题意:
给n串有疾病的DNA序列,现有一串DNA序列,问最少修改几个DNA,能使新的DNA序列不含有疾病的DNA序列。
思路:
构建AC自动机,设定end结点,dp[i][j]表示长度i的前缀串走到自动机的j点最少需要修改几个DNA。状态转移方程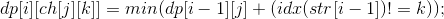 。那么只要转移到下一个的DNA不是end结点就能转移,如果下一个DNA不和原序列不一样就+1。
。那么只要转移到下一个的DNA不是end结点就能转移,如果下一个DNA不和原序列不一样就+1。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
const int N = 50 + 5;
const int M = 1000 + 5;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct AC {
static const int NODE = N * 20;
static const int SIZE = 4;
int ch[NODE][SIZE], fail[NODE], end[NODE];
int sz;
void init();
int idx(char c);
void insert(char *s);
void get_fail();
}ac;
char s[25];
char str[M];
int dp[M][AC::NODE];
int solve() {
int len = strlen (str);
memset (dp, INF, sizeof (dp));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i=1; i<=len; ++i) {
for (int j=0; j<ac.sz; ++j) {
if (dp[i-1][j] == INF) continue;
for (int k=0; k<4; ++k) {
if (!ac.end[ac.ch[j][k]]) {
dp[i][ac.ch[j][k]] = std::min (dp[i][ac.ch[j][k]], dp[i-1][j] + (ac.idx (str[i-1]) != k));
}
}
}
}
int ret = INF;
for (int i=0; i<ac.sz; ++i) {
if (!ac.end[i]) {
ret = std::min (ret, dp[len][i]);
}
}
if (ret == INF) ret = -1;
return ret;
}
int main() {
int n, cas = 0;
while (scanf ("%d", &n) == 1 && n) {
ac.init ();
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) {
scanf ("%s", s);
ac.insert (s);
}
ac.get_fail ();
scanf ("%s", str);
printf ("Case %d: %d
", ++cas, solve ());
}
return 0;
}
void AC::init() {
memset (ch[0], 0, sizeof (ch[0]));
sz = 1;
}
int AC::idx(char c) {
if (c == 'A') {
return 0;
} else if (c == 'G') {
return 1;
} else if (c == 'C') {
return 2;
} else {
return 3;
}
}
void AC::insert(char *s) {
int u = 0;
for (int c, i=0; s[i]; ++i) {
c = idx (s[i]);
if (!ch[u][c]) {
memset (ch[sz], 0, sizeof (ch[sz]));
end[sz] = 0;
ch[u][c] = sz++;
}
u = ch[u][c];
}
end[u] = 1;
}
void AC::get_fail() {
fail[0] = 0;
std::queue<int> que;
for (int c=0; c<SIZE; ++c) {
int u = ch[0][c];
if (u) {
fail[u] = 0;
//last[u] = 0;
que.push (u);
}
}
while (!que.empty ()) {
int r = que.front ();
que.pop ();
for (int c=0; c<SIZE; ++c) {
int &u = ch[r][c];
if (!u) {
u = ch[fail[r]][c];
} else {
int v = fail[r];
while (v && !ch[v][c]) v = fail[v];
fail[u] = ch[v][c];
end[u] |= end[fail[u]];
//last[u] = end[fail[u]] ? fail[u] : last[fail[u]];
que.push (u);
}
}
}
}