SQL基本操作

-- 双中划线+空格: 注释(单行注释),也可以使用#号 -- 创建数据库 create database mydatabase charset utf8; -- 创建关键字数据库 create database database charset utf8; -- 使用反引号 create database `database` charset utf8; -- 创建中文数据库 create database 中国 charset utf8; create database `中国` charset utf8; -- 解决方案: 告诉服务器当前中文的字符集是什么 set names gbk; create database 中国 charset utf8; -- 查看所有数据库 show databases; -- 创建数据库 create database informationtest charset utf8; -- 查看以information_开始的数据库: _需要被转义 show databases like 'information\_%'; show databases like 'information_%'; -- 相当于information% -- 查看数据库创建语句 show create database mydatabase; show create database `database`; -- 关键字需要使用反引号 -- 修改数据库informationtest的字符集 alter database informationtest charset GBK; -- 删除数据库 drop database informationtest; -- 创建表 create table if not exists mydatabase.student( -- 显示的将student表放到mydatabase数据库下 name varchar(10), gender varchar(10), number varchar(10), age int )charset utf8; -- 创建数据表 -- 进入数据库 use mydatabase; -- 创建表 create table class( name varchar(10), room varchar(10) )charset utf8; -- 查看所有表 show tables; -- 查看以s结尾的表 show tables like '%s'; -- 查看表创建语句 show create table studentg -- g ==== ; show create table studentG -- 将查到的结构旋转90度变成纵向 -- 查看表结构 desc class; describe class; show columns from class; -- 重命名表: student表 -> my_student(取数据库名字前两个字母) rename table student to my_student; -- 修改表选项: 字符集 alter table my_student charset = GBK; -- 给学生表增加ID放到第一个位置 alter table my_student add column id int first; -- mysql会自动寻找分号: 语句结束符 -- 将学生表中的number学号字段变成固定长度,且放到第二位(id之后) alter table my_student modify number char(10) after id; -- 修改学生表中的gender字段为sex alter table my_student change gender sex varchar(10); -- 删除学生表中的年龄字段(age) alter table my_student drop age; -- 删除数据表 drop table class; -- 插入数据 insert into my_student values(1,'itcast0001','Jim','male'), (2,'itcast0002','Hanmeimei','female'); -- 插入数据: 指定字段列表 insert into my_student(number,sex,name,id) values ('itcast0003','male','Tom',3), ('itcast0004','female','Lily',4); -- 查看所有数据 select * from my_student; -- 查看指定字段,指定条件数据 select id,number,sex,name from my_student where id = 1; -- 查看满足id为1的学生信息 -- 更新数据 update my_student set sex = 'female' where name = 'jim'; -- 删除数据 delete from my_student where sex = 'male'; -- 插入数据(中文) insert into my_student values(5,'itcast0005','张越','男'); -- 查看所有字符集 show character set; -- 查看服务器默认的对外处理的字符集 show variables like 'character_set%'; -- 修改服务器认为的客户端数据的字符集为GBK set character_set_client = gbk; -- 修改服务器给定数据的字符集为GBK set character_set_results = gbk; -- 快捷设置字符集 set names gbk; -- 查看所有校对集 show collation; -- 创建表使用不同的校对集 create table my_collate_bin( name char(1) )charset utf8 collate utf8_bin; create table my_collate_ci( name char(1) )charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; -- 插入数据 insert into my_collate_bin values('a'),('A'),('B'),('b'); insert into my_collate_ci values('a'),('A'),('B'),('b'); -- 排序查找 select * from my_collate_bin order by name; select * from my_collate_ci order by name; -- 有数据后修改校对集 alter table my_collate_ci collate = utf8_bin; alter table my_collate_ci collate = utf8_general_ci;
二

-- 创建整型表 create table my_int( int_1 tinyint, int_2 smallint, int_3 int, int_4 bigint )charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_int values(100,100,100,100); -- 有效数据 insert into my_int values('a','b','199','f'); -- 无效数据: 类型限定 insert into my_int values(255,10000,100000,1000000); -- 错误: 超出范围 -- 给表增加一个无符号类型 alter table my_int add int_5 tinyint unsigned; -- 无符号类型 -- 插入数据 insert into my_int values(127,1000,10000,1000000,255); alter table my_int add int_6 tinyint(1) unsigned;-- 指定显示宽度为1; insert into my_int values(127,0,0,0,255,255); alter table my_int add int_7 tinyint(2) zerofill; -- 显示宽度为2,0填充 insert into my_int values(1,1,1,1,1,1,1); insert into my_int values(100,100,100,100,100,100,100); -- 浮点数表 create table my_float( f1 float, f2 float(10,2), -- 10位在精度范围之外 f3 float(6,2) -- 6位在精度范围之内 )charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_float values(1000.10,1000.10,1000.10); -- 符合条件 insert into my_float values(1234567890,12345678.90,1234.56); -- 符合条件 insert into my_float values(3e38,3.01e7,1234.56); insert into my_float values(9999999999,99999999.99,9999.99); -- 最大值 -- 超出长度插入数据 insert into my_float values(123456,1234.123456768,123.9876543); -- 小数部分OK insert into my_float values(123456,1234.12,12345.56); -- 整数部分超出 -- 创建定点数表 create table my_decimal( f1 float(10,2), d1 decimal(10,2) )charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_decimal values(12345678.90,12345678.90); -- 有效数据 insert into my_decimal values(1234.123456,1234.1234356); -- 小数部分超出:ok insert into my_decimal values(99999999.99,99999999.99); -- 没有问题 insert into my_decimal values(99999999.99,99999999.999); -- 进位超出范围 -- 创建时间日期表 create table my_date( d1 datetime, d2 date, d3 time, d4 timestamp, d5 year )charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_date values('2015-9-28 11:50:36','2015-9-28','11:50:54','2015-9-28 11:51:08',2015); -- 时间使用负数 insert into my_date values('2015-9-28 11:50:36','2015-9-28','-11:50:54','2015-9-28 11:51:08',2015); insert into