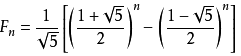You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
算法1:分析:dp[i]为爬到第i个台阶需要的步数,那么dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2], 很容易看出来这是斐波那契数列的公式 本文地址
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
int fbn1 = 0, fbn2 = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int tmp = fbn1 + fbn2;
fbn1 = fbn2;
fbn2 = tmp;
}
return fbn2;
}
};
算法2:还可以根据斐波那契数列的通项公式来求,对于斐波那契数列 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21,通项公式如下,这个方法有个缺陷是:使用了浮点数,但是浮点数精度有限, oj中n应该不大,所以可以通过(当 N>93 时 第N个数的值超过64位无符号整数可表示的范围)
具体推导请参考百度百科
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
//根据斐波那契数列的通项公式
double a = 1/sqrt(5);
double b = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
double c = (1 - sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int)round(a * (pow(b, n+1) - pow(c, n+1)));
}
};
算法3:”编程之美2.9-斐波那契数列“ 中提到了一种logn的算法(实际上利用了幂运算的logn算法),在n比较大时,会高效很多。首先给出本题代码,然后直接截图书上的描述。如果n较大,就需要编写大整数类了
1 struct matrix22 2 { 3 int v11,v12,v21,v22; 4 matrix22(int a,int b,int c,int d) 5 { 6 v11 = a; v12 = b; v21 = c; v22 = d; 7 } 8 matrix22(){} 9 }; 10 matrix22 matMult(const matrix22 &a, const matrix22 &b)//矩阵乘法 11 { 12 matrix22 res; 13 res.v11 = a.v11*b.v11 + a.v12*b.v21; 14 res.v12 = a.v11*b.v12 + a.v12*b.v22; 15 res.v21 = a.v21*b.v11 + a.v22*b.v21; 16 res.v22 = a.v21*b.v12 + a.v22*b.v22; 17 return res; 18 } 19 matrix22 matPow(const matrix22 &a, int exp)//矩阵求幂 20 { 21 matrix22 res(1,0,0,1);//初始化结果为单位矩阵 22 matrix22 tmp = a; 23 for(; exp; exp >>= 1) 24 { 25 if(exp & 1) 26 res = matMult(res, tmp); 27 tmp = matMult(tmp, tmp); 28 } 29 return res; 30 } 31 32 class Solution { 33 public: 34 int climbStairs(int n) { 35 matrix22 A(1,1,1,0); 36 A = matPow(A, n-1); 37 return A.v11 + A.v21; 38 } 39 }; 40 41


【版权声明】转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/TenosDoIt/p/3465356.html