前言
来填坑了,感觉这周贼忙贼累,可能是因为开学第一周的缘故吧,课多活多。最近都不听课了,像数据挖掘,数据库(这个听说挺重要的)啥的,感觉学了对自己现在学的方向没啥帮助,而像计算机操作系统,信安概论这种东西就是讲的太表面,可能自己大学生涯的挂科之旅就此开始了吧。其实之前自己一直觉得上课不听课的="坏学生",但是自己现在觉得大学是一个自由的平台,本就不应该给这些所谓的“规则”所束缚,自己想学啥就去学啥,不去把大好青春浪费就好。可能,这是自己变为一个“坏学生”了吧,亦可能自己的思想“升华”了吧,hhh。最近看了一下TK教主,泉哥等巨佬的事迹博客等,感觉除了技术水平上的天壤之别之外,总感觉他们的思想深度十分高,不说那么远的,就说身边的几个大佬,像吴师傅,刘教授等大佬的思想思维都比自己开阔,对比之下,感觉自己的思想太“狭窄”,可能自己要在漏洞挖掘这个方向深入下去,思维需要改变才行。
好了,不胡扯了,这周上课的时候看了操作系统中关于进程的理论部分,趁着周末的时间,找了一下关于Linux内核中内核相关的基础知识。
注:这里只是我在学习操作系统的基础上去简单了解一下Linux内核中的一些具体的数据结构,并没有很深入。另,如有错误,请大佬们斧正。
进程和线程的概念
Linux的进程和线程有很多异同点,可以Google下。
- 进程是资源分配的基本单位,线程是调度的基本单位
- 进程是资源的集合,这些资源包括内存地址空间,文件描述符等等,一个进程中的多个线程共享这些资源。(在内核中,进程等价于资源)
- CPU对任务进行调度时,可调度的基本单位 (dispatchable entity)是线程。如果一个进程中没有其他线程,可以理解成这个进程中只有一个主线程,这个主进程独享进程中的所有资源。
- 进程的个体间是完全独立的,而线程间是彼此依存,并且共享资源。多进程环境中,任何一个进程的终止,不会影响到其他非子进程。而多线程环境中,父线程终止,全部子线程被迫终止(没有了资源)。
- 内核调度的对象是根据task_struct结构体。可以说是线程,而不是进程。
- Linux系统 对线程和进程并不特别区分。线程仅仅被视为一个与其他线程共享某些资源的进程。每个线程都拥有唯一自己的task_struct。
进程和线程在内核里面的描述
用过Linux系统的应该都知道,在Linux中,pid(process ID)表示我们的进程号,lwd(thread ID)表示我们的线程号。
这里再说明一下,tid也是线程ID,等价于lwd;tgid表示线程组ID,也就是线程组leader的进程ID,tgid用于标识线程组id,在同一进程中的所有线程具有同一tgid。tgid值等于进程第一个线程(主线程)的pid值。
