快速排序算法
想必大多数程序员接触的第一种排序算法是冒泡排序,冒泡排序的特点是:逻辑简单,实现起来也不难,但在数据量比较大的时候性能比较低。
以数字由大到小的排序为例,写一个简单的冒泡排序。
/**
* 冒泡排序
* Created by Administrator on 2017/4/4.
*/
public class BubblingSortArithmetic {
/**
* 冒泡排序实现
* @param array
*/
public static void bubblingSort(int[] array){
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length-i-1; j++) {
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
我们看到,冒泡排序就是两个for循环嵌套,内层循环再加一个if语句做逻辑判断。
通俗点解释冒泡排序就是:外层循环控制冒泡的趟数(数组长度-1),内层循环控制一趟冒泡过程中数组相邻两个元素的比较次数及最大索引位,并且一趟冒泡把这次排序中最大的那个数放到最大索引位处。
冒泡排序性能低的原因是:每一次排序只能计算出最大的数,而且下次排序对数组的切分减一,这样在数据量较大的时候,性能上的劣势就显现出来了。
下面我们来谈一下快速排序这种算法:
首先,快速排序算法是对冒泡排序算法的一种改进其思想是:选择数组中的一个元素作为中位数(一般是数组中第一个元素),通过一趟冒泡把整个数组分成两部分,左边的部分都比该中位数小,右边的部分都比该中位数大,然后通过递归的方式分别对上次排序分成的两部分数组进行排序,直到整个数组有序为止。
从整个排序流程上看,快速排序算法一次排序就可以把整个数组分成一大一小两部分,而且对数组的切分使用了二分的原理,这也是快速排序性能好,速度快的原因。
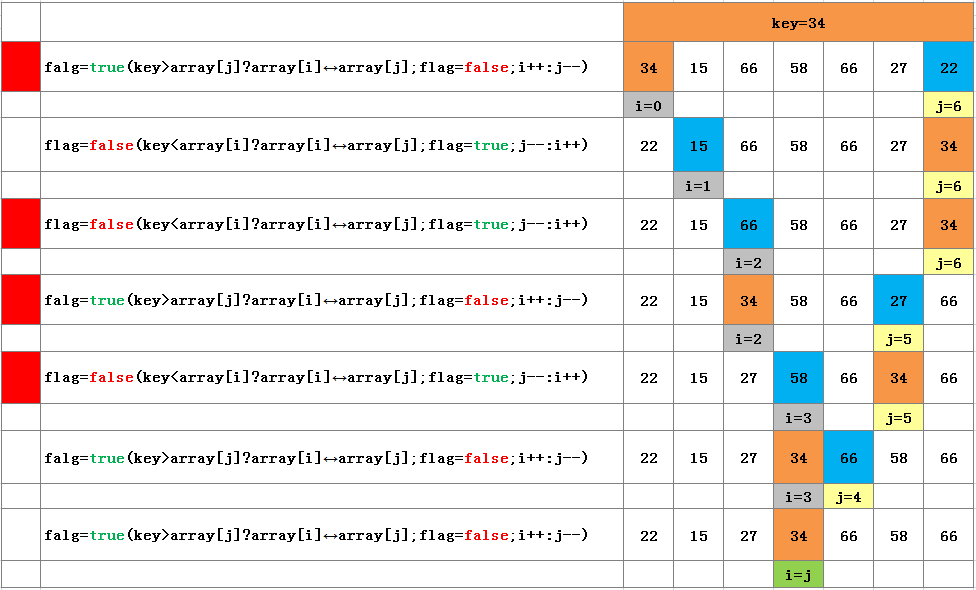
虽然快速排序算法思想理解起来很简单就是把一次排序中作为中位数的那个元素"放中间",让左边的元素比它小右边的元素比它大,看似简单但实现起来并不是那么容易。幸运的是已经有前人对这种算法有了很好的实现,对于快速排序算法的实现,我的理解是:选定数组第一个元素作为key(中位数),当状态值为true时与高位比大,当状态值为false时与低位比小,两头数组的下标(i,j)往中间凑,直到i=j时,一次排序结束,接下来使用递归分别对中位数两侧的数组进行上述的排序规则。
下面以以下数组第一次排序为例,通过一张图来说明这一过程。
int[] arrays = {34,15,66,58,66,27,22};
下面是快速排序算法代码实现:
package com.opensource.arithmetic.sort;
/**
* 快速排序算法
*/
public class QuickSortArithmetic {
/**
* 快速排序算法入口
* @param arrays
* @param lenght
*/
public static void sort_entrance(int[] arrays, int lenght) {
if (null == arrays || lenght < 1) {
System.out.println("input error!");
return;
}
quick_sort(arrays, 0, lenght - 1);
}
/**
* 快速算法实现
* @param arrays
* @param start
* @param end
*/
public static void quick_sort(int[] arrays, int start, int end) {
if(start>=end){
return;
}
int i = start;
int j = end;
int key = arrays[i];
boolean flag = true;
while (i != j) {
if (flag) {
if (key > arrays[j]) {
swop(arrays, i, j);
flag=false;
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}else{
if(key < arrays[i]){
swop(arrays, i, j);
flag=true;
j--;
}else{
i++;
}
}
}
quick_sort(arrays, start, j-1);
quick_sort(arrays, i+1, end);
}
/**
* 用于数组中两个元素之间的交换
* @param arrays
* @param i
* @param j
*/
private static void swop(int[] arrays, int i, int j) {
int temp;
temp = arrays[i];
arrays[i] = arrays[j];
arrays[j] = temp;
}
}
下面我们以长度为100000,数组元素在0~1000范围内的数组中为例,对冒泡排序和快速的性能做一下测试。
首先我们把用于测试的数据放入redis中,这是做一是为了保证多次测试时数据的唯一性,二是防止数据量过大造成的栈溢出。
生成随机数组的工具类:
package com.opensource.arithmetic.util;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/4/4.
*/
public class RandomUtils {
private static Random random = new Random();
