20162317袁逸灏 第四周实验报告:实验一 线性结构
实验内容
- 用Junit单元测试来测试ArrayList和LinkedList
- 用Java的ArrayList和LinkedList实现有序线性表的合并
- 用数组实现线性表List,用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的ArrayList进行测试
- 用链表实现线性表List,用JUnit或自己编写驱动类对自己实现的LinkedList进行测试
- 分析ArrayList和LinkedList的源代码
实验要求
- 单元测试要尽量覆盖正常情况,异常情况,边界情况
实验过程
要实现TDD,类就要继承TestCase,并通过assertEquals方法来测试方法是否行得通。
- 实验一:用TDD来测试ArrayList和LinkedList
(我选择插入的参数)

这个实验主要测试ArrayList以及LinkList中的add,remove,clear方法。
add方法有两种格式,boolean add(E e)和void add(int index,E e)。
- boolean add(E e)
这个方法加入参数后会返回一个布尔类型,要测试这个方法就要得到加入新元素的时候会返回一个true。因此测试的代码为
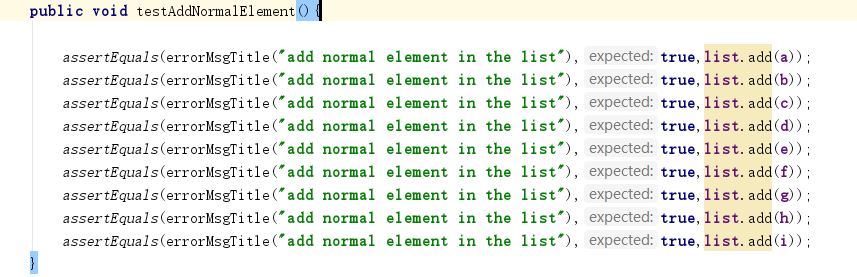

- void add(int index, E e)
这个加入的方法需要传入的参数是列表的下标以及要加入的元素,能够实现将元素加入指定位置。想要测试这个方法要对比加入元素前后列表是否为空来看。因此测试代码为:


- E remove()(LinkedList专有)
这个方法会移除列表中的第一个元素,它会返回一个你移除的元素,因此测试的时候只要看返回的值是不是列表中的第一个元素,并看列表的第一个元素是否发生变化。因此代码为:
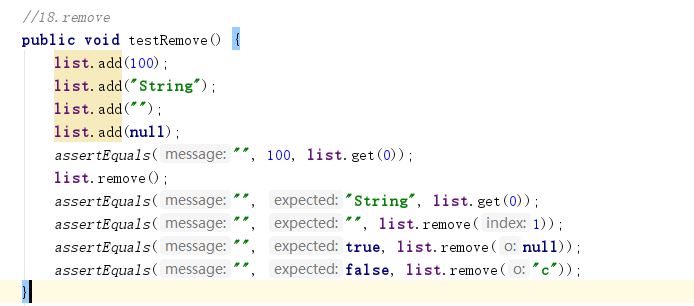
- E remove(int index)
这个方法需要传入的参数是你要删除的元素所在的列表位置,该方法也会返回你选择移除的元素。测试的时候要监视好一个元素,实现移除方法看返回的值是否是选择的那个,再看看列表中该位置的元素。因此代码为:

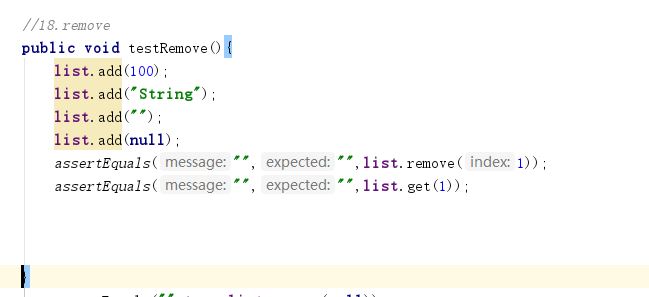
- boolean remove(Object o)
这个方法可以直接将指定的元素移除,测试方法移除指定元素后查看返回的值是否为真。因此代码为:


- void clear()
该方法会将列表中的元素全部清空,测试的时候可以再添加后查看一次列表长度,使用clear方法后看列表长度是否变为0.因此代码为:


测试结果为:


- 实验二:使用ArrayList和LinkedList的方法来将两个非递减的序列按照非递减的顺序放进新的列表中,并写测试类来测试。
根据题目要求,要讲两个非递减的序列按照非递减的顺序许放进新的列表中,就要用到归并的思想。
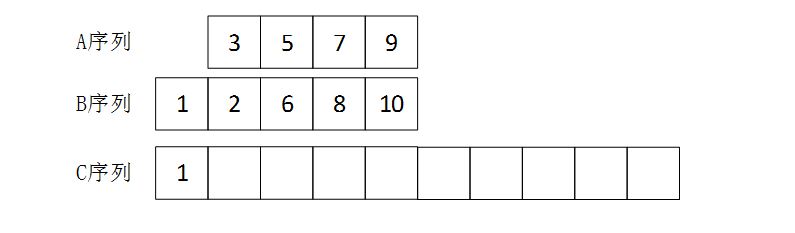
上图的意思就是将最小、次小……这样来将两个序列中的元素,一个个放进新的序列中。
为实现归并功能,我的代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Funny_One on 2017/9/24.