这里一张图片,说明一下父子进程,线程的关系:

从上图可以看到,在pid(tgid)42 new_thread出来的tid 44线程,它的tgid(pid)仍为42。而从pid 42fork出来的子进程的tgid是43。而从内核的视角来看,tid 42,tid 43,tid 44都是独立的调度单位,因为在内核中,线程是调度的基本单位。
需要指出的是,有时候在Linux中进程和线程的区分也是不是十分严格的。即使线程和进程混用,pid和tid混用,根据上下文,还是可以清楚地区分对方想要表达的意思。上图中,从内核视角出发看到了pid 44,是从调度单元的角度出发,但是在top或ps命令中,你是绝对找不到一个pid为44的进程的,只能看到一个lwp(tid)为44的线程。
进程描述符:task_struct(即为Linux系统中的PCB)
linux通过task_struct结构体描述一个进程/线程。
mm 成员:描述内存资源
fs 成员:描述文件系统资源
files 成员:进程运行时打开了多少文件,fd的数组
signal 成员:进程接收的信号资源
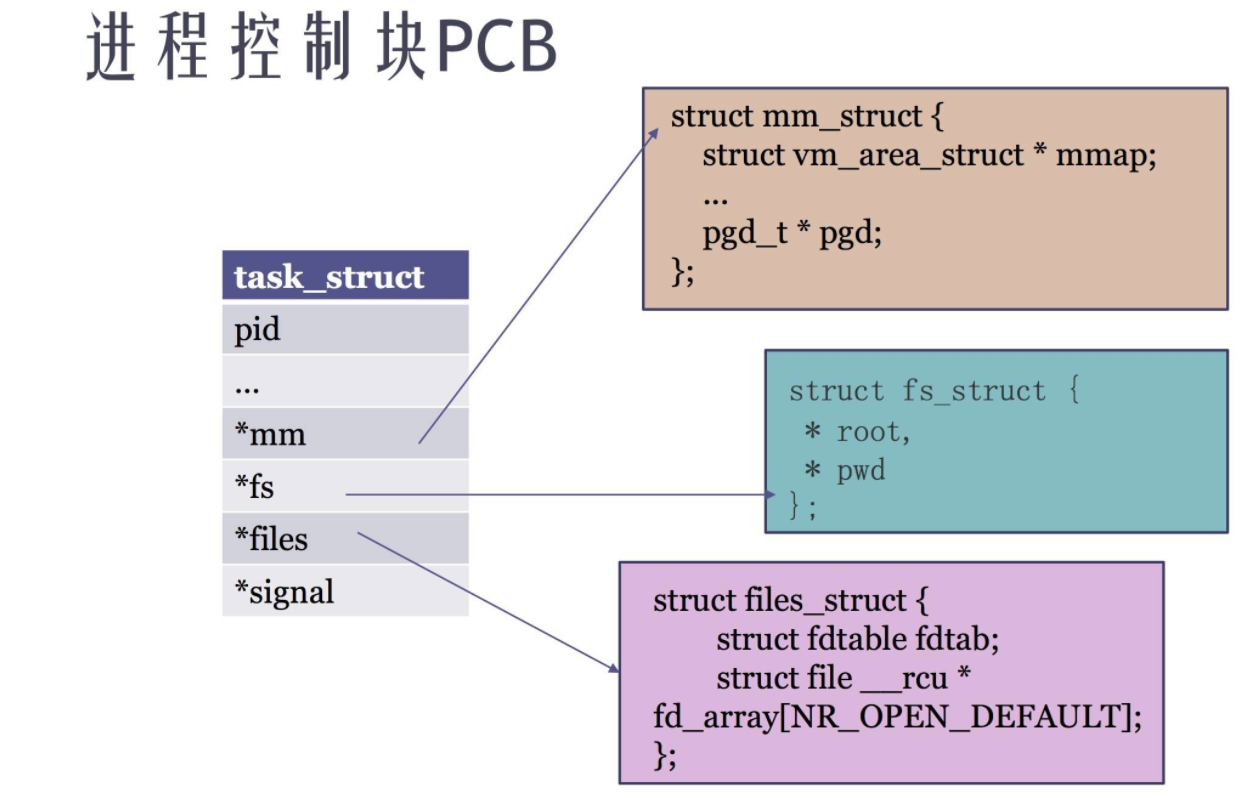
系统利用PCB来描述进程的基本情况和活动情况,进而控制进程和管理进程。
从图中可以看到,进程描述符包含的内容相当多,不仅包含了进程属性的相关内容,还有一些字段包括了其他数据结构的指针,每一个进程、线程都会有对应一个task_struct。
//from Linux-4.19.65
/* /inlude/linux/sched.h */
struct task_struct {
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
/*
* For reasons of header soup (see current_thread_info()), this
* must be the first element of task_struct.
*/
struct thread_info thread_info; //进程通过alloc_thread_info函数分配它的内核栈
#endif
/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped: */
volatile long state; //进程状态
/*
* This begins the randomizable portion of task_struct. Only
* scheduling-critical items should be added above here.