my_date values('2015-9-28 11:50:36','2015-9-28','-211:50:54','2015-9-28 11:51:08',2015); insert into my_date values('2015-9-28 11:50:36','2015-9-28','-2 11:50:54','2015-9-28 11:51:08',2015); -- -2过去2天:48 -- year可以使用2位或者4位 insert into my_date values('2015-9-28 11:50:36','2015-9-28','11:50:54','2015-9-28 11:51:08',69); insert into my_date values('2015-9-28 11:50:36','2015-9-28','11:50:54','2015-9-28 11:51:08',70); -- timestamp: 修改记录 update my_date set d1 = '2015-9-28 11:55:45' where d5 = 2069; -- 创建枚举表 create table my_enum( gender enum('男','女','保密') )charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_enum values('男'),('保密'); -- 有效数据 -- 错误数据 insert into my_enum values('male'); -- 错误: 没有该元素 -- 将字段结果取出来进行+0运算 select gender + 0, gender from my_enum; -- 数值插入枚举元素 insert into my_enum values(1),(2); -- 创建集合表 create table my_set( hobby set('篮球','足球','乒乓球','羽毛球','排球','台球','网球','棒球') -- 足球 台球 网球 -- 集合中: 每一个元素都是对应一个二进制位,被选中为1,没有则为0: 最后反过来 -- 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 -- 反过来 01100010 = 98 )charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_set values('足球,台球,网球'); insert into my_set values(3); -- 查看集合数据 select hobby + 0, hobby from my_set; -- 98转成二进制 = 64 + 32 + 2 = 01100010 -- 颠倒元素出现的顺序 insert into my_set values('网球,台球,足球'); -- 求出varchar在utf8和GBK下的实际最大值 create table my_utf8( name varchar(21844) -- 21844 * 3 + 2 = 65532 + 2 = 65534 )charset utf8; create table my_gbk( name varchar(32766) -- 32766 * 2 + 2 = 65532 + 2 = 65534 )charset gbk; create table my_utf81( age tinyint, -- 1 name varchar(21844) -- 21844 * 3 + 2 = 65532 + 2 = 65534 )charset utf8; create table my_gbk1( age tinyint, -- 1 name varchar(32766) -- 32766 * 2 + 2 = 65532 + 2 = 65534 )charset gbk; -- 释放NULL create table my_utf82( age tinyint not null, -- 1 name varchar(21844) not null -- 21844 * 3 + 2 = 65532 + 2 = 65534 )charset utf8; create table my_gbk2( age tinyint not null, -- 1 name varchar(32766) not null -- 32766 * 2 + 2 = 65532 + 2 = 65534 )charset gbk; -- text占用十个字节长度 create table my_text( name varchar(21841) not null, -- 21841 * 3 + 2 = 65523 + 2 = 65525 content text not null -- 10 )charset utf8; -- 创建班级表 create table my_class( name varchar(20) not null, room varchar(20) null -- 代表允许为空: 不写默认就是允许为空 )charset utf8; -- 创建表 create table my_teacher( name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名', money decimal(10,2) not null comment '工资' )charset utf8; -- 默认值 create table my_default( name varchar(20) not null, age tinyint unsigned default 0, gender enum('男','女','保密') default '男' )charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_default (name) values('高强'); insert into my_default values('范立峰',18,default);
三

-- 增加主键 create table my_pri1( name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名', number char(10) primary key comment '学号: itcast + 0000, 不能重复' )charset utf8; -- 复合主键 create table my_pri2( number char(10) comment '学号: itcast + 0000', course char(10) comment '课程代码: 3901 + 0000', score tinyint unsigned default 60 comment '成绩', -- 增加主键限制: 学号和课程号应该是个对应的,具有唯一性 primary key(number,course) )charset utf8; -- 追加主键 create table my_pri3( course char(10) not null comment '课程编号: 3901 + 0000', name varchar(10) not null comment '课程名字' ); alter table my_pri3 modify course char(10) primary key comment '课程编号: 3901 + 0000'; alter table my_pri3 add primary key(course); -- 向pri1表插入数据 insert into my_pri1 values('古学星','itcast0001'),('蔡仁湾','itcast0002'); insert into my_pri2 values('itcast0001','39010001',90),('itcast0001','39010002',85),('itcast0002','39010001',92); -- 主键冲突(重复) insert into my_pri1 values('刘辉','itcast0002'); -- 不可以: 主键冲突 insert into my_pri2 values('itcast0001','39010001',100); -- 不可以:冲突 -- 删除主键 alter table my_pri3 drop primary key; -- 自增长 create table my_auto( id int primary key auto_increment comment '自动增长', name varchar(10) not null )charset utf8; -- 触发自增长 insert into my_auto(name) values('邓立军'); insert into my_auto values(null,'龚森'); insert into my_auto values(default,'张滔'); -- 指定数据 insert into my_auto values(6,'何思华'); insert into my_auto values(null,'陈少炼'); -- 修改表选项的值 alter table my_auto auto_increment = 4; -- 向下修改(小) alter table my_auto auto_increment = 10; -- 向上修改 -- 查看自增长变量 show variables like 'auto_increment%'; -- 修改自增长步长 set auto_increment_increment = 5; -- 插入记录: 使用自增长 insert into my_auto values(null,'刘阳'); insert into my_auto values(null,'邓贤师'); -- 删除自增长 alter table my_auto modify id int primary key; -- 错误: 主键理论是单独存在 alter table my_auto modify id int; -- 有主键的时候,千万不要再加主键 -- 唯一键 create table my_unique1( number char(10) unique comment '学号: 唯一,允许为空', name varchar(20) not null )charset utf8; create table my_unique2( number char(10) not null comment '学号', name varchar(20) not null, -- 增加唯一键 unique key(number) )charset utf8; create table my_unique3( id int primary key auto_increment, number char(10) not null, name varchar(20) not null)charset utf8; -- 追加唯一键 alter table my_unique3 add unique key(number); -- 插入数据 insert into my_unique1 values(null,'曾光'),('itcast0001','晁松'),(null,'李帅'); insert into my_unique1 