JAVA自学笔记18
1、Map接口:
1)功能:

2)
Map<String,String>m=new HashMap<String,String>();
//添加元素,元素无序
System.out.println("map.put("cc","coco"));//null
//替换键值,返回该键的上一个值,若键不存在,返回null
System.out.println(map);//cc=coco,左边是键,右边是值
//map.clear();//清除所有元素
//System.out.printn(map.remove("cc"));//coco。若键存在,则删除该键,返回该键的键值。若不存在,返回null
System.out.println(map.containsKey("cc"));true.//集合存在该键,则返回true。若不在,则返回false
System.out.println(map.containsKey(map.isEmpty()));//集合为空,则返回false
System.out.println(map.containsKey(map.size);//返回集合中键的数目
//获取功能
System.out.println((map.get(cc));//coco。将获取该键的键值,若键不存在,将返回null
Set<String> set=map.keyset();
for(String key:set){
System.out.println(key);
}//将返回所有的键
Collection<String>con=map.values();
for(String value:value){
System.out.println(value);
}//将返回所有的键值
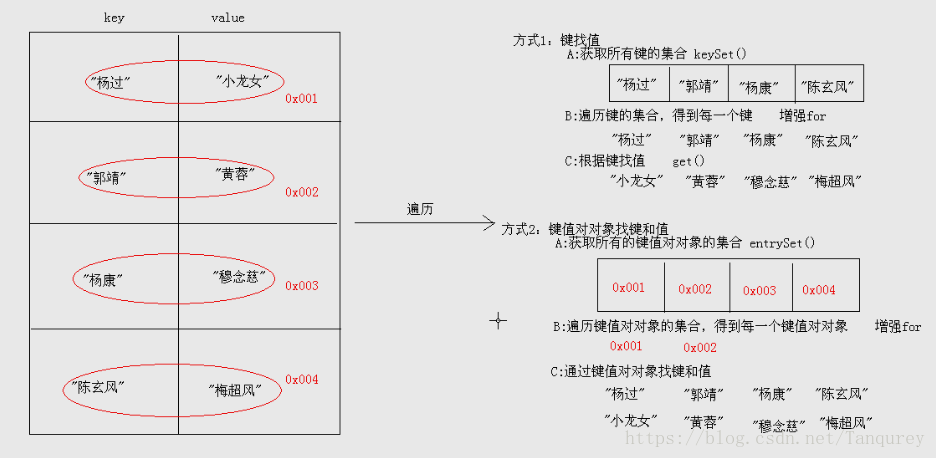
//Map集合的遍历-方式1依键寻值
//获取所有的键-遍历键的集合,获取得到每一个键-根据键去找值
Map<String,String>m=new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("cc","coco");
map.put("jc","jack");
Set<String> set=map.keyset();
for(String key:set){
Strng value=map.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
//Map集合的遍历-方式2
//获取所有的键值段的集合
//遍历键值对对象的集合,得到每一个键值对对象
//根据键值对对象获取键和键值
//键值对对象的表示:Set<Map.Entry<K,V>>entrySet()l;返回键值对对象的集合
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>>set=map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String,String>me:set){
String key=me.getKey();
String value=me.getValue();
}3)两种遍历方式的图解
2、HashMap
1)键是哈希表结构,可以保证键的唯一性,是Map的接口实现
2)HashMap
//创建集合对象
HashMap<String,String>hm=new HashMap<String,String>();
hm.put("cc","coco");
hm.put("jc","jack");
Set<String>set=hm.keySet();
for(String key:Set){
String value=hm.get(key);
System.out.println(value);
}
3)HashMap
HashMap<Integer,String>=new HashMap<Integer,String>();
Integer i=new Integer(55);
String s="jack";
hm.put(i,s);
hm.put(14,"coco");
Set<Integer>set=hm,keySet();
for(Integer key:set){
String value=hm.get(key);
}4)HashMap
//Student类略
HashMap<String,Student>hm=new HashMap<String,Student>();
Student s1=new Student("coco",22);
Student s1=new Student("kiki",23);
//添加元素
hm.put("5414",s1);
hm.put("5415",s2);
//遍历
Set<String>set=hm.keySet();
for(String key:set){
Student value=hm.get(key);
}
5)HashMap
//创建集合对象
HashMap<Student,String>hm=new HashMap<Student,String>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1=new Student("coco",22);
Student s1=new Student("kiki",23);
//添加元素
hm.put(s1,"3f4d");
hm.put(s2,"4f4h");
//遍历
Set<Student>set=hm.keySet();
for(Student key:set){
String value=hm.get(key);
//若出现某几个对象成员变量相同但出现了多次该键时,在Student类中生成HashCode()和equal()即可
}
3、LinkedHashMap
1)Map接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。即键是有序的
2)
LinkedHashMap<String,String>hm=new LinkedHashMap<String,String>();
hm.put("1223","dd");
hm.put("1223","wd");
hm.put("1233","qd");
for(String key:set){
String value=hm.get(key);//输出语句中重复的将覆盖
}4、TreeMap类
1)键为红黑树结构,可以保证键的排序和唯一性
2)TreeMap集合键是String值是String的案例
TreeMap<String,String>tm=new TreeMap<String,String>;
tm.put("coco","cc");
tm.put("jack","jc");