*/
randomized_struct_fields_start
void *stack; //进程内核栈
atomic_t usage;
/* Per task flags (PF_*), defined further below: */
unsigned int flags; //标记,flags反应进程的状态信息,用于内核识别当前进程的状态。
unsigned int ptrace;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct llist_node wake_entry;
int on_cpu;
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
/* Current CPU: */
unsigned int cpu;
#endif
unsigned int wakee_flips;
unsigned long wakee_flip_decay_ts;
struct task_struct *last_wakee;
/*
* recent_used_cpu is initially set as the last CPU used by a task
* that wakes affine another task. Waker/wakee relationships can
* push tasks around a CPU where each wakeup moves to the next one.
* Tracking a recently used CPU allows a quick search for a recently
* used CPU that may be idle.
*/
int recent_used_cpu;
int wake_cpu;
#endif
int on_rq;
int prio;
int static_prio;
int normal_prio;
unsigned int rt_priority;
const struct sched_class *sched_class;
struct sched_entity se;
struct sched_rt_entity rt;
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHED
struct task_group *sched_task_group;
#endif
struct sched_dl_entity dl;
#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_NOTIFIERS
/* List of struct preempt_notifier: */
struct hlist_head preempt_notifiers;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_IO_TRACE
unsigned int btrace_seq;
#endif
unsigned int policy;
int nr_cpus_allowed;
cpumask_t cpus_allowed;
#ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_RCU
int rcu_read_lock_nesting;
union rcu_special rcu_read_unlock_special;
struct list_head rcu_node_entry;
struct rcu_node *rcu_blocked_node;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_RCU */
#ifdef CONFIG_TASKS_RCU
unsigned long rcu_tasks_nvcsw;
u8 rcu_tasks_holdout;
u8 rcu_tasks_idx;
int rcu_tasks_idle_cpu;
struct list_head rcu_tasks_holdout_list;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_TASKS_RCU */
struct sched_info sched_info;
struct list_head tasks;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct plist_node pushable_tasks;
struct rb_node pushable_dl_tasks;
#endif
struct mm_struct *mm;
struct mm_struct *active_mm;
/* Per-thread vma caching: */
struct vmacache vmacache;
#ifdef SPLIT_RSS_COUNTING
struct task_rss_stat rss_stat;
#endif
int exit_state;
int exit_code;
int exit_signal;
/* The signal sent when the parent dies: */
int pdeath_signal;
/* JOBCTL_*, siglock protected: */
unsigned long jobctl;
/* Used for emulating ABI behavior of previous Linux versions: */
unsigned int personality;
/* Scheduler bits, serialized by scheduler locks: */
unsigned sched_reset_on_fork:1;
unsigned sched_contributes_to_load:1;
unsigned sched_migrated:1;
unsigned sched_remote_wakeup:1;
/* Force alignment to the next boundary: */
unsigned :0;
/* Unserialized, strictly 'current' */
/* Bit to tell LSMs we're in execve(): */
unsigned in_execve:1;
unsigned in_iowait:1;
#ifndef TIF_RESTORE_SIGMASK
unsigned restore_sigmask:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG
unsigned in_user_fault:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG_KMEM
unsigned memcg_kmem_skip_account:1;
#endif
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT_BRK
unsigned brk_randomized:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS
/* disallow userland-initiated cgroup migration */
unsigned no_cgroup_migration:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_CGROUP
/* to be used once the psi infrastructure lands upstream. */
unsigned use_memdelay:1;
#endif
unsigned long atomic_flags; /* Flags requiring atomic access. */
struct restart_block restart_block;
pid_t pid; //进程的标识符
pid_t tgid; //线程组标识符
#ifdef CONFIG_STACKPROTECTOR
/* Canary value for the -fstack-protector GCC feature: */
unsigned long stack_canary;
#endif
/*
* Pointers to the (original) parent process, youngest child, younger sibling,
* older sibling, respectively. (p->father can be replaced with
* p->real_parent->pid)
*/
/* Real parent process: */
struct task_struct __rcu *real_parent;
/* Recipient of SIGCHLD, wait4() reports: */
struct task_struct __rcu *parent;
/*
* Children/sibling form the list of natural children:
*/
struct list_head children;
struct list_head sibling;
struct task_struct *group_leader;
/*
* 'ptraced' is the list of tasks this task is using ptrace() on.