values('itcast0001','周江'); -- 删除唯一键 alter table my_unique3 drop index number; -- 插入数据 insert into my_class values('PHP0810','B203'); insert into my_class values('PHP0810','B205'); insert into my_class values('PHP0710','B203'); -- 主键冲突: 更新 insert into my_class values('PHP0810','B205') -- 冲突处理 on duplicate key update -- 更新教室 room = 'B205'; -- 主键冲突:替换 replace into my_class values('PHP0710','A203'); replace into my_class values('PHP0910','B207'); -- 复制创建表 create table my_copy like my_gbk; -- 蠕虫复制 insert into my_copy select * from my_collate_bin; insert into my_copy select * from my_copy; -- 更新部分a变成c update my_copy set name = 'c' where name = 'a' limit 3; -- 删除数据:限制记录数为10 delete from my_copy where name = 'b' limit 10; -- 清空表: 重置自增长 truncate my_student; -- select选项 select * from my_copy; select all * from my_copy; -- 去重 select distinct * from my_copy; insert into my_student values(null,'itcast0001','张三','男'), (null,'itcast0002','李四','男'), (null,'itcast0003','王五','女'), (null,'itcast0004','赵六','男'), (null,'itcast0005','小明','男'); -- 字段别名 select id, number as 学号, name as 姓名, sex 性别 from my_student; -- 多表数据源 select * from my_student,my_class; -- 子查询 select * from (select * from my_student) as s; -- 增加age和height字段 alter table my_student add age tinyint unsigned; alter table my_student add height tinyint unsigned; -- 增加值: rand取得一个0到1之间的随机数, floor向下取整 update my_student set age=floor(rand() * 20 + 20),height = floor(rand()*20 + 170); -- 找学生id为1,3,5的学生 select * from my_student where id = 1 || id = 3 || id = 5; -- 逻辑判断 select * from my_student where id in(1,3,5); -- 落在集合中 -- 找身高在180到190之间的学生 select * from my_student where height >= 180 and height <= 190; select * from my_student where height between 180 and 190; select * from my_student where height between 190 and 180; -- 根据性别分组 select * from my_student group by sex; -- 分组统计: 身高高矮,年龄平均和总年龄 select sex,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex; select sex,count(*),count(age),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex; select sex,count(*),count(age),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex desc; -- 多字段分组: 先班级,后男女 select c_id,sex,count(*),group_concat(name) from my_student group by c_id,sex; -- 多字段排序 -- 统计 select c_id,count(*) from my_student group by c_id; -- 回溯统计 select c_id,count(*) from my_student group by c_id with rollup; -- 多字段分组回溯统计 select c_id,sex,count(*),group_concat(name) from my_student group by c_id,sex; -- 多字段排序 select c_id,sex,count(*),group_concat(name) from my_student group by c_id,sex with rollup; -- 求出所有班级人数大于等于2的学生人数 select c_id,count(*) from my_student group by c_id having count(*) >= 2; select c_id,count(*) from my_student where count(*) >= 2 group by c_id ; select c_id,count(*) as total from my_student group by c_id having total >= 2; select c_id,count(*) as total from my_student where total >= 2 group by c_id ; -- 排序 select * from my_student group by c_id; select * from my_student order by c_id; -- 多字段排序: 先班级排序,后性别排序 select * from my_student order by c_id, sex desc; -- 查询学生: 前两个 select * from my_student limit 2; -- 查询学生: 前两个 select * from my_student limit 0,2; -- 记录数是从0开始编号 select * from my_student limit 2,2; select * from my_student limit 4,2;
四

-- 交叉连接 select * from my_student cross join my_class; -- my_student cross join my_class是数据源 -- 内连接 select * from my_student inner join my_class on my_student.c_id = my_class.id; select * from my_student inner join my_class on c_id = my_class.id; select * from my_student inner join my_class on c_id = id; -- 两张表都有id字段 -- 字段和表别名 select s.*,c.name as c_name,c.room from -- 字段别名 my_student as s inner join my_class as c -- 表别名 on s.c_id = c.id; -- where代替on select s.*,c.name as c_name,c.room from -- 字段别名 my_student as s inner join my_class as c -- 表别名 where s.c_id = c.id; -- 左连接 select s.*,c.name as c_name,c.room from my_student as s left join my_class as c -- 左表为主表: 最终记录数至少不少于左表已有的记录数 on s.c_id = c.id; -- 右连接 select s.*,c.name as c_name,c.room from my_student as s right join my_class as c -- 右表为主表: 最终记录数至少不少于右表已有的记录数 on s.c_id = c.id; select s.*,c.name as c_name,c.room from my_class as c right join my_student as s -- 左表为主表: 最终记录数至少不少于左表已有的记录数 on s.c_id = c.id; -- 自然内连接 select * from my_student natural join my_class; -- 自然左外连接 select * from my_student natural left join my_class; -- 外连接模拟自然外连接: using select * from my_student left join my_class using(id);
五

