time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Recently, Masha was presented with a chessboard with a height of n n and a width of m m .
The rows on the chessboard are numbered from 1 1 to n n from bottom to top. The columns are numbered from 1 1 to m m from left to right. Therefore, each cell can be specified with the coordinates (x,y) (x,y) , where x x is the column number, and y y is the row number (do not mix up).
Let us call a rectangle with coordinates (a,b,c,d) (a,b,c,d) a rectangle lower left point of which has coordinates (a,b) (a,b) , and the upper right one — (c,d) (c,d) .
The chessboard is painted black and white as follows:
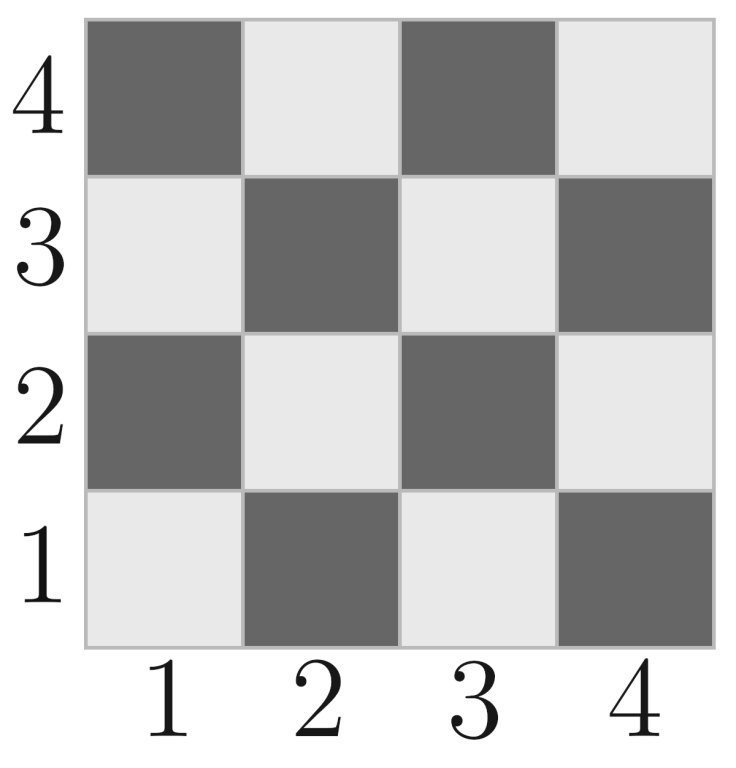
An example of a chessboard.
Masha was very happy with the gift and, therefore, invited her friends Maxim and Denis to show off. The guys decided to make her a treat — they bought her a can of white and a can of black paint, so that if the old board deteriorates, it can be repainted. When they came to Masha, something unpleasant happened: first, Maxim went over the threshold and spilled white paint on the rectangle (x 1 ,y 1 ,x 2 ,y 2 ) (x1,y1,x2,y2) . Then after him Denis spilled black paint on the rectangle (x 3 ,y 3 ,x 4 ,y 4 ) (x3,y3,x4,y4) .
To spill paint of color color color onto a certain rectangle means that all the cells that belong to the given rectangle become color color . The cell dyeing is superimposed on each other (if at first some cell is spilled with white paint and then with black one, then its color will be black).
Masha was shocked! She drove away from the guests and decided to find out how spoiled the gift was. For this, she needs to know the number of cells of white and black color. Help her find these numbers!
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t (1≤t≤10 3 1≤t≤103 ) — the number of test cases.
Each of them is described in the following format:
The first line contains two integers n n and m m (1≤n,m≤10 9 1≤n,m≤109 ) — the size of the board.
The second line contains four integers x 1 x1 , y 1 y1 , x 2 x2 , y 2 y2 (1≤x 1 ≤x 2 ≤m,1≤y 1 ≤y 2 ≤n 1≤x1≤x2≤m,1≤y1≤y2≤n ) — the coordinates of the rectangle, the white paint was spilled on.