*/
public class MergeSort {
//
public static List<? extends Comparable> mergeSortedList(List<? extends Comparable> aList, List<? extends Comparable> bList) {
List mergeList = new ArrayList();
while (true) {
if (bList.get(0).compareTo(aList.get(0)) < 0) {
mergeList.add(bList.get(0));
bList.remove(0);
} else if (bList.get(0).compareTo(aList.get(0)) == 0) {
mergeList.add(bList.get(0));
bList.remove(0);
mergeList.add(aList.get(0));
aList.remove(0);
} else if (bList.get(0).compareTo(aList.get(0)) > 0) {
mergeList.add(aList.get(0));
aList.remove(0);
}
if (aList.isEmpty() || bList.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
}
if (!aList.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < aList.size(); i++) {
mergeList.add(aList.get(i));
}
} else if (!bList.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < bList.size(); i++) {
mergeList.add(bList.get(i));
}
}
return mergeList;
}
}
/*if (aList.get(index).compareTo(bList.get(index)) < 0) {
mergeList.add(aList.get(index));
} else if (aList.get(index).compareTo(bList.get(index)) == 0) {
mergeList.add(aList.get(index));
mergeList.add(bList.get(index));
} else {
mergeList.add(bList.get(index));
}*/
测试代码为:
import junit.framework.Test;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import junit.framework.TestSuite;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Funny_One on 2017/9/25.
*/
public class MergeSortTest extends TestCase {
public static Test suite(){
TestSuite suite = new TestSuite("MergeSort Test");
suite.addTestSuite(MergeSortTest.class);
return suite;
}
List bList = new ArrayList();
List aList = new ArrayList();
public void testMergeSortedListSize1(){
bList.add(1);
bList.add(9);
bList.add(70);
bList.add(80);