-- 创建外键 create table my_foreign1( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null comment '学生姓名', c_id int comment '班级id', -- 普通字段 -- 增加外键 foreign key(c_id) references my_class(id) )charset utf8; -- 创建表 create table my_foreign2( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null comment '学生姓名', c_id int comment '班级id' -- 普通字段 )charset utf8; -- 增加外键 alter table my_foreign2 add -- 指定外键名 constraint student_class_1 -- 指定外键字段 foreign key(c_id) -- 引用父表主键 references my_class(id); -- 删除外键 alter table my_foreign1 drop foreign key my_foreign1_ibfk_1; -- 插入数据:外键字段在父表中不存在 insert into my_foreign2 values(null,'张自忠',4); -- 没有4班级 insert into my_foreign2 values(null,'项羽',1); insert into my_foreign2 values(null,'刘邦',2); insert into my_foreign2 values(null,'韩信',2); -- 更新父表记录 update my_class set id = 4 where id = 1; -- 失败: id=1记录已经被学生引用 update my_class set id = 4 where id = 3; -- 可以: 没有引用 -- 插入数据 insert into my_foreign1 values(null,'马超',3); -- 增加外键 alter table my_foreign1 add foreign key(c_id) references my_class(id); -- 创建外键: 指定模式: 删除置空,更新级联 create table my_foreign3( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, c_id int, -- 增加外键 foreign key(c_id) -- 引用表 references my_class(id) -- 指定删除模式 on delete set null -- 指定更新默认 on update cascade)charset utf8; -- 插入数据 insert into my_foreign3 values(null,'刘备',1), (null,'曹操',1), (null,'孙权',1), (null,'诸葛亮',2), (null,'周瑜',2); -- 更新父表主键 update my_class set id = 3 where id = 1; -- 删除父表主键 delete from my_class where id = 2; -- 联合查询 select * from my_class union -- 默认去重 select * from my_class; select * from my_class union all -- 不去重 select * from my_class; select id,c_name,room from my_class union all -- 不去重 select name,number,id from my_student; -- 需求: 男生升序,女生降序(年龄) (select * from my_student where sex = '男' order by age asc limit 9999999) union (select * from my_student where sex = '女' order by age desc limit 9999999); -- 标量子查询 select * from my_student where c_id = (select id from my_class where c_name = 'PHP0710'); select * from my_student having c_id = (select id from my_class where c_name = 'PHP0710'); -- 列子查询 select * from my_student where c_id in(select id from my_class); -- any,some,all select * from my_student where c_id =any(select id from my_class); select * from my_student where c_id =some(select id from my_class); select * from my_student where c_id =all(select id from my_class); select * from my_student where c_id !=any(select id from my_class); -- 所有结果(null除外) select * from my_student where c_id !=some(select id from my_class); -- 所有结果(null除外) select * from my_student where c_id !=all(select id from my_class); -- 2(null除外) select * from my_student where age = (select max(age) from my_student) and height = (select max(height) from my_student); -- 行子查询 select * from my_student where -- (age,height)称之为行元素 (age,height) = (select max(age),max(height) from my_student); -- 表子查询 select * from my_student group by c_id order by height desc; select * from (select * from my_student order by height desc) as student group by c_id; -- exists子查询 select * from my_student where exists(select * from my_class where id = 1); select * from my_student where exists(select * from my_class where id = 2); -- 视图: 单表+多表 create view my_v1 as select * from my_student; create view my_v2 as select * from my_class; create view my_v3 as select * from my_student as s left join my_class c on s.c_id = c.id; -- id重复 -- 多表视图 create view my_v3 as select s.*,c.c_name,c.room from my_student as s left join my_class c on s.c_id = c.id; -- 查看视图创建语句 show create view my_v3G -- 视图使用 select * from my_v1; select * from my_v2; select * from my_v3; -- 修改视图 alter view my_v1 as select id,name,age,sex,height,c_id from my_student; -- 删除视图 drop view my_v4; -- 多表视图插入数据 insert into my_v3 values(null,'itcast0008','张三丰','男',150,180,1,'PHP0326','D306'); -- 单表视图插入数据: 视图不包含所有不允许为空字段(学号) insert into my_v1 values(null,'张无忌',68,'男',174,2); -- 单表视图插入数据 insert into my_v2 values(2,'PHP0326','D306'); -- 多表视图删除数据 delete from my_v3 where id = 1; -- 单表视图删除数据 delete from my_v2 where id = 4; -- 多表视图更新数据 update my_v3 set c_id = 3 where id = 5; -- 视图: age字段限制更新 create view my_v4 as select * from my_student where age > 30 with check option; -- 表示视图的数据来源都是年龄大于30岁:where age > 30决定 -- with check option: 决定通过视图更新的时候,不能将已经得到的数据age > 30的改成小于30的 -- 将视图可以查到的数据改成小于30 update my_v4 set age = 29 where id = 1; -- 可以修改数据让视图可以查到: 可以改,但是无效果 update my_v4 set age = 32 where id = 6; -- 获取所有班级中最高的一个学生 create view my_v5 as select * from my_student order by height desc; select * from my_v5 group by c_id; -- 指定算法为临时表 create algorithm=temptable view my_v6 as select * from my_student order by height desc; select * from my_v6 group by c_id; -- 创建myisam表 create table my_myisam( id int)charset utf8 engine = myisam; -- 单表数据备份 select * into outfile 'D:/server/temp/student.txt' from my_student; select * into outfile 'D:/server/temp/class.txt' from my_class; -- 指定备份处理方式 select * into outfile 'D:/server/temp/class1.txt' -- 字段处理 fields enclosed by '"' -- 数据使用双引号包裹 terminated by '|' -- 使用竖线分隔字段数据 -- 行处理 lines starting by 'START:' from my_class; -- 还原数据 load data infile 'D:/server/temp/class1.txt' into table my_class -- 字段处理 fields enclosed by '"' -- 数据使用双引号包裹 terminated by '|' -- 使用竖线分隔字段数据 -- 行处理 lines starting by 'START:'; -- SQL 备份 mysqldump -uroot -proot mydatabase my_student > D:/server/temp/student.sql -- 整库备份 mysqldump -uroot -proot mydatabase > D:/server/temp/mydatabase.sql -- 还原数据:mysql客户端还原 mysql -uroot -proot mydatabase < D:/server/temp/student.sql -- SQL 指令还原SQL备份 source D:/server/temp/student.sql;
联合查询
联合查询: 将多次查询(多条select语句), 在记录上进行拼接(字段不会增加)
基本语法
多条select语句构成: 每一条select语句获取的字段数必须严格一致(但是字段类型无关)
Select 语句1
Union [union选项]
Select语句2...