set<String>set=tm.eySet();
for(String key:set){
String value=tm.get(key);
//使用的是自然排序
}3)TreeMap集合键是Student值是String的案例
TreeMap<String,String>tm=new TreeMap<String,String>(new Comparator<Student>(){
public int compare(Student s1,Student s2){
int num=s1.getAge()-s2.getAge();
//以下是次要条件
int num2=num==0?s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()):num;
return num2;
}
});//比较器排序,按年龄从低到高排序
Student s1=new Student ("kiki",23);
Student s2=new Student ("jiji",24);
tm.put(s1,"5821");
tm.put(s1,"5851");
set<String>set=tm.keySet();
for(String key:set){
String value=tm.get(key);
//要重写compareTo方法实现Comparable接口才能实现自然排序@例题1:统计字符串中每个字符出现的次数
图解
Scannner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
//键盘录入一个字符串
String line=sc.nextLine();
//定义TreeMap集合
TreeMap<Character,Integer>tm=new TreeMap<Character,Integer>();
//把字符串转换为字符数组
char[] chs=line,toCharArray();
//遍历数组
for(char ch:chs){
Integer i=tm.get(ch,1);
}else{
i++;
tm.put(ch,i);
}}
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
Set<Character>set=tm.keySet();
for(Character key:set){
Integer value=tm.get(key);
sb.append(key).append)("(").append(value).append(")");
String result=sb.toString;
System.out,println(result);
}@例题3:HashMap嵌套HashMap
//创建集合对象
HashMap<String,HashMap><String,Integer>>czbkMap=new HashMap<String,HashMap><String,Integer>>();
//创建基础班集合对象
HashMap<String,Integer>jcMap=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
jcMap.put("cc",12);
jcMap.put("bb",14);
//添加到大集合中
czbkMap.put("jc",jcMap);
//创建就业班集合对象
HashMap<String,Integer>jyMap=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
jcMap.put("aa",13);
jcMap.put("dd",15);
//添加到大集合中
czbkMap.put("jy",jyMap);
//遍历集合
Set<String>czbkMapSet=czbkMap.keySet();
for(String czbkMapKey:czbkMapSet){
HashMap<String,Integer>czbkMapValue=czbkMap.get(czbkMapSet);
Set<String > czbkMapValueSet=czbkMapValueSet.keySet();
for(String czbkMapValueKey:czbkMapValueSet){
Integer czbkMapValueValue=czbkMapValue.get(czbkMapValueKey);
System.out,println(czbkMapValueKey+","czbkValueValue);
}
}
@例题4:HashMap集合嵌套ArrayList
//创建集合对象
HashMap<String,ArrayList<String>>hm=new HashMap<String,ArrayList<String>>();
//创建元素集合1
ArrayList<String>array1=new ArrayList<String>();
array1.add("黄盖");
array1.add("孙权");
bjczbkMap.put("jc",array1)
bjczbkMap.put("jc",array2)
hm.put("三国","array1");//添加键
//创建元素集合2
ArrayList<String>array2=new ArrayList<String>();
array3.add("孙悟空");
array3.add("观音");
hm.put("西游记","array2");//添加键
//创建元素集合1
ArrayList<String>array3=new ArrayList<String>();
array4.add("贾宝玉");
array4.add("薛宝钗");
bjczbkMap.put("jc",array3)
bjczbkMap.put("jc",array4)
hm.put("红楼","array3");//添加键
//遍历集合
Set<String>set=hm.keySet();
for(String key:set){
System.out.println(key);
ArrayList<String> array=hmget(key);
for(String s:value){
System.out.println(" "+s);
}
}@例题6:ArrayListq嵌套HashMap
//创建集合对象
ArrayList<HashMap><String.String>>array=new ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>>();
//创建元素1
HashMap<String,String>hm1=new HashMap<String,String>();
hm1.put("周瑜","小乔");