bList.add(90);
aList.add(1);
aList.add(3);
aList.add(5);
aList.add(7);
aList.add(90);
assertEquals("",10,MergeSort.mergeSortedList(aList,bList).size());
}
public void testMergeSortedListSize2(){
bList.add(1);
bList.add(9);
bList.add(70);
bList.add(80);
bList.add(90);
aList.add(1);
aList.add(3);
aList.add(5);
assertEquals("",8,MergeSort.mergeSortedList(aList,bList).size());
}
public void testAfterMergeSortedElement(){
bList.add(1);
bList.add(9);
bList.add(70);
aList.add(1);
aList.add(3);
aList.add(5);
List mergeList =MergeSort.mergeSortedList(aList,bList);
assertEquals("",1,mergeList.get(0));
assertEquals("",1,mergeList.get(1));
assertEquals("",3,mergeList.get(2));
assertEquals("",5,mergeList.get(3));
assertEquals("",9,mergeList.get(4));
assertEquals("",70,mergeList.get(5));
}
public void testAfterMergeSortedUnnormalElement1(){
bList.add(1);
bList.add("");
bList.add(70);
aList.add(1);
aList.add(9);
aList.add(5);
List mergeList =MergeSort.mergeSortedList(aList,bList);
assertEquals("",1,mergeList.get(0));
assertEquals("",1,mergeList.get(1));
assertEquals("",3,mergeList.get(2));
assertEquals("",5,mergeList.get(3));
assertEquals("",9,mergeList.get(4));
assertEquals("",70,mergeList.get(5));
}
public void testAfterMergeSortedUnnormalElement2(){
bList.add(1);
bList.add(3);
bList.add(70);
aList.add(1);
aList.add(null);
aList.add(5);
List mergeList =MergeSort.mergeSortedList(aList,bList);
assertEquals("",1,mergeList.get(0));
assertEquals("",1,mergeList.get(1));
assertEquals("",3,mergeList.get(2));
assertEquals("",5,mergeList.get(3));
assertEquals("",9,mergeList.get(4));
assertEquals("",70,mergeList.get(5));
}
}
TDD测试效果:
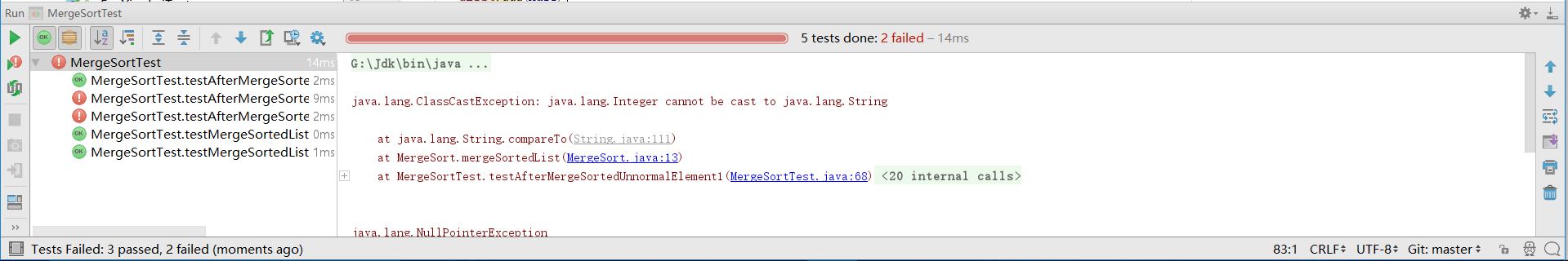
这里之所以会出现错误是因为我测试了两个非正常元素:""和null。
