iOS Category 添加属性实现原理 - 关联对象
RunTime为Category动态关联对象
- 使用RunTime给系统的类添加属性,首先需要了解对象与属性的关系。对象一开始初始化的时候其属性为nil,给属性赋值其实就是让属性指向一块存储内容的内存,使这个对象的属性跟这块内存产生一种关联。
- 那么如果想动态的添加属性,其实就是动态的产生某种关联就好了。而想要给系统的类添加属性,只能通过分类。
1.使用举例
-
这里给NSObject添加height属性,创建NSObject的分类
// 我们可以使用@property给分类添加属性 @property(nonatomic,assign)int height; -
虽然在分类中可以写@property添加属性,但是不会自动生成私有属性,也不会生成set,get方法的实现,只会生成set,get的声明,需要我们自己去实现。
方法一:我们可以通过使用静态全局变量给分类添加属性
```
static int height_;
-(void)setHeight:(int)height
{
height_ = height;
}
- (int)height
{
return height_;
}
```
- 缺点1:这个
height_静态全局变量与类并没有关联,无论对象创建与销毁,只要程序在运行height_变量就存在,并不是真正意义上的属性。 - 缺点2:改变第二个对象会影响到第一个对象的属性的值
NSObject *obj1 = [[NSObject alloc] init]; obj1.height = 10; NSLog(@"obj1:%i",obj1.height); // 打印结果10 NSObject *obj2 = [[NSObject alloc] init]; obj2.height = 120; NSLog(@"obj1:%i",obj1.height); // 打印结果120 NSLog(@"obj2:%i",obj2.height); // 打印结果120
方法二:使用字典保存对象对应的value
NSMutableDictionary *dictionary_;
+ (void)load
{
dictionary_ = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
}
-(void)setHeight:(int)height
{
// 对象的指针地址作为Key,保证唯一
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%p",self];
dictionary_[key] = @(height);
}
- (int)height
{
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%p",self];
return [dictionary_[key] intValue];
}
- 缺点1:这个
dictionary_静态全局变量与类并没有关联,无论对象创建与销毁,只要程序在运行dictionary_变量就存在,并不是真正意义上的属性。 - 缺点2:全局对象会造成内存泄露问题。
- 缺点3:线程安全问题,同一时间访问。
方法三:使用RunTime关联对象动态添加属性
-
RunTime提供了动态添加属性和获得属性的方法
static const char Myheight; -(void)setHeight:(int)height { objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &Myheight, @(height), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC); } - (int)height { return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &Myheight) intValue]; }
方法四:使用RunTime关联对象动态添加属性,key 值改进
```
-(void)setHeight:(int)height
{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(height), @(height), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (int)height
{ _cmd = @selector(height);
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @selector(height)) intValue];
}
```
RunTime关联对象方法介绍
-
动态添加属性方法:objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy);
- 参数一:id object : 给哪个对象添加属性,这里要给自己添加属性,用self。
- 参数二:void *key == id key : 属性名,根据key获取关联对象的属性的值,在objc_getAssociatedObject中通过此key获得属性的值并返回。key值只要是一个指针即可,我们可以传入@selector(name)
- 参数三:id value : 关联的值,也就是set方法传入的值给属性去保存。
- 参数四:objc_AssociationPolicy policy : 策略,属性以什么形式保存。
- 有以下几种
typedef OBJC_ENUM(uintptr_t, objc_AssociationPolicy) { OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN = 0, // 指定一个弱引用相关联的对象 OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC = 1, // 指定相关对象的强引用,非原子性 OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC = 3, // 指定相关的对象被复制,非原子性 OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN = 01401, // 指定相关对象的强引用,原子性 OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY = 01403 // 指定相关的对象被复制,原子性 }; -
获得属性方法:objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key);
- 参数一:id object : 获取哪个对象里面的关联的属性。
- 参数二:void * == id key : 什么属性,与objc_setAssociatedObject中的key相对应,即通过key值取出value。
-
移除所有关联对象方法: objc_removeAssociatedObjects
- (void)removeAssociatedObjects { // 移除所有关联对象 objc_removeAssociatedObjects(self); }
可以看出关联对象的使用非常简单,接下来我们来探寻关联对象的底层原理
2.关联对象原理
1. 实现关联对象技术的核心对象有
- 其中Map同我们平时使用的字典类似。通过key-value一一对应存值。
- AssociationsManager
- AssociationsHashMap
- ObjectAssociationMap
- ObjcAssociation
2.对关联对象技术的核心对象有了一个大概的意识,我们通过源码来探寻这些对象的存在形式以及其作用
-
runtime源码,objc_setAssociatedObject函数在objc-runtime.mm 文件中,首先找到objc_setAssociatedObject函数,其实现
void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy) { _object_set_associative_reference(object, (void *)key, value, policy); } -
