- 导语
在学习操作系统的过程中,PV操作是很重要的一个环节。然而面对书本上枯燥的代码,每一个爱好技术的人总是想能亲自去实现。现在我要推出一个专题,专门讲述如何用Java实现PV操作,让操作系统背后的逻辑跃然屏上。
如有错误,请广大网友斧正,感激不尽!
经典问题1、生产者与消费者
- PV操作数据结构的构建
在书本上,我们给出了一种数据结构,叫做信号量。这种信号量有两个元素:
一个是count,如果是正值则表示当前资源的个数,如果是0,表示有一个进程在执行临界区的代码(也就是说这个进程位于临界区);并且没有进程处于阻塞队列中。如果是负值,这个值的绝对值(abs(count))表示阻塞队列中进程的个数。
一个是queue,即为阻塞进程队列。当进程不能申请相应的资源是,则使用P操作,将自己插入阻塞队列中。当运行的进程执行完临界区代码时,就执行V操作,唤醒一个阻塞队列中的进程。
现在我们定义一个PV操作类:syn。在这个类中我们可以通过构造函数设置count的值。可以看到这个类中并没有阻塞进程所在的queue,我是通过java的this.wait()与this.notifyAll()来实现的。
并且,通过关键字【synchronized】,保证了PV操作是一条【原语】,即在运行过程中,占有完整的一个时间片,不可分割。
1 class syn{//PV操作类 2 int count=0;//信号量 3 syn(){} 4 syn(int a){count=a;} 5 public synchronized void Wait(){ //关键字 synchronized 保证了此操作是一条【原语】 6 count--; 7 if(count<0){//等于0 :有一个进程进入了临界区 8 try { //小于0:abs(count)=阻塞的进程数目 9 this.wait(); 10 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 public synchronized void Signal(){ //关键字 synchronized 保证了此操作是一条【原语】 16 count++; 17 if(count<=0){//如果有进程阻塞 18 this.notify(); 19 } 20 } 21 }
注1:P操作wait中,应为if(count<0)而不是while(count<0) 。在后续的编写中,发现如果引入了多个生产者与消费者,用语句while(count<0) 就会出错。
注2:V操作signal中,应为this.notify()而不是this.notifyAll()。也就是说只需要从阻塞队列中唤醒一个进程。
- 单个生产者与消费者的模型构建
我们构建实现了Runnable接口的生产者类和消费者类,使用empty(表示空缓冲区的数目)和full(表示满缓冲区的数目)两个信号量来实现进程的同步。(不同类型的进程共享某一资源为同步关系)
代码如下:
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Producer p=new Producer(); 5 Consumer c=new Consumer(); 6 Thread pp=new Thread(p); 7 Thread cp=new Thread(c); 8 pp.start(); 9 cp.start(); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class Global{ 14 static syn empty=new syn(8); 15 static syn full=new syn(0); 16 static int buffer []=new int[8];//缓冲区 17 } 18 19 //生产者类 20 class Producer implements Runnable{ 21 int count=0; 22 public void run(){ 23 while(count<20){ 24 Global.empty.Wait(); 25 //临界区 26 int index=count%8; 27 