普通测试效果:
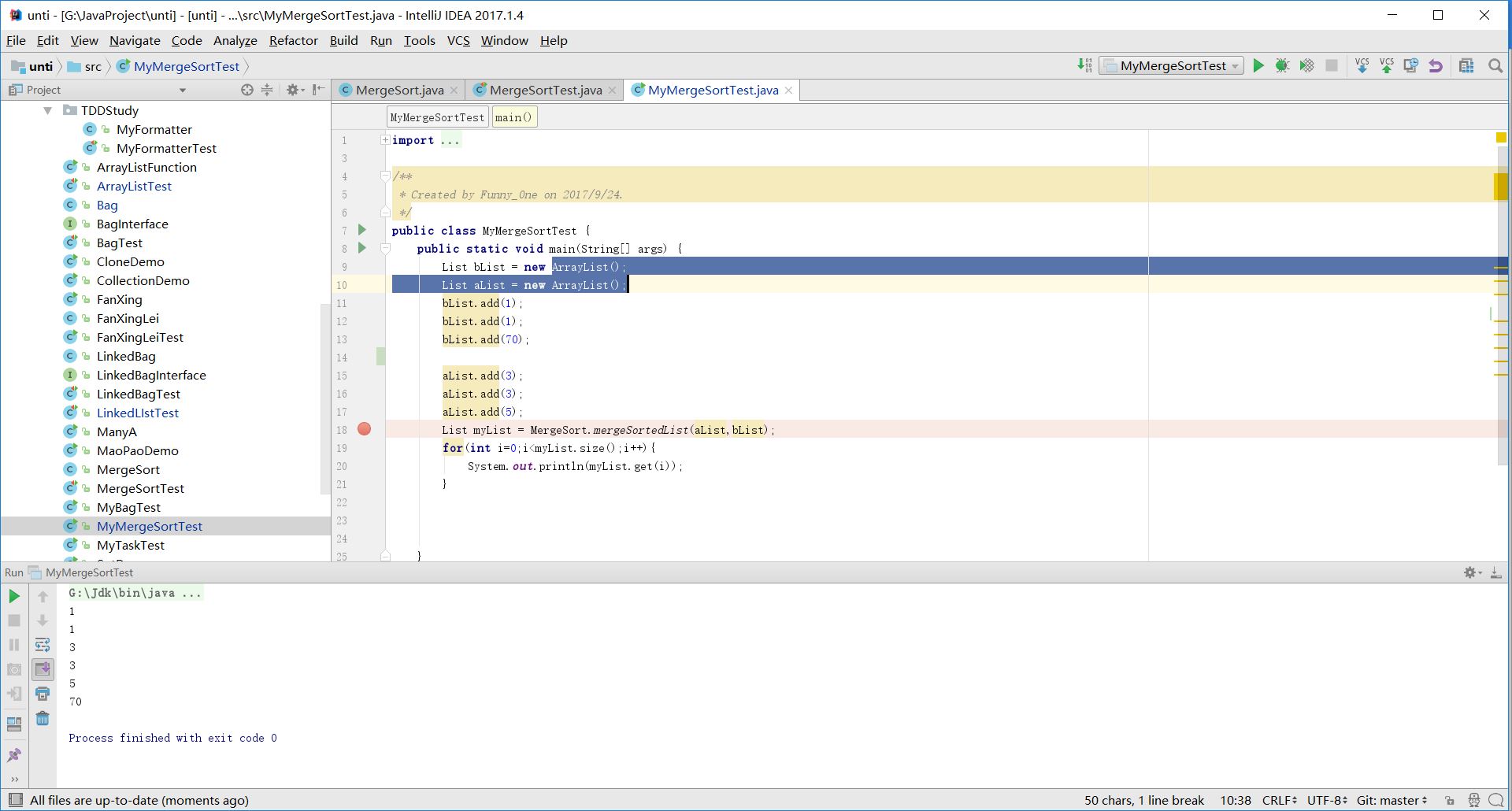
- 实验三:用数组来实现list的几个基本的方法(add、remove、clear、isEmpty)为了能够快速实现方法,将装有Listt方法的BagInterface接口给实现。此外,为能够能尽可能地像List能够规定加入的元素种类,这里就应用到了泛型的知识点。
/**
2 An interface that describes the operations of a bag of objects.
3
4 */
public interface BagInterface<T>
{
/** Gets the current number of entries in this bag.
8 @return The integer number of entries currently in the bag. */
public int getCurrentSize();
/** Sees whether this bag is empty.
12 @return True if the bag is empty, or false if not. */
public boolean isEmpty();
/** Adds a new entry to this bag.
16 @param newEntry The object to be added as a new entry.
17 @return True if the addition is succes sful, or false if not. */
public boolean add(T newEntry);
/** Removes one unspecified entry from this bag, if possible.
21 @return Either the removed entry, if the removal
22 was successful, or null. */
public T remove();
/** Removes one occurrence of a given entry from this bag, if possible.
26 @param anEntry The entry to be removed.
27 @return True if the removal was successful, or false if not. */
public boolean remove (T anEntry);
/** Removes all entries from this bag. */
public void clear();
/** Counts the number of times a given entry appears in this bag.
34 @param anEntry The entry to be counted.
35 @return The number of times anEntry appears in the bag. */
public int getFrequencyOf(T anEntry);
/** Tests whether this bag contains a given entry.
39 @param anEntry The entry to locate.
40 @return True if the bag contains anEntry, or false if not. */
public boolean contains(T anEntry);
/** Retrieves all entries that are in this bag.
44 @return A newly allocated array of all the entries in the bag.