Union选项: 与select选项一样有两个
All: 保留所有(不管重复)
Distinct: 去重(整个重复): 默认的
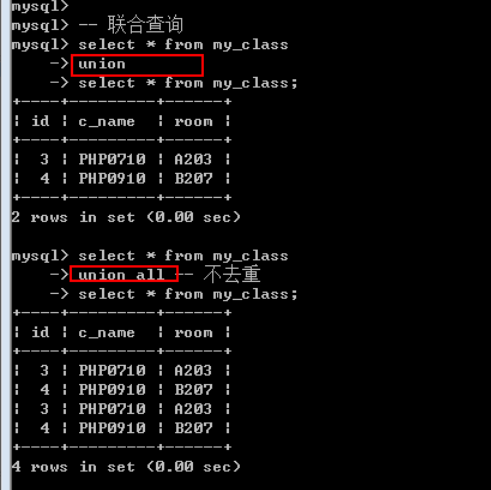
联合查询只要求字段一样, 跟数据类型无关
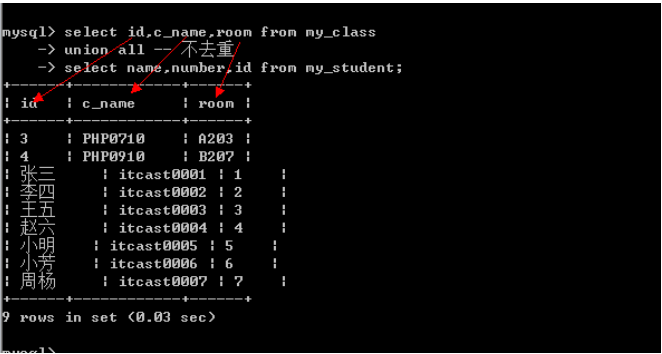
意义
联合查询的意义分为两种:
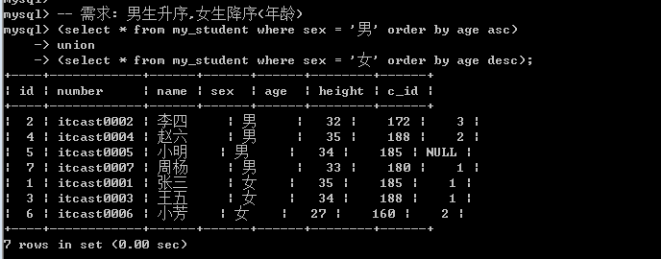
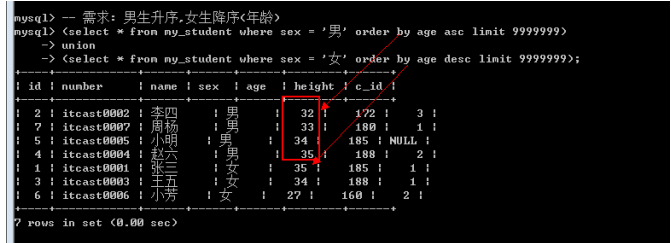
1.查询同一张表,但是需求不同: 如查询学生信息, 男生身高升序, 女生身高降序.
2.多表查询: 多张表的结构是完全一样的,保存的数据(结构)也是一样的.
Order by使用
在联合查询中: order by不能直接使用,需要对查询语句使用括号才行
若要orderby生效: 必须搭配limit: limit使用限定的最大数即可.
子查询
子查询: sub query, 查询是在某个查询结果之上进行的.(一条select语句内部包含了另外一条select语句).
子查询分类
子查询有两种分类方式: 按位置分类; 按结果分类
按位置分类: 子查询(select语句)在外部查询(select语句)中出现的位置
From子查询: 子查询跟在from之后
Where子查询: 子查询出现where条件中
Exists子查询: 子查询出现在exists里面
按结果分类: 根据子查询得到的数据进行分类(理论上讲任何一个查询得到的结果都可以理解为二维表)
标量子查询: 子查询得到的结果是一行一列
列子查询: 子查询得到的结果是一列多行
行子查询: 子查询得到的结果是多列一行(多行多列)
上面几个出现的位置都是在where之后
表子查询: 子查询得到的结果是多行多列(出现的位置是在from之后)
标量子查询
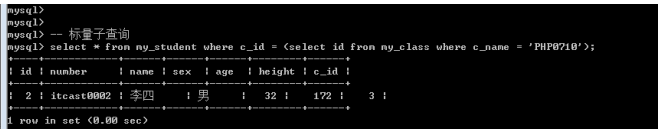
需求: 知道班级名字为PHP0710,想获取该班的所有学生.
1. 确定数据源: 获取所有的学生
Select * from my_student where c_id = ?;
2. 获取班级ID: 可以通过班级名字确定
Select id from my_class where c_name = ‘PHP0710’;-- id一定只有一个值(一行一列)
标量子查询实现
列子查询
需求: 查询所有在读班级的学生(班级表中存在的班级)
1. 确定数据源: 学生
Select * from my_student where c_id in (?);
2. 确定有效班级的id: 所有班级id
Select id from my_class;
列子查询

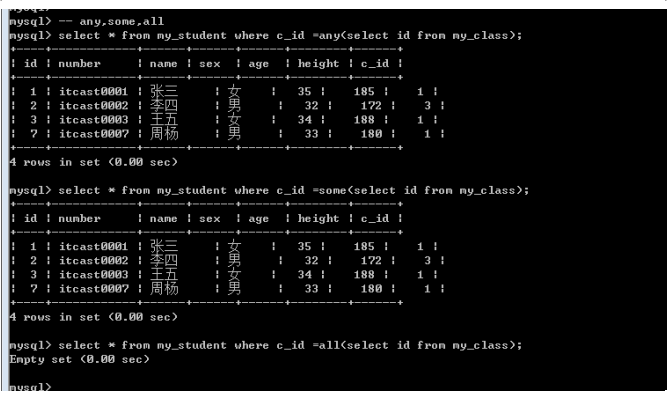
列子查询返回的结果会比较: 一列多行, 需要使用in作为条件匹配: 其实在mysql中有还有几个类似的条件: all, some, any
=Any ==== in; -- 其中一个即可
Any ====== some;-- any跟some是一样
=all ==== 为全部
肯定结果
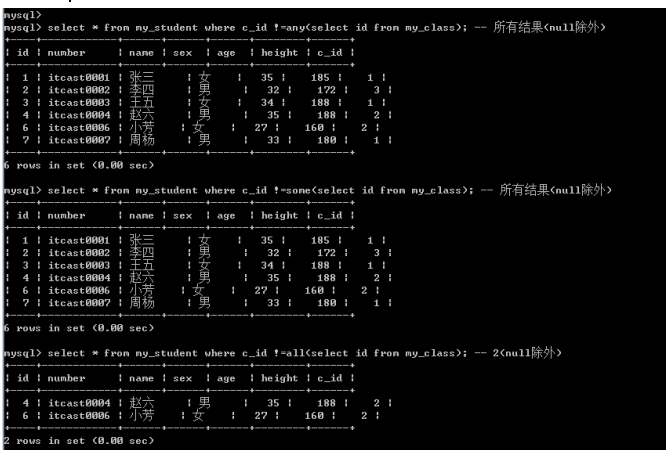
否定结果
行子查询
行子查询: 返回的结果可以是多行多列(一行多列)
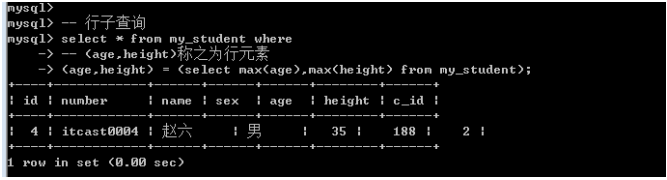
需求: 要求查询整个学生中,年龄最大且身高是最高的学生.