Global.buffer[index]=count; 28 System.out.println("生产者在缓冲区"+index+"中生产了物品"+count); 29 count++; 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(10); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 // end of 临界区 37 Global.full.Signal(); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 //消费者类 43 class Consumer implements Runnable{ 44 int count=0; 45 public void run(){ 46 while(count<20){ 47 Global.full.Wait(); 48 //临界区 49 int index=count%8; 50 int value=Global.buffer[index]; 51 System.out.println("消费者在缓冲区"+index+"中消费了物品"+value); 52 count++; 53 try { 54 Thread.sleep(10); 55 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 56 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 57 e.printStackTrace(); 58 } 59 // end of 临界区 60 Global.empty.Signal(); 61 } 62 } 63 }
运行结果:
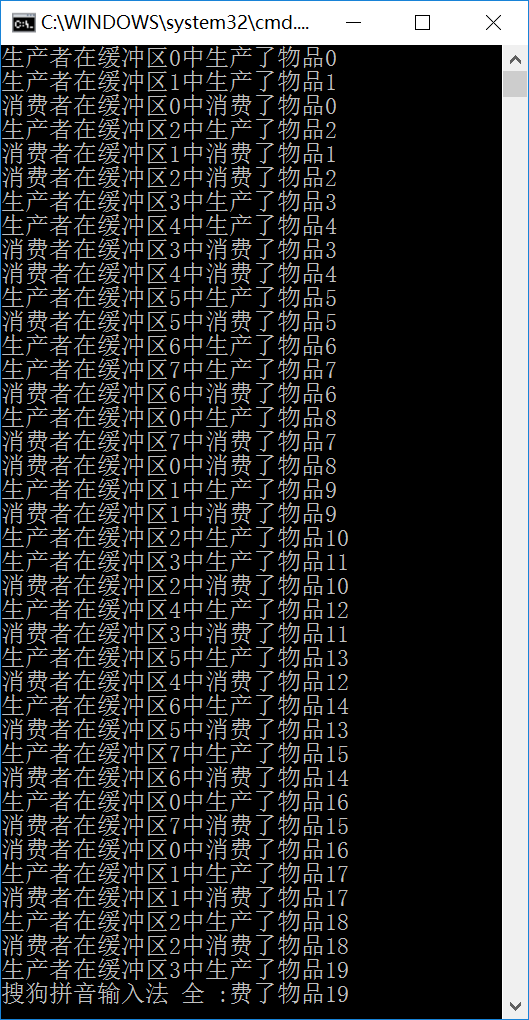
可以看出进程严格按照先生产再消费的顺序,完美运行。
- 引入多个生产者与消费者
为保证同一类进程在进行访问时能保证互斥(互斥是同类进程共享某一资源时的方式)我们引入mutex信号量。
static syn pMutex=new syn(1);//保证生产者之间互斥 static syn cMutex=new syn(1);//保证消费者之间互斥
运行结果:
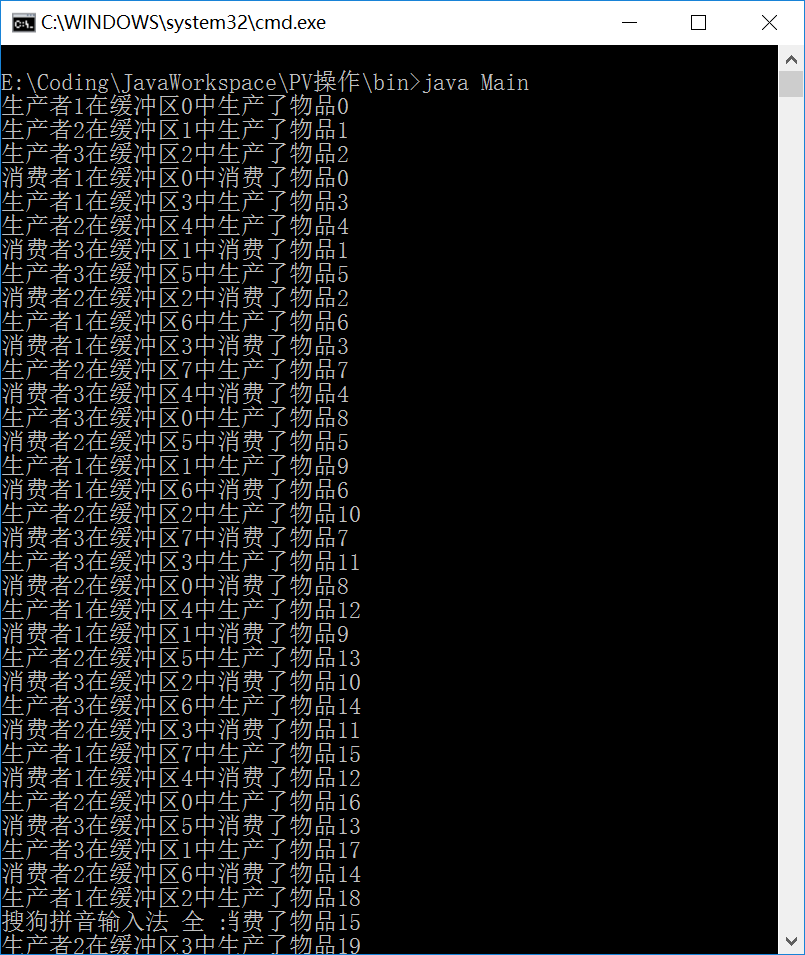
可见程序完美运行。
完整Java代码:
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Producer p[]=new Producer[3];//3个生产者 5 Consumer c[]=new Consumer[3]; 6 int i; 7 8 for(i=0;i<3;i++){ 9 p[i]=new Producer(i+1); 10 } 11 for(i=0;i<3;i++){ 12 c[i]=new Consumer(i+1); 13 } 14 15 Thread pp[]=new Thread[3]; 16 Thread cp[]=new Thread[3]; 17 18 for(i=0;i<3;i++){ 19 pp[i]=new Thread(p[i]); 20 } 21 for(i=0;i<3;i++){ 22 cp[i]=new Thread(c[i]); 23 } 24 25 for(i=0;i<3;i++){ 26 pp[i].start(); 27 } 28 for(i=0;i<3;i++){ 29 cp[i].start(); 30 } 31 32 } 33 } 34 35 class Global{ 36 static syn empty=new syn(8); 37 static syn full=new syn(0); 38 static syn pMutex=new syn(1);//保证生产者之间互斥 39 static syn cMutex=new syn(1);//保证消费者之间互斥 40 static int buffer []=new int[8];//缓冲区 41 static