/**
* 用于生成scope以内,长度为length的随机数组。
* @param length
* @param scope
* @return
*/
public static int[] getArrays(int length,int scope){
int[] arrays = new int[length];
for (int i=0; i<length; i++){
arrays[i] = random.nextInt(scope);
}
return arrays;
}
}
字符串和int类型数组转换的工具类:
package com.opensource.arithmetic.util;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/4/4.
*/
public class StringUtils {
/**
* 用于数组转换字符串后首尾“[","]"切割
* @param arrays
* @return
*/
public static String getArrayToString(int[] arrays){
String str = Arrays.toString(arrays);
return str.substring(1,str.length()-1);
}
/**
* 用于把字符串转换为int类型数组
* @param str
* @return
*/
public static int[] getStringToArrays(String str){
String[] strArray = str.split(", ");//这里以逗号加空格切分字符串,空格一定不能少。
int length = strArray.length;
int[] arrays = new int[length];
for (int i = 0; i <length ; i++) {
arrays[i] = Integer.parseInt(strArray[i]);
}
return arrays;
}
}
把数据存入redis
package com.opensource.arithmetic.util;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/4/4.
*/
public class RedisUtil {
public static Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
/**
* 向redis中存入数据
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public static void setData(String key,String value){
jedis.set(key,value);
}
public static String getData(String kye){
return jedis.get(kye);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] testArrays = RandomUtils.getArrays(100000,1000);
String StrArrays = StringUtils.getArrayToString(testArrays);
setData("arrays",StrArrays);
}
}
测试类:
package com.opensource.arithmetic.test;
import com.opensource.arithmetic.sort.BubblingSortArithmetic;
import com.opensource.arithmetic.sort.QuickSortArithmetic;
import com.opensource.arithmetic.util.RedisUtil;
import com.opensource.arithmetic.util.StringUtils;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/4/4.
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String StrData = RedisUtil.getData("arrays");
int[] arrays = StringUtils.getStringToArrays(StrData);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
QuickSortArithmetic.quickSort(arrays,arrays.length);
//BubblingSortArithmetic.bubblingSort(arrays);
System.out.println( System.currentTimeMillis()-start);
}
}
使用冒泡排序,对arrays数组排序时间在27.5秒左右。
使用快速排序,对arrays数组排序时间在0.047秒左右。
最后说一点,我们作为程序员,研究问题还是要仔细深入一点的。当你对原理了解的有够透彻,开发起来也就得心应手了,很多开发中的问题和疑惑也就迎刃而解了,而且在面对其他问题的时候也可做到触类旁通。当然在开发中没有太多的时间让你去研究原理,开发中要以实现功能为前提,可等项目上线的后,你有大把的时间或者空余的时间,你大可去刨根问底,深入的去研究一项技术,这对一名程序员的成长是很重要的事情。