*
* This includes both natural children and PTRACE_ATTACH targets.
* 'ptrace_entry' is this task's link on the p->parent->ptraced list.
*/
struct list_head ptraced;
struct list_head ptrace_entry;
/* PID/PID hash table linkage. */
struct pid *thread_pid;
struct hlist_node pid_links[PIDTYPE_MAX];
struct list_head thread_group;
struct list_head thread_node;
struct completion *vfork_done;
/* CLONE_CHILD_SETTID: */
int __user *set_child_tid;
/* CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID: */
int __user *clear_child_tid;
u64 utime;
u64 stime;
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SCALED_CPUTIME
u64 utimescaled;
u64 stimescaled;
#endif
u64 gtime;
struct prev_cputime prev_cputime;
#ifdef CONFIG_VIRT_CPU_ACCOUNTING_GEN
struct vtime vtime;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NO_HZ_FULL
atomic_t tick_dep_mask;
#endif
/* Context switch counts: */
unsigned long nvcsw;
unsigned long nivcsw;
/* Monotonic time in nsecs: */
u64 start_time;
/* Boot based time in nsecs: */
u64 real_start_time;
/* MM fault and swap info: this can arguably be seen as either mm-specific or thread-specific: */
unsigned long min_flt;
unsigned long maj_flt;
#ifdef CONFIG_POSIX_TIMERS
struct task_cputime cputime_expires;
struct list_head cpu_timers[3];
#endif
/* Process credentials: */
/* Tracer's credentials at attach: */
const struct cred __rcu *ptracer_cred;
/* Objective and real subjective task credentials (COW): */
const struct cred __rcu *real_cred;
/* Effective (overridable) subjective task credentials (COW): */
const struct cred __rcu *cred;
/*
* executable name, excluding path.
*
* - normally initialized setup_new_exec()
* - access it with [gs]et_task_comm()
* - lock it with task_lock()
*/
char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN];
struct nameidata *nameidata;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSVIPC
struct sysv_sem sysvsem;
struct sysv_shm sysvshm;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DETECT_HUNG_TASK
unsigned long last_switch_count;
unsigned long last_switch_time;
#endif
/* Filesystem information: */
struct fs_struct *fs;
/* Open file information: */
struct files_struct *files;
/* Namespaces: */
struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
/* Signal handlers: */
struct signal_struct *signal;
struct sighand_struct *sighand;
sigset_t blocked;
sigset_t real_blocked;
/* Restored if set_restore_sigmask() was used: */
sigset_t saved_sigmask;
struct sigpending pending;
unsigned long sas_ss_sp;
size_t sas_ss_size;
unsigned int sas_ss_flags;
struct callback_head *task_works;
struct audit_context *audit_context;
#ifdef CONFIG_AUDITSYSCALL
kuid_t loginuid;
unsigned int sessionid;
#endif
struct seccomp seccomp;
/* Thread group tracking: */
u32 parent_exec_id;
u32 self_exec_id;
/* Protection against (de-)allocation: mm, files, fs, tty, keyrings, mems_allowed, mempolicy: */
spinlock_t alloc_lock;
/* Protection of the PI data structures: */
raw_spinlock_t pi_lock;
struct wake_q_node wake_q;
#ifdef CONFIG_RT_MUTEXES
/* PI waiters blocked on a rt_mutex held by this task: */
struct rb_root_cached pi_waiters;
/* Updated under owner's pi_lock and rq lock */
struct task_struct *pi_top_task;
/* Deadlock detection and priority inheritance handling: */
struct rt_mutex_waiter *pi_blocked_on;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES
/* Mutex deadlock detection: */
struct mutex_waiter *blocked_on;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGS
unsigned int irq_events;
unsigned long hardirq_enable_ip;
unsigned long hardirq_disable_ip;