1. 确定数据源
Select * from my_student where age = ? And height = ?;
2. 确定最大的年龄和最高的身高;
Select max(age),max(height) from my_student;
行子查询: 需要构造行元素: 行元素由多个字段构成
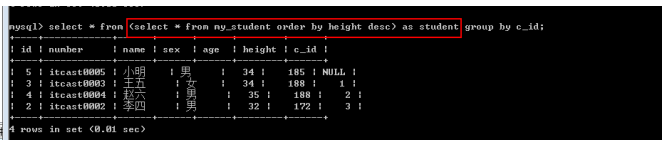
表子查询
表子查询: 子查询返回的结果是多行多列的二维表: 子查询返回的结果是当做二维表来使用
需求: 找出每一个班最高的一个学生.
1. 确定数据源: 先将学生按照身高进行降序排序
Select * from my_student order by height desc;
2. 从每个班选出第一个学生
Select * from my_student group by c_id; -- 每个班选出第一个学生
表子查询: from子查询: 得到的结果作为from的数据源
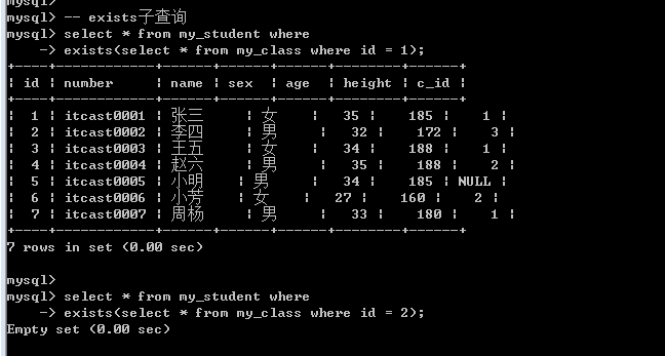
Exists子查询
Exists: 是否存在的意思, exists子查询就是用来判断某些条件是否满足(跨表), exists是接在where之后: exists返回的结果只有0和1.
需求: 查询所有的学生: 前提条件是班级存在
1. 确定数据源
Select * from my_student where ?;
2. 确定条件是否满足
Exists(Select * from my_class); -- 是否成立
Exists子查询
增删改查必知必会

select name,address,age from user order by address,age ; --按多个列排序 select name,address,age from user order by 2,3 ; --按位置排序排序 select name,address,age from user order by address desc,age ; --先按价格降序,在按年龄升序 where 子句操作符 = <> != < <= !< > >= !> BETWEEN IS NULL 字符串比较加上''号 BETWEEN AND 圆括号()> AND >OR 圆括号()优先级最高,sql会优先执行AND,圆括号()括起来比AND select name,address,age from user where (address = '广州' or address = '北京') and age >20; IN IN完成了OR 相同的功能,最大优点可以包含其他select语句 NOT NOT从不单独使用,否定其后所跟的任何条件,NOT关键字可以用在要过滤列前,而不仅是在其后 select name,address,age from user where NOT address = '广州' 通配符like, _, ([]) like不会匹配产品名称为Null的行 select name,address,age from user where address like'%海';--以海结尾 select name,address,age from user where address like'广%';--以广开头 select name,address,age from user where address like'%徽合%'; --中间包含的 select name,address,age from user where address like'广%州%';--保证数据中间存在空格也可以匹配到 _一个_只匹配一个字符 select name,address,age from user WHERE name like '张__' select name,address,age from user WHERE name like '张_' 拼接(concatenate) 适用MySQL SELECT CONCAT(name,age) FROM `user` SELECT CONCAT(name,'(',age,')') FROM user 适用Oracle SELECT name + '(',address,')'FROM user SELECT name || '(',address,')'FROM user RTRIM函数:去掉值右边的所有空格 SELECT RTRIM(name) + '('+RTRIM(address)+')'FROM user SELECT RTRIM(name) || '('|| RTRIM(address) ||')'FROM user 算术计算 (+,-,*,/),可用圆括号区分优先顺序 SELECT age*dept FROM user 聚集函数 AVG() 返回某列平均值 COUNT() 返回某列的行数 MAX() 返回某列的最大值 MIN() 返回某列最小值 SUM() 返回某列值之和 AVG()只用于单个列,为了获得多个列的平均值,必须使用多个AVG() select AVG(age) from employee select AVG(age) from employee WHERE post = 'teacher' select AVG(age),AVG(salary) from employee WHERE post = 'teacher' count() 1.count(*)对表中行的数目进行计数,不管表中包含是空值(NULL)还是非空值 2.count(列名) 对特定列中具有的值进行计数,忽略NUll值 select COUNT(*) from employee select COUNT(age) from employee MAX和MIN 最大值和最小值 要求指定列名,忽略为NUll的 select MAX(age) from employee select MIN(age) from employee SUM()返回指定列值的和(总计) select SUM(age) from user select SUM(age*dept) from user 聚集不同值 ALL(默认) 和 DISTINCT(去重) select SUM(DISTINCT age) from employee --求和只参考不同年龄 select AVG(DISTINCT age) from employee --平均值只参考不同年龄 distinct不能用于count(*),只能用于count(),distinct必须使用列名 组合聚集函数 select COUNT(*)AS num, AVG(DISTINCT age)AS a,MAX(age)AS b,MIN(age)AS C from employee 数据分组(一般都配合聚集函数一起使用) select COUNT(*)AS num,age from employee group by age ; --根据年龄分组,统计数量 select COUNT(*)AS num,age AS A ,sex from employee group by A,sex --先按年龄分组,在按性别分组,统计数量 select COUNT(*)AS num,age AS A ,sex from employee group by 2,3 --通过相对位置分组 GROUP BY 重要规定 1. GROUP BY 子句可用包含任意数目的列,因而可以对分组进行嵌套,更细致的进行分组 2. 如果GROUP BY子句中嵌套了分组,数据将在最后指定的分组上进行汇总.换句话说,在建立分组时, 指定的所有列都一起计算(所有不能从个别的列取回数据) 3. GROUP BY子句中列出的每一列都必须是检索列或有效表达式(但不能是聚集函数). 如果在SELECT中使用表达式,必须在GROUP BY子句中指定相同的表达式.不能使用别名 4.大多数SQL实现不允许GROUP BY 列带有长度可变的数据类型(如文本或备注型字段) 5.除聚集计算语句外,SELECT语句中的每一列都必须在GROUP BY 子句中给出 6.