其实内部调用的是_object_set_associative_reference函数,_object_set_associative_reference函数
void _object_set_associative_reference(id object, void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) { // retain the new value (if any) outside the lock. ObjcAssociation old_association(0, nil); id new_value = value ? acquireValue(value, policy) : nil; { AssociationsManager manager; AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations()); disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object); if (new_value) { // break any existing association. AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object); if (i != associations.end()) { // secondary table exists ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second; ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key); if (j != refs->end()) { old_association = j->second; j->second = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value); } else { (*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value); } } else { // create the new association (first time). ObjectAssociationMap *refs = new ObjectAssociationMap; associations[disguised_object] = refs; (*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value); object->setHasAssociatedObjects(); } } else { // setting the association to nil breaks the association. AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object); if (i != associations.end()) { ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second; ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key); if (j != refs->end()) { old_association = j->second; refs->erase(j); } } } } // release the old value (outside of the lock). if (old_association.hasValue()) ReleaseValue()(old_association); } -
_object_set_associative_reference函数内部我们可以全部找到我们上面说过的实现关联对象技术的核心对象。接下来我们来一个一个看其内部实现原理探寻他们之间的关系。
-
AssociationsManager, 通过AssociationsManager内部源码发现,AssociationsManager内部有一个AssociationsHashMap对象。
class AssociationsManager { // associative references: object pointer -> PtrPtrHashMap. static AssociationsHashMap *_map; public: AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.lock(); } ~AssociationsManager() { AssociationsManagerLock.unlock(); } AssociationsHashMap &associations() { if (_map == NULL) _map = new AssociationsHashMap(); return *_map; } }; -
AssociationsHashMap,AssociationsHashMap内部的源码。
#if TARGET_OS_WIN32 typedef hash_map<void *, ObjcAssociation> ObjectAssociationMap; typedef hash_map<disguised_ptr_t, ObjectAssociationMap *> AssociationsHashMap; #else typedef ObjcAllocator<std::pair<void * const, ObjcAssociation> > ObjectAssociationMapAllocator; class ObjectAssociationMap : public std::map<void *, ObjcAssociation, ObjectPointerLess, ObjectAssociationMapAllocator> { public: void *operator new(size_t n) { return ::malloc(n); } void operator delete(void *ptr) { ::free(ptr); } }; typedef ObjcAllocator<std::pair<const disguised_ptr_t, ObjectAssociationMap*> > AssociationsHashMapAllocator; class AssociationsHashMap : public unordered_map<disguised_ptr_t, ObjectAssociationMap *, DisguisedPointerHash, DisguisedPointerEqual, AssociationsHashMapAllocator> { public: void *operator new(size_t n) { return ::malloc(n); } void operator delete(void *ptr) { ::free(ptr); } }; #endif } -
通过AssociationsHashMap内部源码我们发现AssociationsHashMap继承自unordered_map首先来看一下unordered_map内的源码