unsigned int hardirq_enable_event;
unsigned int hardirq_disable_event;
int hardirqs_enabled;
int hardirq_context;
unsigned long softirq_disable_ip;
unsigned long softirq_enable_ip;
unsigned int softirq_disable_event;
unsigned int softirq_enable_event;
int softirqs_enabled;
int softirq_context;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
# define MAX_LOCK_DEPTH 48UL
u64 curr_chain_key;
int lockdep_depth;
unsigned int lockdep_recursion;
struct held_lock held_locks[MAX_LOCK_DEPTH];
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_UBSAN
unsigned int in_ubsan;
#endif
/* Journalling filesystem info: */
void *journal_info;
/* Stacked block device info: */
struct bio_list *bio_list;
#ifdef CONFIG_BLOCK
/* Stack plugging: */
struct blk_plug *plug;
#endif
/* VM state: */
struct reclaim_state *reclaim_state;
struct backing_dev_info *backing_dev_info;
struct io_context *io_context;
/* Ptrace state: */
unsigned long ptrace_message;
siginfo_t *last_siginfo;
struct task_io_accounting ioac;
#ifdef CONFIG_TASK_XACCT
/* Accumulated RSS usage: */
u64 acct_rss_mem1;
/* Accumulated virtual memory usage: */
u64 acct_vm_mem1;
/* stime + utime since last update: */
u64 acct_timexpd;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CPUSETS
/* Protected by ->alloc_lock: */
nodemask_t mems_allowed;
/* Seqence number to catch updates: */
seqcount_t mems_allowed_seq;
int cpuset_mem_spread_rotor;
int cpuset_slab_spread_rotor;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS
/* Control Group info protected by css_set_lock: */
struct css_set __rcu *cgroups;
/* cg_list protected by css_set_lock and tsk->alloc_lock: */
struct list_head cg_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_INTEL_RDT
u32 closid;
u32 rmid;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FUTEX
struct robust_list_head __user *robust_list;
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
struct compat_robust_list_head __user *compat_robust_list;
#endif
struct list_head pi_state_list;
struct futex_pi_state *pi_state_cache;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PERF_EVENTS
struct perf_event_context *perf_event_ctxp[perf_nr_task_contexts];
struct mutex perf_event_mutex;
struct list_head perf_event_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_PREEMPT
unsigned long preempt_disable_ip;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
/* Protected by alloc_lock: */
struct mempolicy *mempolicy;
short il_prev;
short pref_node_fork;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA_BALANCING
int numa_scan_seq;
unsigned int numa_scan_period;
unsigned int numa_scan_period_max;
int numa_preferred_nid;
unsigned long numa_migrate_retry;
/* Migration stamp: */
u64 node_stamp;
u64 last_task_numa_placement;
u64 last_sum_exec_runtime;
struct callback_head numa_work;
/*
* This pointer is only modified for current in syscall and
* pagefault context (and for tasks being destroyed), so it can be read
* from any of the following contexts:
* - RCU read-side critical section
* - current->numa_group from everywhere
* - task's runqueue locked, task not running
*/
struct numa_group __rcu *numa_group;
/*
* numa_faults is an array split into four regions:
* faults_memory, faults_cpu, faults_memory_buffer, faults_cpu_buffer
* in this precise order.
*
* faults_memory: Exponential decaying average of faults on a per-node
* basis. Scheduling placement decisions are made based on these
* counts. The values remain static for the duration of a PTE scan.
* faults_cpu: Track the nodes the process was running on when a NUMA
* hinting fault was incurred.