hm1.put("吕布","貂蝉");
//把元素添加到array里
array.add(hm1);
//创建元素2
HashMap<String,String>hm1=new HashMap<String,String>();
hm1.put("牛魔王","铁扇");
hm1.put("金角","银角");
//把元素添加到array里
array.add(hm2);
//创建元素1
HashMap<String,String>hm1=new HashMap<String,String>();
hm1.put("牛肉","牛肉面");
hm1.put("陈靖仇","于小雪");
//把元素添加到array里
array.add(hm1);
//遍历
for(HashMap<String,String>hm:array){
Set<String>set=hm.keySet();
for(String key:set){
String value=hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key+" "+value)
}
}@例题7:HashMap嵌套HashMap嵌套HashMap
//创建大集合
HashMap<String,HashMap<String,ArrayList<Student>>>czbkMap=new HashMap<String,HashMap<String,ArrayList<Student>>>();
//北京校区
HashMap<String,ArrayList<Student>> bjczbkMap=new HashMap<String,ArrayList<Student>>();
ArrayList<Student>array1=new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1=new Student("林青霞","27");
Student s2=new Student("风清扬","30");
array1.add(s1);
array1.add(s2);
ArrayList<Student>array2=new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s3=new Student("董存瑞","17");
Student s4=new Student("李云龙","60");
array2.add(s3);
array2.add(s4);
//其余类比不再给出
//遍历集合
Set<String>czbkMapSet=czbkMap.keySet();
for(String czbkMapKey:czbkMapSet){
for(String czbkMapKey:czbkMapSet){
System,out.println(czbkMapKey);
HashMap<String,ArrayList<Student>>czbkMapValue=cabkMap.get(czbkMapKey);
set<String>czbkMapValueSet=czbkMapValue.keySet();
for(String czbkMapValueKey:czbkMapValueSet){
ArrayList<Student>czbkMapValueValue=czbkMapValue.get(czbkMapValueKey);
for(Student s:czbkMapValueValue){
System.out.println(s.getName);
}
}
}
}
@例题8:HashMap与Hashtable的区别
Hashtable:此类实现一个哈希表,与HashMap用法几乎一样,但它不允许null键和null值 。它是同步的,HashMap是不同步的。
@例题9:Ltst,Set,Map接口是否都继承自Map接口?
List,Set不继承自Map接口,它们继承自Collection接口,Map本身就是一个顶层接口
2、Collections类:
1)针对集合操作的工具类
2 )Collection与Collections的区别:前者是单列集合的顶层接口。后者是对集合操作的工具类
3)成员方法
①public static <T> void sort(List<T>List)
排序。默认进行自然排序
public static <T> int binarySearch(List<?>list,T key)
进行二分查找
public static <T> max(collection<?> coll)
求最大值
public static void reverse(List<?>list)
反转
public static void shuffle (List<?>list)
随机置换
List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<Integer>()'
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(10);
list.add(60);
list.add(5);
list.add(200);
Collections.sort(list);
int index=Collections(list,10);
System.out.println(Collections.max(list));
Collections.reverse(list);
Collections.shuffle(list);@例题10:ArrayList存储自定义对象并排序
//学生类略
Public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
public int compareTo(Student s){
int num=this.age-s.age;
int num2=num==0?this.name.comparaTo(s.name):num;
return num2;
}
List<Student>list=new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1=new Student("huh",34);
Student s2=new Student("hh",44);
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
//自然排序
//collections.sort(list);
//比较器排序,以比较器为主
Collections.sort(list,new Comparator)<Student>(){
public int compare(Student s1,Student s2){
int num=s2.getAge()-s1.getAge();