int pCount=0; 42 static int cCount=0; 43 } 44 45 //生产者类 46 class Producer implements Runnable{ 47 int ID=0; 48 Producer(){} 49 Producer(int id){ID=id;} 50 public void run(){ 51 while(Global.pCount<20){ 52 Global.empty.Wait(); 53 Global.pMutex.Wait(); 54 //临界区 55 int index=Global.pCount%8; 56 Global.buffer[index]=Global.pCount; 57 System.out.println("生产者"+ID+"在缓冲区"+index+"中生产了物品"+Global.pCount); 58 Global.pCount++; 59 try { 60 Thread.sleep(10); 61 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 62 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } 65 // end of 临界区 66 Global.pMutex.Signal(); 67 Global.full.Signal(); 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 72 //消费者类 73 class Consumer implements Runnable{ 74 int ID=0; 75 Consumer(){} 76 Consumer(int id){ID=id;} 77 public void run(){ 78 while(Global.cCount<20){ 79 Global.full.Wait(); 80 Global.cMutex.Wait(); 81 //临界区 82 int index=Global.cCount%8; 83 int value=Global.buffer[index]; 84 System.out.println("消费者"+ID+"在缓冲区"+index+"中消费了物品"+value); 85 Global.cCount++; 86 try { 87 Thread.sleep(10); 88 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 89 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 90 e.printStackTrace(); 91 } 92 // end of 临界区 93 Global.cMutex.Signal(); 94 Global.empty.Signal(); 95 } 96 } 97 } 98 99 class syn{//PV操作类 100 int count=0;//信号量 101 syn(){} 102 syn(int a){count=a;} 103 public synchronized void Wait(){ //关键字 synchronized 保证了此操作是一条【原语】 104 count--; 105 if(count<0){//等于0 :有一个进程进入了临界区 106 try { //小于0:abs(count)=阻塞的进程数目 107 this.wait(); 108 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 109 e.printStackTrace(); 110 } 111 } 112 } 113 public synchronized void Signal(){ //关键字 synchronized 保证了此操作是一条【原语】 114 count++; 115 if(count<=0){//如果有进程阻塞 116 this.notify();//All 117 } 118 } 119 }