* faults_memory_buffer and faults_cpu_buffer: Record faults per node
* during the current scan window. When the scan completes, the counts
* in faults_memory and faults_cpu decay and these values are copied.
*/
unsigned long *numa_faults;
unsigned long total_numa_faults;
/*
* numa_faults_locality tracks if faults recorded during the last
* scan window were remote/local or failed to migrate. The task scan
* period is adapted based on the locality of the faults with different
* weights depending on whether they were shared or private faults
*/
unsigned long numa_faults_locality[3];
unsigned long numa_pages_migrated;
#endif /* CONFIG_NUMA_BALANCING */
#ifdef CONFIG_RSEQ
struct rseq __user *rseq;
u32 rseq_len;
u32 rseq_sig;
/*
* RmW on rseq_event_mask must be performed atomically
* with respect to preemption.
*/
unsigned long rseq_event_mask;
#endif
struct tlbflush_unmap_batch tlb_ubc;
struct rcu_head rcu;
/* Cache last used pipe for splice(): */
struct pipe_inode_info *splice_pipe;
struct page_frag task_frag;
#ifdef CONFIG_TASK_DELAY_ACCT
struct task_delay_info *delays;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FAULT_INJECTION
int make_it_fail;
unsigned int fail_nth;
#endif
/*
* When (nr_dirtied >= nr_dirtied_pause), it's time to call
* balance_dirty_pages() for a dirty throttling pause:
*/
int nr_dirtied;
int nr_dirtied_pause;
/* Start of a write-and-pause period: */
unsigned long dirty_paused_when;
#ifdef CONFIG_LATENCYTOP
int latency_record_count;
struct latency_record latency_record[LT_SAVECOUNT];
#endif
/*
* Time slack values; these are used to round up poll() and
* select() etc timeout values. These are in nanoseconds.
*/
u64 timer_slack_ns;
u64 default_timer_slack_ns;
#ifdef CONFIG_KASAN
unsigned int kasan_depth;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FUNCTION_GRAPH_TRACER
/* Index of current stored address in ret_stack: */
int curr_ret_stack;
int curr_ret_depth;
/* Stack of return addresses for return function tracing: */
struct ftrace_ret_stack *ret_stack;
/* Timestamp for last schedule: */
unsigned long long ftrace_timestamp;
/*
* Number of functions that haven't been traced
* because of depth overrun:
*/
atomic_t trace_overrun;
/* Pause tracing: */
atomic_t tracing_graph_pause;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACING
/* State flags for use by tracers: */
unsigned long trace;
/* Bitmask and counter of trace recursion: */
unsigned long trace_recursion;
#endif /* CONFIG_TRACING */
#ifdef CONFIG_KCOV
/* Coverage collection mode enabled for this task (0 if disabled): */
unsigned int kcov_mode;
/* Size of the kcov_area: */
unsigned int kcov_size;
/* Buffer for coverage collection: */
void *kcov_area;
/* KCOV descriptor wired with this task or NULL: */
struct kcov *kcov;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMCG
struct mem_cgroup *memcg_in_oom;
gfp_t memcg_oom_gfp_mask;
int memcg_oom_order;
/* Number of pages to reclaim on returning to userland: */
unsigned int memcg_nr_pages_over_high;
/* Used by memcontrol for targeted memcg charge: */
struct mem_cgroup *active_memcg;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_CGROUP
struct request_queue *throttle_queue;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_UPROBES
struct uprobe_task *utask;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_BCACHE) || defined(CONFIG_BCACHE_MODULE)
unsigned int sequential_io;
unsigned int sequential_io_avg;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SLEEP
unsigned long task_state_change;
#endif
int pagefault_disabled;
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
struct task_struct *oom_reaper_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_VMAP_STACK
struct vm_struct *stack_vm_area;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_THREAD_INFO_IN_TASK
/* A live task holds one reference: */
atomic_t stack_refcount;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LIVEPATCH
int patch_state;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
/* Used by LSM modules for access restriction: */
void *security;
#endif
/*
* New fields for task_struct should be added above here, so that
* they are included in the randomized portion of task_struct.