如果分组列中包含NUll值得行,则NUll将作为一个分组返回.如果列中有多行Null值,它们将分为一组 7.GROUP BY 必须在 where 之后 ,order by 之前 HAVING(过滤分组) HAVING支持所有WHERE得操作符,where是在分组前进行过滤,having是在分组后进行过滤,where排除的行不包括在分组中 HAVING和where非常类似,如果不指定GROUP BY,则大多数DBMS会同等对待它们,不过我们要区分这一点,使用having时应该 结合GROUP BY子句 select COUNT(*),age from employee group by age HAVING COUNT(*)>=2 子查询 作为子查询的select语句只能时单个列,企图检索多个列将返回错误 select *FROM employee1 WHERE dep_id in(SELECT id FROM department WHERE id = 200) 作为计算字段使用子查询 select cust_name ,cust_status,(select count(*) from orders where Orders.cust_id = Customers.cust_id) AS orders from Customers; 联表 自然联结 select prod_name,vend_name,quantity from Orders,Products,Vendors where Products.vend_id = Vendors.vend_id AND Orders.prod_id = Products.prod_id AND order_num = 20211103 创建高级联结 1.使用表别名 2.外联结 关键字 OUTER JOIN ,在使用OUTER JOIN语法时,必须使用right 或 left left outer join ; right outer join 组合查询 - 创建组合查询使用UNION操作符 UNION基本规则 1.UNION 必须由两条或两条以上的SELECT语句组成,语句之间用关键字UNION(如果组合了4条select语句,将使用3个UNION关键字) 2.UNION中每个查询必须包含相同的列,表达式或聚集函数(不过,各个列不需要以相同的次序列出) 3.列数据类型必须兼容,单必须是DBMS可以隐含的转换类型(例如:不同的数值类型或不同的日期类型) 4.UNION 默认重复行会被字段取消,如果想返回所有匹配的行,课使用UNION ALL 5.UNION组合查询时,只能使用一条order by 语句而且必须位于最后一条select 语句之后 select name,contact,email from Customers where state in ('IL','IN','IM') UNION select name,contact,email from Customers where name = '张三'; 插入数据 insert into test values(1,'22') insert into test(id,name) values(1,'22') 插入检索出的数据(insert select检索出多少行就插入多少行) insert into test(id,name) select id,name from test2 ; update(更新)和delete(删除) update 表名 set 列名=xxx where 条件 update (不要省略where),省略了就会更新表中所有的行 更新多个列 update 表名 set name = 'wind',age = 18 where id = 1 update语句使用子查询 UPDATE employee1 set employee1.name = (SELECT name FROM department WHERE id = 200) WHERE id = 1 UPDATE employee1 set employee1.name = '哈哈124' WHERE dep_id = (SELECT id FROM department WHERE id = 200) delete(删除数据) delete从表中删除的是行不是列,不要省略where,省略了就会更新表中所有的行 1 .从表中删除特定的行 DELETE FROM employee1 WHERE id =1 2 .从表中删除所有的行 DELETE FROM employee1 --(!!!非常危险!!!) delete语句使用子查询 DELETE FROM employee1 WHERE dep_id = (SELECT name FROM department WHERE id = 200)
select name,address,age from user order by address,age ; --按多个列排序
select name,address,age from user order by 2,3 ; --按位置排序排序
select name,address,age from user order by address desc,age ; --先按价格降序,在按年龄升序
where 子句操作符
= <> != < <= !< > >= !> BETWEEN IS NULL
字符串比较加上''号
BETWEEN AND
圆括号()> AND >OR
圆括号()优先级最高,sql会优先执行AND,圆括号()括起来比AND
select name,address,age from user where (address = '广州' or address = '北京') and age >20;
IN
IN完成了OR 相同的功能,最大优点可以包含其他select语句
NOT
NOT从不单独使用,否定其后所跟的任何条件,NOT关键字可以用在要过滤列前,而不仅是在其后
select name,address,age from user where NOT address = '广州'
通配符like, _, ([])
like不会匹配产品名称为Null的行
select name,address,age from user where address like'%海';--以海结尾
select name,address,age from user where address like'广%';--以广开头
select name,address,age from user where address like'%徽合%'; --中间包含的
select name,address,age from user where address like'广%州%';--保证数据中间存在空格也可以匹配到
_一个_只匹配一个字符
select name,address,age from user WHERE name like '张__'
select name,address,age from user WHERE name like '张_'
拼接(concatenate)
适用MySQL
SELECT CONCAT(name,age) FROM `user`
SELECT CONCAT(name,'(',age,')') FROM user
适用Oracle
SELECT name + '(',address,')'FROM user
SELECT name || '(',address,')'FROM user
RTRIM函数:去掉值右边的所有空格
SELECT RTRIM(name) + '('+RTRIM(address)+')'FROM user
SELECT RTRIM(name) || '('|| RTRIM(address) ||')'FROM user
算术计算 (+,-,*,/),可用圆括号区分优先顺序
SELECT age*dept FROM user
聚集函数
AVG() 返回某列平均值