template <class _Key, class _Tp, class _Hash = hash<_Key>, class _Pred = equal_to<_Key>, class _Alloc = allocator<pair<const _Key, _Tp> > > class _LIBCPP_TEMPLATE_VIS unordered_map { public: // types typedef _Key key_type; typedef _Tp mapped_type; typedef _Hash hasher; typedef _Pred key_equal; typedef _Alloc allocator_type; typedef pair<const key_type, mapped_type> value_type; typedef pair<key_type, mapped_type> __nc_value_type; typedef value_type& reference; typedef const value_type& const_reference; static_assert((is_same<value_type, typename allocator_type::value_type>::value), "Invalid allocator::value_type"); private: -
从unordered_map源码中我们可以看出_Key和_Tp也就是前两个参数对应着map中的Key和Value,那么对照上面AssociationsHashMap内源码发现_Key中传入的是disguised_ptr_t,_Tp中传入的值则为ObjectAssociationMap*。
紧接着我们来到ObjectAssociationMap中,我们发现ObjectAssociationMap中同样以key、Value的方式存储着ObjcAssociation。
接着我们来到ObjcAssociation中class ObjcAssociation { uintptr_t _policy; id _value; public: ObjcAssociation(uintptr_t policy, id value) : _policy(policy), _value(value) {} ObjcAssociation() : _policy(0), _value(nil) {} uintptr_t policy() const { return _policy; } id value() const { return _value; } bool hasValue() { return _value != nil; } }; -
我们发现ObjcAssociation存储着_policy、_value,而这两个值我们可以发现正是我们调用objc_setAssociatedObject函数传入的值,也就是说我们在调用objc_setAssociatedObject函数中传入的value和policy这两个值最终是存储在ObjcAssociation中的。
-
现在我们已经对AssociationsManager、 AssociationsHashMap、 ObjectAssociationMap、ObjcAssociation四个对象之间的关系有了简单的认识,那么接下来我们来细读源码,看一下objc_setAssociatedObject函数中传入的四个参数分别放在哪个对象中充当什么作用。
重新回到_object_set_associative_reference函数实现中 -
细读上述_object_set_associative_reference源码我们可以发现,首先根据我们传入的value经过acquireValue函数处理获取new_value。acquireValue函数内部其实是通过对策略的判断返回不同的值
static id acquireValue(id value, uintptr_t policy) { switch (policy & 0xFF) { case OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_RETAIN: return objc_retain(value); case OBJC_ASSOCIATION_SETTER_COPY: return ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(value, SEL_copy); } return value; } -
之后创建AssociationsManager manager;以及拿到manager内部的AssociationsHashMap即associations。
-
再之后我们看到了我们传入的第一个参数object
object经过DISGUISE函数被转化为了disguised_ptr_t类型的disguised_object。typedef uintptr_t disguised_ptr_t; inline disguised_ptr_t DISGUISE(id value) { return ~uintptr_t(value); } inline id UNDISGUISE(disguised_ptr_t dptr) { return id(~dptr); } -
DISGUISE函数其实仅仅对object做了位运算,之后我们看到被处理成new_value的value,同policy被存入了ObjcAssociation中。而ObjcAssociation对应我们传入的key被存入了ObjectAssociationMap中。disguised_object和ObjectAssociationMap则以key-value的形式对应存储在associations中也就是AssociationsHashMap中。
// create the new association (first time). ObjectAssociationMap *refs = new ObjectAssociationMap; associations[disguised_object] = refs; (*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value); object->setHasAssociatedObjects(); -
如果我们value设置为nil的话那么会执行下面的代码
// setting the association to nil breaks the association. AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object); if (i != associations.end()) { ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second; ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key); if (j != refs->end()) { old_association = j->second; refs->erase(j); } } -
从上述代码中可以看出,如果我们设置value为nil时,就会将关联对象从ObjectAssociationMap中移除。
-
最后我们通过一张图可以很清晰的理清楚其中的关系
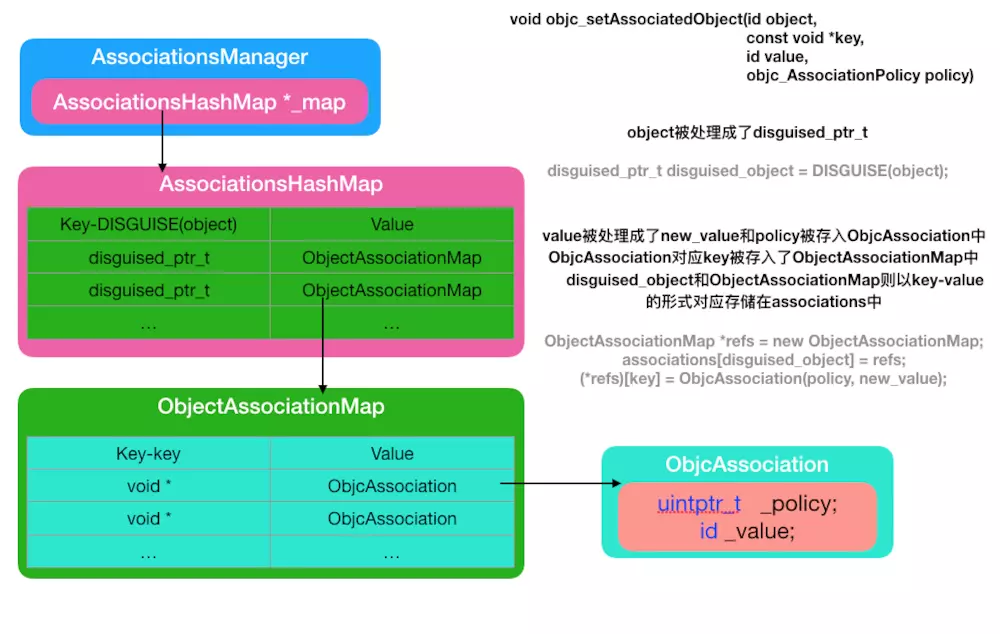
-
通过上图我们可以总结为:一个实例对象就对应一个ObjectAssociationMap,而ObjectAssociationMap中存储着多个此实例对象的关联对象的key以及ObjcAssociation,为ObjcAssociation中存储着关联对象的value和policy策略。
-
由此我们可以知道关联对象并不是放在了原来的对象里面,而是自己维护了一个全局的map用来存放每一个对象及其对应关联属性表格。
3. objc_getAssociatedObject函数
-
objc_getAssociatedObject内部调用的是_object_get_associative_reference
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void *key) { return _object_get_associative_reference(object, (void *)key); } -
_object_get_associative_reference函数