*/
randomized_struct_fields_end
/* CPU-specific state of this task: */
struct thread_struct thread;
/*
* WARNING: on x86, 'thread_struct' contains a variable-sized
* structure. It *MUST* be at the end of 'task_struct'.
*
* Do not put anything below here!
*/
};
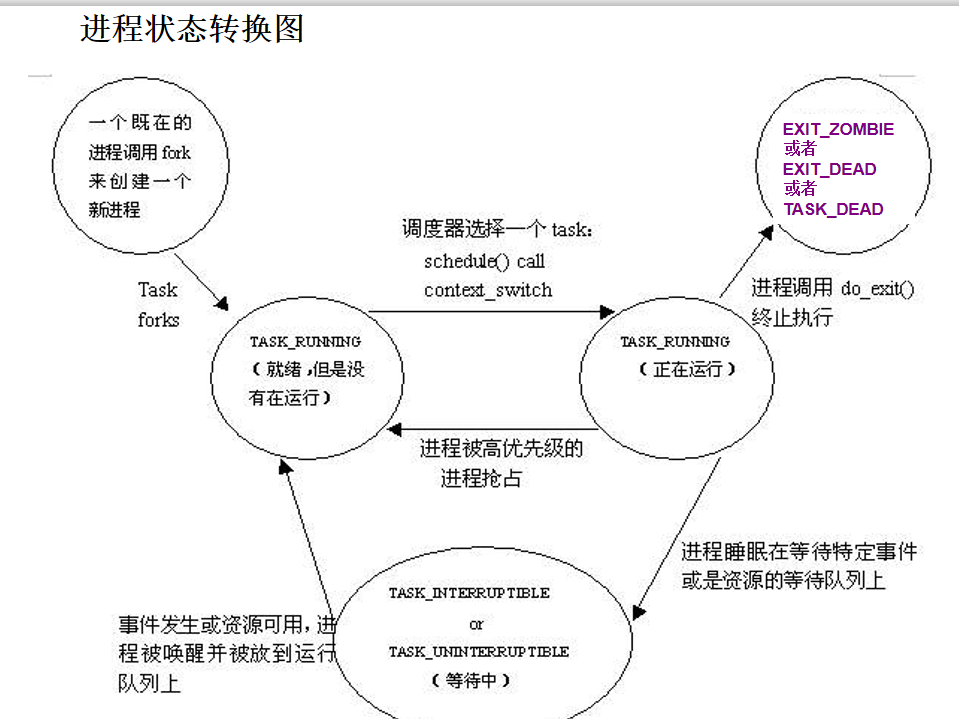
这里说几个重要的变量
进程状态
volatile long state;
int exit_state;
state的可能取值(我们可以看到变量定义后面的注释,它说明变量内容<0是不运行的,=0是运行状态,>0是停止状态。)
/* Used in tsk->state: */
/* Used in tsk->state: */
#define TASK_RUNNING 0x0000
#define TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 0x0001
#define TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE 0x0002
#define __TASK_STOPPED 0x0004
#define __TASK_TRACED 0x0008
/* Used in tsk->exit_state: */
#define EXIT_DEAD 0x0010
#define EXIT_ZOMBIE 0x0020
#define EXIT_TRACE (EXIT_ZOMBIE | EXIT_DEAD)
/* Used in tsk->state again: */
#define TASK_PARKED 0x0040
#define TASK_DEAD 0x0080
#define TASK_WAKEKILL 0x0100
#define TASK_WAKING 0x0200
#define TASK_NOLOAD 0x0400
#define TASK_NEW 0x0800
#define TASK_STATE_MAX 0x1000
-
TASK_RUNNING表示进程要么正在执行,要么正要准备执行。
-
TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE表示进程被阻塞(睡眠),直到某个条件变为真。条件一旦达成,进程的状态就被设置为TASK_RUNNING。
-
TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE的意义与TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE类似,除了不能通过接受一个信号来唤醒以外。
-
__TASK_STOPPED表示进程被停止执行。
-
__TASK_TRACED表示进程被debugger等进程监视。
-
EXIT_ZOMBIE表示进程的执行被终止,但是其父进程还没有使用wait()等系统调用来获知它的终止信息。
-
EXIT_DEAD表示进程的最终状态。
可以看看下面的转换图:
进程标识符(PID)
pid_t pid;
pid_t tgid;
在CONFIG_BASE_SMALL配置为0的情况下,PID的取值范围是0到32767,即系统中的进程数最大为32768个。
在Linux系统中,一个线程组中的所有线程使用和该线程组的领头线程(该组中的第一个轻量级进程)相同的PID,并被存放在tgid成员中。只有线程组的领头线程的pid成员才会被设置为与tgid相同的值。注意,getpid()系统调用返回的是当前进程的tgid值而不是pid值。
进程标记符(flag)
unsigned int flags;
flags可能的取值:
/*
* Per process flags
*/
#define PF_IDLE 0x00000002 /* I am an IDLE thread */
#define PF_EXITING 0x00000004 /* Getting shut down */
#define PF_EXITPIDONE 0x00000008 /* PI exit done on shut down */
