You are given integer nn. You have to arrange numbers from 11 to 2n2n, using each of them exactly once, on the circle, so that the following condition would be satisfied:
For every nn consecutive numbers on the circle write their sum on the blackboard. Then any two of written on the blackboard 2n2n numbers differ not more than by 11.
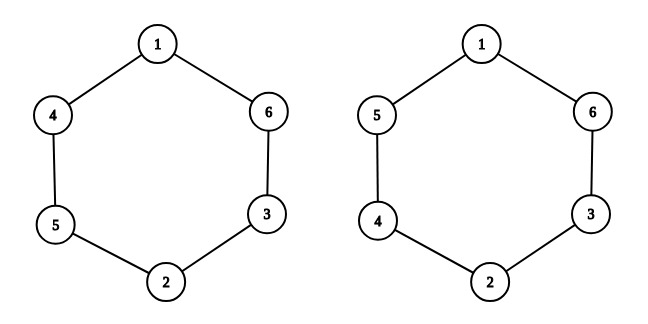
For example, choose n=3n=3. On the left you can see an example of a valid arrangement: 1+4+5=101+4+5=10, 4+5+2=114+5+2=11, 5+2+3=105+2+3=10, 2+3+6=112+3+6=11, 3+6+1=103+6+1=10, 6+1+4=116+1+4=11, any two numbers differ by at most 11. On the right you can see an invalid arrangement: for example, 5+1+6=125+1+6=12, and 3+2+4=93+2+4=9, 99 and 1212 differ more than by 11.
The first and the only line contain one integer nn (1≤n≤1051≤n≤105).
If there is no solution, output "NO" in the first line.
If there is a solution, output "YES" in the first line. In the second line output 2n2n numbers — numbers from 11 to 2n2n in the order they will stay in the circle. Each number should appear only once. If there are several solutions, you can output any of them.
3
YES
1 4 5 2 3 6
4
NO
Example from the statement is shown for the first example.
It can be proved that there is no solution in the second example.
cin , cout , printf ,scanf 一定不要混淆使用,关闭同步后会影响输出顺序,2个小时的BUG -_-|
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
//
#define lson rt<<1, l, m
#define rson rt<<1|1, m+1, r
//
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define pq priority_queue<int>
#define ok return 0;
#define oi(x) cout<<x<<endl;
#define os(str) cout<<string(str)<<endl;
#define gcd __gcd
#define mem(s,t) memset(s,t,sizeof(s))
#define debug(a,n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cout<<a[i]<<" "; cout<<endl;
#define debug1(a,n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
#define Debug(a,n,m) for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
cout<<a[i][j]<<" "; cout<<endl; }
#define input(a,k) for (int i = 1; i <= (int)(k); i++) {cin>>a[i];}
#define INPUT(a,n,m) for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
cin>>a[i][j] ; }
#define TLE std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL); cout.precision(10);
using namespace std;
inline void NO() { cout<<"NO"<<endl; }
inline void YES(){ cout<<"YES"<<endl;}
const int mxn = 2e5+10;
#define rep(k) for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
#define rep1(j,k) for (int i=j;i<=k; i++)
#define per(j,k) for (int i=j;i>=k; i--)
#define per(k) for (int i=k-1;i>=0;i--)
int a[mxn];
int main()
{
int n;
TLE;
while(cin>>n)
{
if(n&1)
{
rep1(1,n)
{
if(i%2)
{
a[i]=2*i-1;
a[i+n] = 2*i;
}
else
{
a[i]=2*i;
a[i+n] = 2*i-1;
}
}
YES();
debug1(a,2*n);
cout<<endl;
}
else
NO();
}