id _object_get_associative_reference(id object, void *key) { id value = nil; uintptr_t policy = OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN; { AssociationsManager manager; AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations()); disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object); AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object); if (i != associations.end()) { ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second; ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key); if (j != refs->end()) { ObjcAssociation &entry = j->second; value = entry.value(); policy = entry.policy(); if (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_RETAIN) { objc_retain(value); } } } } if (value && (policy & OBJC_ASSOCIATION_GETTER_AUTORELEASE)) { objc_autorelease(value); } return value; } -
从_object_get_associative_reference函数内部可以看出,向set方法中那样,反向将value一层一层取出最后return出去。
4. objc_removeAssociatedObjects函数
- objc_removeAssociatedObjects用来删除所有的关联对象,
-
objc_removeAssociatedObjects函数内部调用的是_object_remove_assocations函数
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object) { if (object && object->hasAssociatedObjects()) { _object_remove_assocations(object); } } -
_object_remove_assocations函数
void _object_remove_assocations(id object) { vector< ObjcAssociation,ObjcAllocator<ObjcAssociation> > elements; { AssociationsManager manager; AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations()); if (associations.size() == 0) return; disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object); AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object); if (i != associations.end()) { // copy all of the associations that need to be removed. ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second; for (ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->begin(), end = refs->end(); j != end; ++j) { elements.push_back(j->second); } // remove the secondary table. delete refs; associations.erase(i); } } // the calls to releaseValue() happen outside of the lock. for_each(elements.begin(), elements.end(), ReleaseValue()); } -
上述源码可以看出_object_remove_assocations函数将object对象向对应的所有关联对象全部删除
总结
-
关联对象并不是存储在被关联对象本身内存中,而是存储在全局的统一的一个AssociationsManager中,如果设置关联对象为nil,就相当于是移除关联对象。
此时我们我们在回过头来看objc_AssociationPolicy policy 参数: 属性以什么形式保存的策略。/** * Policies related to associative references. * These are options to objc_setAssociatedObject() */ typedef OBJC_ENUM(uintptr_t, objc_AssociationPolicy) { OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN = 0, /**< Specifies a weak reference to the associated object. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC = 1, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object. * The association is not made atomically. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC = 3, /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied. * The association is not made atomically. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN = 01401, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object. * The association is made atomically. */ OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY = 01403 /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied. * The association is made atomically. */ };-
我们会发现其中只有RETAIN和COPY而为什么没有weak呢?
-
总过上面对源码的分析我们知道,object经过DISGUISE函数被转化为了 disguised_ptr_t类型的disguised_object。
-
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
-
而同时我们知道,weak修饰的属性,当没有拥有对象之后就会被销毁,并且指针置位nil,那么在对象销毁之后,虽然在map中既然存在值object对应的AssociationsHashMap,但是因为object地址已经被置位nil,会造成坏地址访问而无法根据object对象的地址转化为disguised_object了。
-
-
Category能否添加成员变量?如果可以,如何给Category添加成员变量?
- 不能直接添加成员变量,但是可以通过runtime的方式间接实现添加成员变量的效果。