The third line contains four integers x 3 x3 , y 3 y3 , x 4 x4 , y 4 y4 (1≤x 3 ≤x 4 ≤m,1≤y 3 ≤y 4 ≤n 1≤x3≤x4≤m,1≤y3≤y4≤n ) — the coordinates of the rectangle, the black paint was spilled on.
Output
Output t t lines, each of which contains two numbers — the number of white and black cells after spilling paint, respectively.
Example
Input
Copy
5
2 2
1 1 2 2
1 1 2 2
3 4
2 2 3 2
3 1 4 3
1 5
1 1 5 1
3 1 5 1
4 4
1 1 4 2
1 3 4 4
3 4
1 2 4 2
2 1 3 3
Output
Copy
0 4
3 9
2 3
8 8
4 8
Note
Explanation for examples:
The first picture of each illustration shows how the field looked before the dyes were spilled. The second picture of each illustration shows how the field looked after Maxim spoiled white dye (the rectangle on which the dye was spilled is highlighted with red). The third picture in each illustration shows how the field looked after Denis spoiled black dye (the rectangle on which the dye was spilled is highlighted with red).
In the first test, the paint on the field changed as follows:
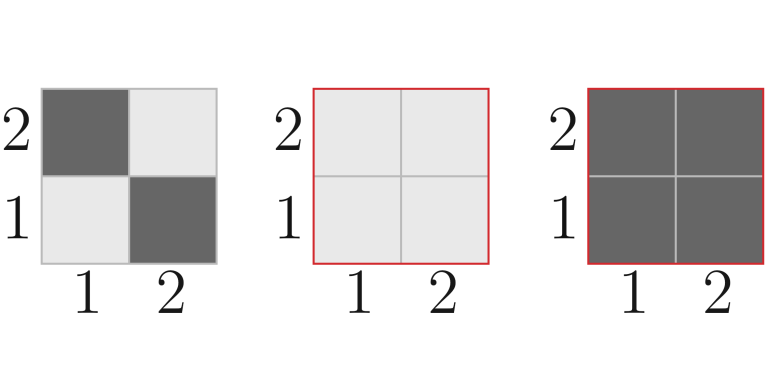
In the second test, the paint on the field changed as follows:
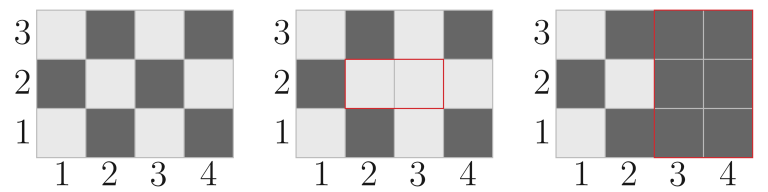
In the third test, the paint on the field changed as follows:
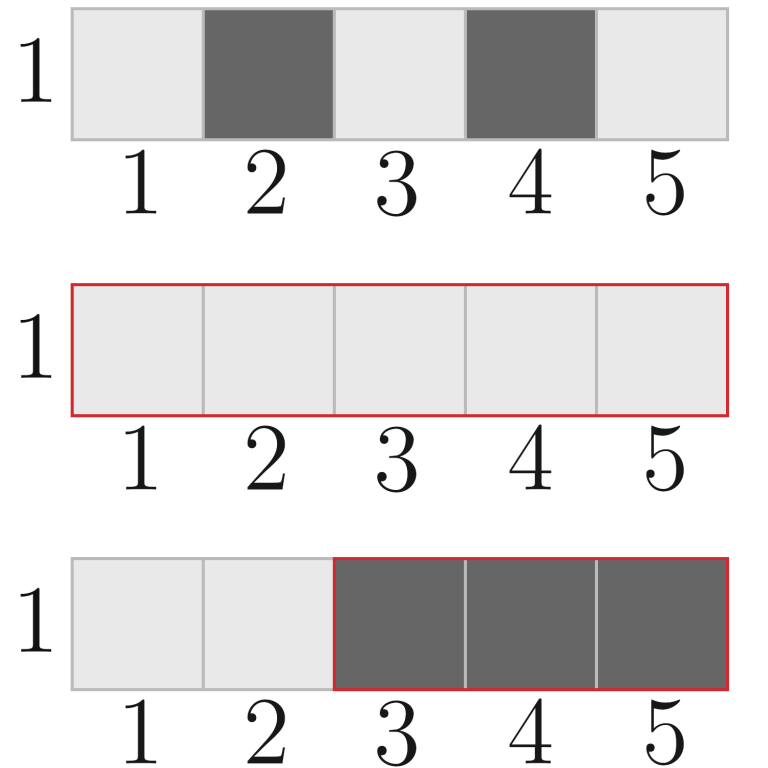
