网络通信协议:

通信链路的端点就被称为“套接字”(英文名Socket) 是提供给应用程序的接口。
基于TCP协议的Socket编程:
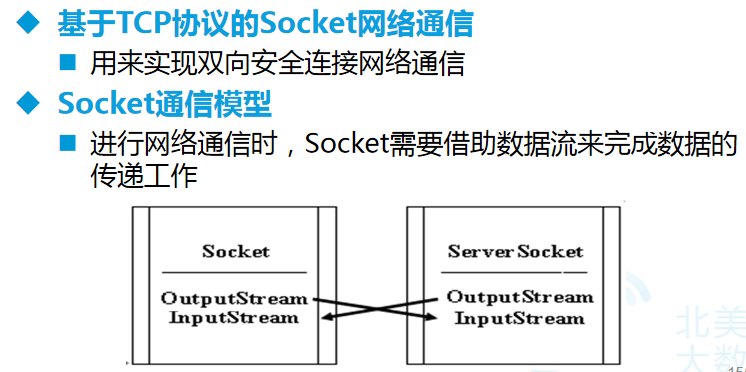
基于多线程的客户端与服务器端的信息交流:
一,读取Socket对象流的类
public class ReadThread implements Runnable{ //定义一个Socket类型的私有变量 private Socket socket; public void run(){ try { //对Socket对象的流进行包装 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); while(true){ //打印线程名和读取的信息 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+br.readLine()); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public ReadThread(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; } }
二,写入Socket对象流的类
public class WriteThread implements Runnable{ //定义一个Socket类型的私有变量 private Socket socket; public void run(){ try { //对socket的对象流进行包装 PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream()); //对要在控制台输入的数据进行包装 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); while(true){ try { //把控制台上输入的数据输出出去 pw.println(br.readLine()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ pw.flush(); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public WriteThread(Socket socket) { super(); this.socket = socket; } }
三、创建服务器端
public class ServiceSocket { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //实例化ServerSocket对象 ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(55555); //等待客户端发起请求 Socket socket=server.accept(); System.out.println("连接成功!"); //创建线程对象 ReadThread read=new ReadThread(socket); WriteThread write=new WriteThread(socket); //分别调用读、写线程,并启动 Thread t1=new Thread(read,"客户端"); Thread t2=new Thread(write); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
四、创建客户端
public class ClientSocket { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //创建Socket对象 Socket socket=new Socket("localhost",55555); ReadThread read=new ReadThread(socket); WriteThread write=new WriteThread(socket); //调用读线程 Thread t1=new Thread(read,"服务器"); //调用写线程 Thread t2=new Thread(write); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
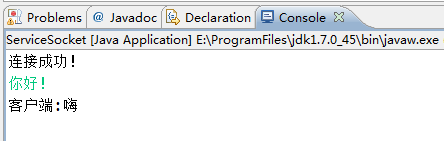
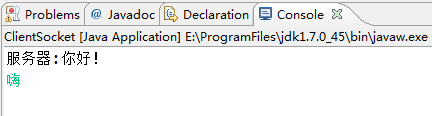
运行结果:由结果可知客户端和服务器端实现了信息的交流
基于多线程的服务器与客户端的对象的传输:
一、创建一个可序列化的类
public class User implements Serializable{//通过实现Serializble来实现类的可序列化 private String name; private String password; public User(String name, String password) { this.name = name; this.password = password; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
二、创建一个线程类,来处理服务器传过来的对象的判断
public class UserThread extends Thread{ //创建Socket类型的私有变量 private Socket socket; public UserThread(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; } public void run(){ try { //包装socket的流 ObjectInputStream ob=new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream()); //接收传过来的对象 User user=(User) ob.readObject();
//获取客户端的IP地址
InetAddress ia=socket.getInetAddress();
String s=ia.getHostAddress();
if(user!=null){ //输出判断结果 pw.println("登录成功!"); pw.flush(); }else{ pw.println("登录失败!"); pw.flush(); } ob.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
三、创建服务器
public class UserService { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //创建ServerSocket对象 ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(57889); while(true){ Socket socket=server.accept(); System.out.println("连接成功!"); new UserThread(socket).start(); } } }
四、创建两个客户端
public class UserClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Socket socket=new Socket("localhost",57889); User user=new User("张三","123"); //把对象输出出去 ObjectOutputStream ob=new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); ob.writeObject(user); //读取socket输入流中的数据 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); System.out.println(br.readLine()); br.close(); ob.close(); socket.close(); } }
public class UserClient02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Socket socket=new Socket("localhost",57889); //创建空对象 User user=null; //包装socket对象的流 ObjectOutputStream obi=new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); obi.writeObject(user); //读取socket输入流中的数据 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); System.out.println(br.readLine()); br.close(); obi.close(); socket.close(); } }
运行结果截图:由结果可得,两个客户端都连接成功了,但是UserClient02中的对象为null,所以登录失败了。由此可得对象传输是正确的。

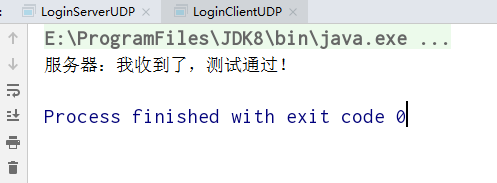
基于UDP的DatagramPacket和DatagramSocket
一、创建服务器类
public class LoginServerUDP { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义一个空数组 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024]; //定义一个空包 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length); //定义socket对象 DatagramSocket ds=null; try { ds= new DatagramSocket(55555); //接受发送过来的数据包 ds.receive(dp); //报数据包中的数据转换成字符串 String s=new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getData().length); System.out.println("客户端:"+s); String info="我收到了,测试通过!"; //字符串打散放进数组 byte[] bytes1=info.getBytes(); //获得ip地址 SocketAddress sa = dp.getSocketAddress(); //把数据、ip包装起来 DatagramPacket dp2=new DatagramPacket(bytes1,0,bytes1.length,sa); //发送数据包 ds.send(dp2); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { ds.close(); } } }
二、创建客户端类
public class LoginClientUDP { public static void main(String[] args) { String info="我要测试UDP协议"; byte[] bytes=info.getBytes(); //创建ip对象 InetAddress id= null; //创建socket对象 DatagramSocket ds=null; try { //通过ip名获得ip id = InetAddress.getByName("localhost"); //把要发送的数据,发往的ip和端口,包装起来 DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length,id,55555); ds=new DatagramSocket(); //发送包 ds.send(dp); //定义一个空数组 byte[] bytes2=new byte[1024]; //定义一个空包 DatagramPacket dp2=new DatagramPacket(bytes2,bytes2.length); //用空包接受发送过来的数据包 ds.receive(dp2); //把包中的数据转换成字符串 String s=new String(dp2.getData(),0,dp2.getData().length); System.out.println("服务器:"+s); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { ds.close(); } } }
三、运行结果