | 长度必须是5个字符 |
| length | "Product/{ProductName:length(5)}" | 长度在5-10之间 |
| maxlength | "Product/{ProductId:maxlength(10)}" | 最大长度为10 |
| minlength | "Product/{ProductId:minlength(3)}" | 最小长度为3 |
| min | "Product/{ProductId:min(3)}" | 大于等于3 |
| max | "Product/{ProductId:max(10)}" | 小于等于10 |
| range | "Product/{ProductId:range(5,10)}" | 对应的数组在5-10之间 |
| regex | "Product/{ProductId:regex(^d{4}$)}" | 符合指定的正则表达式 |
- 路由数据
- 路由数据也是请求数据的一部分
- 路由数据与表单数据一样,也可以绑定到参数上
- 默认是通过名称进行匹配,也可以通过
FormRouteAttribute匹配参数与路由数据的映射关系
public IActionResult Index([FromRoute] int? id)
{
return View();
}
第六课 应用发布与部署
- 发布
- 发布方法
- 使用
Visual Studio发布应用:项目右键 -> 发布 -> 发布方式选择... - 使用
dotnet publish命令行工具发布:dotnet publish --configuration Release --runtime win7-x64 --output c:svc
- 使用
- 发布方法
- 视图预编译
- 少了运行时编译过程,启动速度快
- 预编译后,整个程序包更小
- 可以通过MvcRazorCompileOnPublish配置是否开启,默认是开启状态
- 关闭视图预编译:
- 打开项目的
.csproj文件 - 配置
MvcRazorCompileOnPublish为false
- 打开项目的
- 关闭视图预编译:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp2.1</TargetFramework>
<!-- 关闭视图预编译 -->
<MvcRazorCompileOnPublish>false</MvcRazorCompileOnPublish>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.App" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Razor.Design" Version="2.1.2" PrivateAssets="All" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.VisualStudio.Web.CodeGeneration.Design" Version="2.1.1" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
- 部署
- IIS 部署
- 目标机器安装对应版本的.NET Core Sdk
- 安装.NET Core Windows Server 托管程序
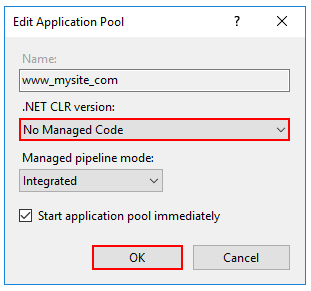
- 应用程序池的“.NET CLR版本”设置为“无托管代码”
- 自宿主发布
- 发布成一个exe直接运行
- 不用依赖IIS
- RuntimeIdentifier
- .NET Core RID Catalog
- IIS 部署
<!-- 依赖框架的部署 (FDD) -->
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp2.2</TargetFramework>
<RuntimeIdentifier>win7-x64</RuntimeIdentifier>
<SelfContained>false</SelfContained>
<IsTransformWebConfigDisabled>true</IsTransformWebConfigDisabled>
</PropertyGroup>
<!-- 独立部署 (SCD) -->
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp2.2</TargetFramework>
<RuntimeIdentifier>win7-x64</RuntimeIdentifier>
<IsTransformWebConfigDisabled>true</IsTransformWebConfigDisabled>
</PropertyGroup>
...
...
...
源码地址
- DncLesson 喜欢的话,请Star一下哦。你的支持是我们源源不断更新的动力!