参考来源:
https://am207.github.io/2017/wiki/lab4.html#traveling-salesman-problem-tsp
《现代优化理论与方法》黄庆道等编.上册P165,
在解决旅行商问题时,用到了模拟退火算法。
1.Metropolis准则
该准则表示以概率接受新状态。假设在温度$t$时刻,由当前状态$n$产生新状态$n+1$,两者能量分别为$E(n)$和$E(n+1)$.
则 接受新状态的概率为
(1) 如果$E(n+1) < E(n)$,则概率1接受新状态$E(n+1)$
(2)如果$E(n+1) geq E(n)$,则判断条件[e^{-frac{E(n+1)-E(n)}{T}} > [0,1)区间内的随机数]
如果成立接受新状态$E(n+1)$,否则保留$E(n)$为当前状态。
算法思路:
(1)给定初温$t=t_0$,随机指定初始状态$s=s_0,k=0$。
(2)一般迭代:
重复以下过程:
产生新状态 $s_j = Generate(s)$;
if min${1, exp[-(C(s_j)-C(s))]} geq random[0,1]$ , 则$s=s_j$
直到抽样稳定准则满足
退温$t_k = update(t_k),令k=k+1$
(3)输出算法结果。
自己用python写了一个类似的,有一些效果,应该有一些参数设置不够完善。
2.Python代码
退火代码:
def sa_tsp(points, T0, k): "模拟退火算法,T0为初温,k为内循环的次数" accumulator = [] best_path = points[:] best_length = calLength(points) old_length = best_length new_length = best_length old_path = points[:] new_path = [] Tmin = 0.99 T = T0 best_time = 0 #外循环 while(T > Tmin): #内循环 for i in range(k): new_path.clear() #产生新路径 new_path = generate_newpath(old_path) #计算新路径的长度 new_length = calLength(new_path) alpha = np.exp( (old_length-new_length)/T) #metropolis判断准则 if (new_length < old_length) or np.random.uniform() < alpha: # print() accumulator.append((T, new_length, new_path)) if new_length < best_length: best_length = new_length best_path = new_path[:] best_time = T #满足则保留当前状态 old_path = new_path[:] # print(len(old_path)) old_length = new_length else: #keep the old stuff #不满足则保留旧状态 accumulator.append((T, old_length, old_path)) #温度更新函数 T = 0.8 * T print_path(accumulator) return (best_path, best_length)
全部代码

#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from time import time import math from collections import namedtuple import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt Point = namedtuple("Point", ['index', 'x', 'y']) #画图函数 def plot_lines(points, style='bo-'): "Plot lines to connect a series of points" plt.plot([p.x for p in points], [p.y for p in points], style) plt.axis('scaled') plt.axis('off') #画图函数 def plot_tour(points): "Plot the cities as circles and the tour as lines between them." "Start city is red square" start = points[0] plot_lines(points+[start]) plot_lines([start], 'rs') #计算两个城市的欧几里德距离 def length(point1, point2): return math.sqrt((point1.x - point2.x)**2 + (point1.y - point2.y)**2) #计算整个旅程的距离 def calLength(points): dist = 0 dist += length(points[0], points[-1]) for i in range(len(points)-1): dist += length(points[i], points[i+1]) return dist #通过在[i,j]的元素逆序排放,产生邻域的方法1 def reverse_segment(points, i, j): "Reverse segment points[i:j] of a tour " new_path = points[:] new_path[i:j] = reversed(points[i:j]) return new_path #交换i,j位置的元素,产生邻域的方法2 def swap_point(points, i, j): "swap two cities at index i and index j" point0 = points[i] point1 = points[j] new_points = points[:] #swap two points new_points[i] = point1 new_points[j] = point0 return new_points #选择某种得到邻域的方法 change_point = reverse_segment #生成新路径 def generate_newpath(input_points): "change a tour for tsp iteration" #假设起点位置始终是0,故只在[1,len(input_points)-1]的区间取随机数 indices = range(1, len(input_points)) #print("indices'length is {0}.".format(len(indices))) #take two random indices to swap #生成两个随机数 c1 = np.random.choice(indices) c2 = np.random.choice(indices) new_path = change_point(input_points, c1, c2) #print("new path'length is {0}.".format(len(new_path))) return new_path def print_path(accumulator): f = open("path info", 'w+') #print("accumulator's length is {0}.".format(len(accumulator))) for i in range(len(accumulator)): print("{0}, {1}.".format(accumulator[i][0], accumulator[i][1]), file=f) def sa_tsp(points, T0, k): "模拟退火算法,T0为初温,k为内循环的次数" accumulator = [] best_path = points[:] best_length = calLength(points) old_length = best_length new_length = best_length old_path = points[:] new_path = [] Tmin = 0.99 T = T0 best_time = 0 #外循环 while(T > Tmin): #内循环 for i in range(k): new_path.clear() #产生新路径 new_path = generate_newpath(old_path) #计算新路径的长度 new_length = calLength(new_path) alpha = np.exp( (old_length-new_length)/T) #metropolis判断准则 if (new_length < old_length) or np.random.uniform() < alpha: # print() accumulator.append((T, new_length, new_path)) if new_length < best_length: best_length = new_length best_path = new_path[:] best_time = T #满足则保留当前状态 old_path = new_path[:] # print(len(old_path)) old_length = new_length else: #keep the old stuff #不满足则保留旧状态 accumulator.append((T, old_length, old_path)) #温度更新函数 T = 0.8 * T print_path(accumulator) return (best_path, best_length) def solve_it(input_data): # Modify this code to run your optimization algorithm # parse the input lines = input_data.split(' ') nodeCount = int(lines[0]) cnt = 0 points = [] for i in range(1, nodeCount+1): line = lines[i] parts = line.split() points.append(Point(cnt, float(parts[0]), float(parts[1]))) cnt += 1 # build a trivial solution # visit the nodes in the order they appear in the file solution = range(0, nodeCount) result_path,result_length = sa_tsp(points, 1000, 10000) #画图函数 plot_tour(result_path) plt.show() solution2 = [] #print("sa_tsp_result length is {0}".format(result_length)) for point in result_path: #print(point.index, end=' ') solution2.append(point.index) #print() #print("test the result: {0}.".format(calLength(result_path))) # calculate the length of the tour '''obj = length(points[solution[-1]], points[solution[0]]) for index in range(0, nodeCount-1): obj += length(points[solution[index]], points[solution[index+1]]) ''' obj = result_length # prepare the solution in the specified output format output_data = '%.2f' % obj + ' ' + str(0) + ' ' output_data += ' '.join(map(str, solution2)) return output_data import sys if __name__ == '__main__': import sys start = time() if len(sys.argv) > 1: file_location = sys.argv[1].strip() with open(file_location, 'r') as input_data_file: input_data = input_data_file.read() print(solve_it(input_data)) else: print('This test requires an input file. Please select one from the data directory. (i.e. python solver.py ./data/tsp_51_1)') end = time() print('running time is {0} s.'.format(end-start))
设置初温T0=100,内循环为k=100时的路线
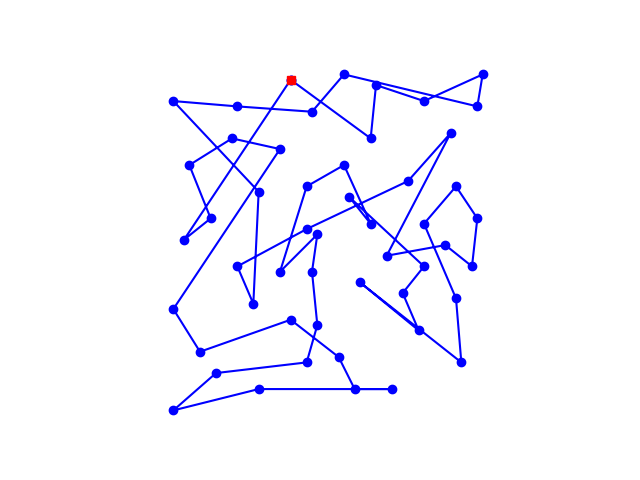
以及设置初温T0=1000,内循环为k=1000时的路线
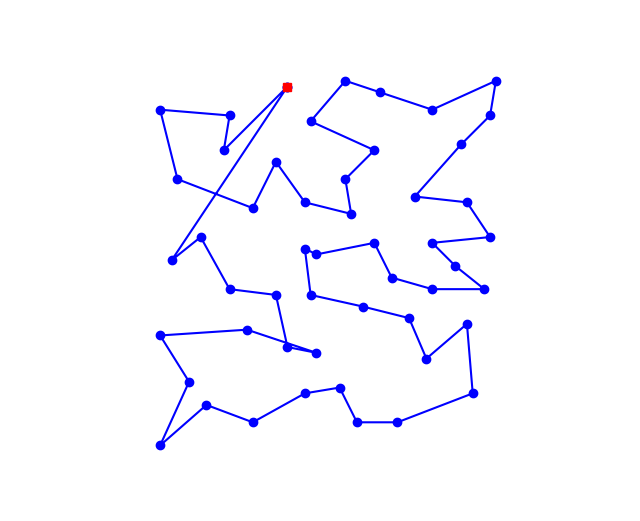
以及设置初温T0=1000,内循环为k=10000时的路线
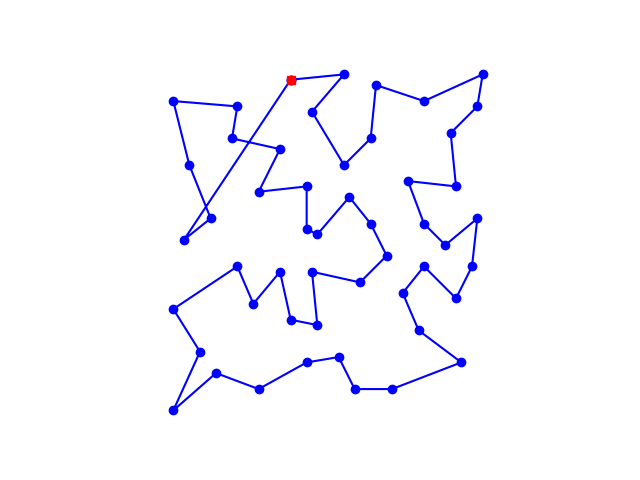
效果还不错,就是时间久了一点。