In the fourth test, the paint on the field changed as follows:
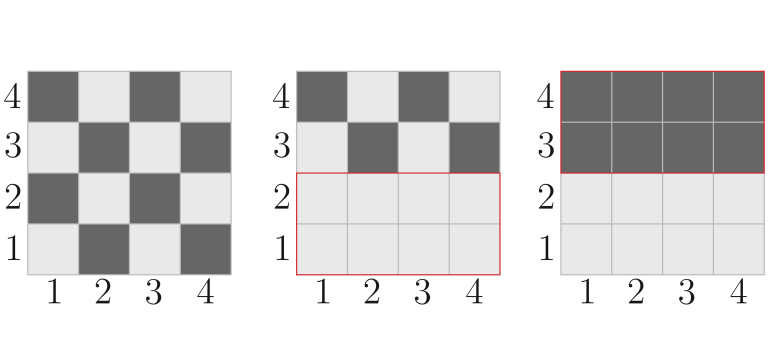
In the fifth test, the paint on the field changed as follows:
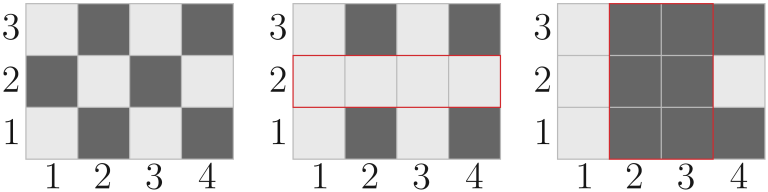
题解: 这个题的关键是判断有没有交集,怎么处理这些“块”(词穷),具体看代码注释叭。qwq
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
struct rect{
ll x1,y1,x2,y2;
rect(){}
rect(ll x1,ll y1,ll x2,ll y2){
this->x1=x1;
this->y1=y1;
this->x2=x2;
this->y2=y2;
}
void init(){
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
}
ll sz(){
return (x2-x1+1)*(y2-y1+1);
}
};
rect interse(rect a,rect b){//理论求交集
rect c(max(a.x1,b.x1),max(a.y1,b.y1),min(a.x2,b.x2),min(a.y2,b.y2)); //一个往右贴,一个往左贴。得到的两个坐标就是这个交集的对角坐标
return c;
}
ll get_black(rect a){ //特殊的棋盘
ll ans=a.sz()/2;
if((a.x1+a.y1)%2==1)
ans=a.sz()-ans;
return ans;
}
ll get_white(rect a){
return (a.sz()-get_black(a));
}
int main(){
ll t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
ll n,m; cin>>n>>m;
rect a;
a=rect(1,1,n,m);//总的n*m
rect black,white;
white.init();//要变为白色的范围
black.init();//要变为黑色的范围
//ans 黑
ll ans=get_black(a);//黑的个数
ans-=get_black(white);//第一步染色为白色
ans+=get_white(black);//第二步染色为黑色
rect both=interse(black,white);//交集
if(both.x1<=both.x2 && both.y1<=both.y2){//判断交集是否存在
ans+=get_black(both);
}
cout<<a.sz()-ans<<" "<<ans<<endl;// 白 黑
}
return 0;
}