#define PF_VCPU 0x00000010 /* I'm a virtual CPU */
#define PF_WQ_WORKER 0x00000020 /* I'm a workqueue worker */
#define PF_FORKNOEXEC 0x00000040 /* Forked but didn't exec */
#define PF_MCE_PROCESS 0x00000080 /* Process policy on mce errors */
#define PF_SUPERPRIV 0x00000100 /* Used super-user privileges */
#define PF_DUMPCORE 0x00000200 /* Dumped core */
#define PF_SIGNALED 0x00000400 /* Killed by a signal */
#define PF_MEMALLOC 0x00000800 /* Allocating memory */
#define PF_NPROC_EXCEEDED 0x00001000 /* set_user() noticed that RLIMIT_NPROC was exceeded */
#define PF_USED_MATH 0x00002000 /* If unset the fpu must be initialized before use */
#define PF_USED_ASYNC 0x00004000 /* Used async_schedule*(), used by module init */
#define PF_NOFREEZE 0x00008000 /* This thread should not be frozen */
#define PF_FROZEN 0x00010000 /* Frozen for system suspend */
#define PF_KSWAPD 0x00020000 /* I am kswapd */
#define PF_MEMALLOC_NOFS 0x00040000 /* All allocation requests will inherit GFP_NOFS */
#define PF_MEMALLOC_NOIO 0x00080000 /* All allocation requests will inherit GFP_NOIO */
#define PF_LESS_THROTTLE 0x00100000 /* Throttle me less: I clean memory */
#define PF_KTHREAD 0x00200000 /* I am a kernel thread */
#define PF_RANDOMIZE 0x00400000 /* Randomize virtual address space */
#define PF_SWAPWRITE 0x00800000 /* Allowed to write to swap */
#define PF_NO_SETAFFINITY 0x04000000 /* Userland is not allowed to meddle with cpus_allowed */
#define PF_MCE_EARLY 0x08000000 /* Early kill for mce process policy */
#define PF_MUTEX_TESTER 0x20000000 /* Thread belongs to the rt mutex tester */
#define PF_FREEZER_SKIP 0x40000000 /* Freezer should not count it as freezable */
#define PF_SUSPEND_TASK 0x80000000 /* This thread called freeze_processes() and should not be frozen */
这里说明以下几个常用的状态
| 状态 | 描述 |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| PF_FORKNOEXEC | 表示进程刚被创建,但还没有执行 |
| PF_SUPERPRIV | 表示进程拥有超级用户特权 |
| PF_SIGNALED | 表示进程被信号杀出、 |
|PF_EXITING|表示进程开始关闭|