COUNT() 返回某列的行数
MAX() 返回某列的最大值
MIN() 返回某列最小值
SUM() 返回某列值之和
AVG()只用于单个列,为了获得多个列的平均值,必须使用多个AVG()
select AVG(age) from employee
select AVG(age) from employee WHERE post = 'teacher'
select AVG(age),AVG(salary) from employee WHERE post = 'teacher'
count()
1.count(*)对表中行的数目进行计数,不管表中包含是空值(NULL)还是非空值
2.count(列名) 对特定列中具有的值进行计数,忽略NUll值
select COUNT(*) from employee
select COUNT(age) from employee
MAX和MIN 最大值和最小值
要求指定列名,忽略为NUll的
select MAX(age) from employee
select MIN(age) from employee
SUM()返回指定列值的和(总计)
select SUM(age) from user
select SUM(age*dept) from user
聚集不同值
ALL(默认) 和 DISTINCT(去重)
select SUM(DISTINCT age) from employee --求和只参考不同年龄
select AVG(DISTINCT age) from employee --平均值只参考不同年龄
distinct不能用于count(*),只能用于count(),distinct必须使用列名
组合聚集函数
select COUNT(*)AS num, AVG(DISTINCT age)AS a,MAX(age)AS b,MIN(age)AS C from employee
数据分组(一般都配合聚集函数一起使用)
select COUNT(*)AS num,age from employee group by age ; --根据年龄分组,统计数量
select COUNT(*)AS num,age AS A ,sex from employee group by A,sex --先按年龄分组,在按性别分组,统计数量
select COUNT(*)AS num,age AS A ,sex from employee group by 2,3 --通过相对位置分组
GROUP BY 重要规定
1. GROUP BY 子句可用包含任意数目的列,因而可以对分组进行嵌套,更细致的进行分组
2. 如果GROUP BY子句中嵌套了分组,数据将在最后指定的分组上进行汇总.换句话说,在建立分组时,
指定的所有列都一起计算(所有不能从个别的列取回数据)
3. GROUP BY子句中列出的每一列都必须是检索列或有效表达式(但不能是聚集函数).
如果在SELECT中使用表达式,必须在GROUP BY子句中指定相同的表达式.不能使用别名
4.大多数SQL实现不允许GROUP BY 列带有长度可变的数据类型(如文本或备注型字段)
5.除聚集计算语句外,SELECT语句中的每一列都必须在GROUP BY 子句中给出
6.如果分组列中包含NUll值得行,则NUll将作为一个分组返回.如果列中有多行Null值,它们将分为一组
7.GROUP BY 必须在 where 之后 ,order by 之前
HAVING(过滤分组)
HAVING支持所有WHERE得操作符,where是在分组前进行过滤,having是在分组后进行过滤,where排除的行不包括在分组中
HAVING和where非常类似,如果不指定GROUP BY,则大多数DBMS会同等对待它们,不过我们要区分这一点,使用having时应该
结合GROUP BY子句
select COUNT(*),age from employee group by age HAVING COUNT(*)>=2
子查询
作为子查询的select语句只能时单个列,企图检索多个列将返回错误
select *FROM employee1 WHERE dep_id in(SELECT id FROM department WHERE id = 200)
作为计算字段使用子查询
select cust_name ,cust_status,(select count(*) from orders where Orders.cust_id = Customers.cust_id) AS orders from Customers;
联表
自然联结
select prod_name,vend_name,quantity from Orders,Products,Vendors where Products.vend_id = Vendors.vend_id AND
Orders.prod_id = Products.prod_id AND order_num = 20211103
创建高级联结
1.使用表别名
2.外联结
关键字 OUTER JOIN ,在使用OUTER JOIN语法时,必须使用right 或 left
left outer join ; right outer join
组合查询 - 创建组合查询使用UNION操作符
UNION基本规则
1.UNION 必须由两条或两条以上的SELECT语句组成,语句之间用关键字UNION(如果组合了4条select语句,将使用3个UNION关键字)
2.UNION中每个查询必须包含相同的列,表达式或聚集函数(不过,各个列不需要以相同的次序列出)
3.列数据类型必须兼容,单必须是DBMS可以隐含的转换类型(例如:不同的数值类型或不同的日期类型)
4.UNION 默认重复行会被字段取消,如果想返回所有匹配的行,课使用UNION ALL
5.UNION组合查询时,只能使用一条order by 语句而且必须位于最后一条select 语句之后
select name,contact,email from Customers where state in ('IL','IN','IM')
UNION
select name,contact,email from Customers where name = '张三';
插入数据
insert into test values(1,'22')
insert into test(id,name) values(1,'22')
插入检索出的数据(insert select检索出多少行就插入多少行)
insert into test(id,name) select id,name from test2 ;
update(更新)和delete(删除)
update 表名 set 列名=xxx where 条件
update (不要省略where),省略了就会更新表中所有的行
更新多个列
update 表名 set name = 'wind',age = 18 where id = 1
update语句使用子查询
UPDATE employee1 set employee1.name = (SELECT name FROM department WHERE id = 200) WHERE id = 1
UPDATE employee1 set employee1.name = '哈哈124' WHERE dep_id = (SELECT id FROM department WHERE id = 200)
delete(删除数据)
delete从表中删除的是行不是列,不要省略where,省略了就会更新表中所有的行
1 .从表中删除特定的行
DELETE FROM employee1 WHERE id =1
2 .从表中删除所有的行
DELETE FROM employee1 --(!!!非常危险!!!)
delete语句使用子查询
DELETE FROM employee1 WHERE dep_id = (SELECT name FROM department WHERE id = 200)
必知必会