return num;
}
})
for(Student s:List){
System.out.println(s.getName())
}@例题11:模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌
ArrayList<String> array=new ArrayList<String>();
String[] colors={"方块","梅花","红桃","黑桃"}
String[] numbers={"A","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K"};
for(String color:colors){
for(String number:numbers){
array.add(color.concat(number));
}
}
array.add(大王);
array.add(小王);
//洗牌
Collections.shuffle(array);
//发牌
ArrayList<String>p1=new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String>p2=new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String>p3=new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList dipai=new ArrayList<String>();
for(int x=0;x<array.size();x++){
if(x>array.size()-3){
diPai.add(array.get(x));
else if(x%3==0){p1.add(array.get(x))
}
else if(x%3==1){p2.add(array.get(x))
}
else if(x%3==2){p3.add(array.get(x))
}
}
}
//看牌
lookPoker("p1",p1);
lookPoker("p2",p2);
lookPoker("p3",p3);
public static void lookPoker(String name,ArrayList<String>array){
System.out.println(name+"的牌是");
for(String s:array){
System.out.println(s+" ")
}
System.out.println(" ")
}
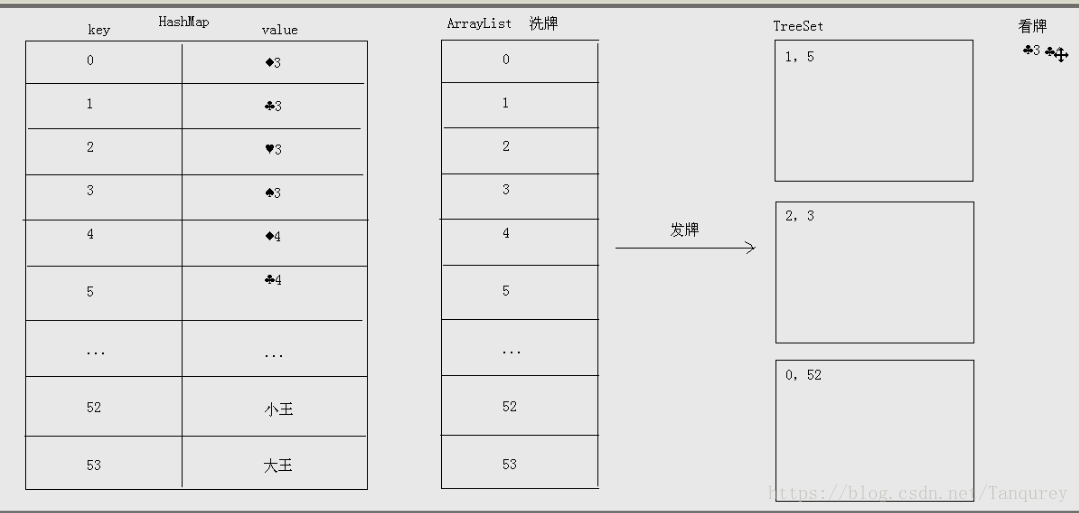
图解:
//完整代码
//创建一个HashMap集合
//创建一个ArrayList集合
//创建花色和点数数组
//从0开始往HashMap里面存储编号,并存储对应的牌。同时往ArrayList里面存储编号即可
//洗牌(洗的是编号)
//发牌(发的是编号,为了使得在看牌时编号是排序的,就创建TreeSet集合接收)
//看牌(遍历TreeSet集合,获取编号,到HashMap里找对应的牌)
//创建一个HashMap集合
// 创建一个HashMap集合
HashMap<Integer, String> hm = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// 创建一个ArrayList集合
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 创建花色数组和点数数组
// 定义一个花色数组
String[] colors = { "♠", "♥", "♣", "♦" };
// 定义一个点数数组
String[] numbers = { "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "J", "Q",
"K", "A", "2", };
// 从0开始往HashMap里面存储编号,并存储对应的牌,同时往ArrayList里面存储编号即可。
int index = 0;
for (String number : numbers) {
for (String color : colors) {
String poker = color.concat(number);
hm.put(index, poker);
array.add(index);
index++;
}
}
hm.put(index, "小王");
array.add(index);
index++;
hm.put(index, "大王");
array.add(index);
// 洗牌(洗的是编号)
Collections.shuffle(array);
// 发牌(发的也是编号,为了保证编号是排序的,就创建TreeSet集合接收)
TreeSet<Integer> fengQingYang = new TreeSet<Integer>();
TreeSet<Integer> linQingXia = new TreeSet<Integer>();
TreeSet<Integer> liuYi = new TreeSet<Integer>();
TreeSet<Integer> diPai = new TreeSet<Integer>();
for (int x = 0; x < array.size(); x++) {
if (x >= array.size() - 3) {
diPai.add(array.get(x));
} else if (x % 3 == 0) {
fengQingYang.add(array.get(x));
} else if (x % 3 == 1) {
linQingXia.add(array.get(x));
} else if (x % 3 == 2) {
liuYi.add(array.get(x));
}
}
// 看牌(遍历TreeSet集合,获取编号,到HashMap集合找对应的牌)
lookPoker("风清扬", fengQingYang, hm);
lookPoker("林青霞", linQingXia, hm);
lookPoker("刘意", liuYi, hm);
lookPoker("底牌", diPai, hm);
}
// 写看牌的功能
public static void lookPoker(String name, TreeSet<Integer> ts,
HashMap<Integer, String> hm) {
System.out.print(name + "的牌是:");
for (Integer key : ts) {
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}