45 Note: If the bag is empty, the returned array is empty. */
public T[] toArray();
} // end BagInterf
public class Bag<T> implements BagInterface<T>,Comparable{
private Object[] myarray = new Object[5];
/*
int 空的格子=0,有元素的格子=0
for(遍历一遍数组){
if(元素为空){
空格++}
}
有元素的格子=数组长度-空的格子
返回 有元素的格子
*/
@Override
public int getCurrentSize() {
int emptyBlock=0;
int having=0;
for(int indedx=0;indedx<myarray.length;indedx++){
if(myarray[indedx]==null){
emptyBlock++;
}
}
having = myarray.length-emptyBlock;
return having;
}
/*
boolean 判断
int 空格数
for(遍历数组){
if(数组的第i项为空{
空格数++
}
}
if(空格数==数组长度){
返回真
}else{
返回假
}
*/
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
boolean judge = true;
int emptyTimes = 0;
for (int i =0;i<myarray.length;i++){
if(myarray[i]==null){
emptyTimes++;
}
}
if(emptyTimes == myarray.length){
judge = true;
}else{
judge = false;
}
return judge;
}
/*
for(遍历数组){
if(数组第i项为空){
数组第i项 = newEntry;
停止循环
}
}
* */
@Override
public boolean add(Object newEntry) {
for(int i=0;i<myarray.length;i++){
if(myarray[i]==null){
myarray[i]=newEntry;
break;
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public T remove() {
myarray[0]=null;
return (T)myarray[0];
}
/**
* for(遍历数组){
* if(数组第i项 == anEntry){
* 数组第i项变为空
* }
* }
*/
@Override
public boolean remove(Object anEntry) {
for(int i=0;i<myarray.length;i++){
if(myarray[i]==anEntry){
myarray[i]=null;
}
}
return true;
}
/*
*for(遍历数组){
* 数组的每一项变为空
* }
*/
@Override
public void clear() {
for(int index=0;index<myarray.length;index++){
myarray[index] = null;
}
}
/**
* int 次数
* for(遍历数组){
* if(数组第index 项 == anEntry){
* 次数++
* }
* }
*/
@Override
public int getFrequencyOf(T anEntry) {
int times =0;
for(int index=0;index<myarray.length;index++){
if(myarray[index].equals(anEntry)){
times++;
}
if(myarray[index]==null){
break;
}
}
return times;
}
/**
* boolean 判断
* for(遍历数组){
* if(数组第index == anEntry){
* 判断为真
* }
* 停止循环
* }
*/
@Override
public boolean contains(Object anEntry) {
boolean judge = true;
for(int index=0;index<myarray.length;index++){
if (myarray[index]==anEntry){
judge = true;
}
break;
}
return judge;
}
/**
* Object[] 篮子
* for(遍历数组){
* 数组元素复制
* }
*
*
*/
@Override
public T[] toArray() {
T[] basket = (T[]) new Object[myarray.length];
for (int index=0;index<myarray.length;index++){
basket[index]=(T)myarray[index];
}
return basket;
}
public void MSG(){
if(isEmpty()==true){
System.out.println("My Bag is empty");
}else {
System.out.println("My Bag isn't empty");
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
int r =0;
if(this.compareTo(o)==0){
r= 0;
}
return r;
}
}
因为想要重现List的方法,因此测试Bag.java的方法与之前测试ArrayList方法和LinkedList的方法差不多。
import junit.framework.Test;
import junit.framework.TestCase;
import junit.framework.TestSuite;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* Created by Funny_One on 2017/9/22.
*/
public class BagTest extends TestCase {
private static final String TEST_FAILURE_MSG = "test fail";
private Bag bag = new Bag();
public static Test suite(){
TestSuite suite = new TestSuite("Bag Test");
suite.addTestSuite(BagTest.class);
return suite;
}
public void testisEmpty() {
assertEquals(errorMsgTitle("背包为空的时候返回true"), true, bag.isEmpty());
}
public void testadd(){
assertEquals(errorMsgTitle("当加入数据时返回为真"),true,bag.add(100));
}
public void testremove(){
assertEquals(errorMsgTitle("当消除存在的数据的时候返回真"),true,bag.remove(1000));
}
public void testgetCurrentSize(){
bag.add(100);
bag.add("String");
bag.add(1.05);
assertEquals(errorMsgTitle("传入数据后能够看到Bag中存3个元素"),3,bag.getCurrentSize());
}
public void testremove2(){
assertEquals(errorMsgTitle("使用该方法时,第一个元素变为null"),null,bag.remove());
}
public void testclear(){
bag.add(1000);
bag.add("String");
bag.add(1.05);
bag.clear();
assertEquals(errorMsgTitle("有效元素为0个"),0,bag.getCurrentSize());
}
public void testContains(){
bag.add(1000);
assertEquals(errorMsgTitle("输入1000会返回true"),true,bag.contains(1000));
}
private String errorMsgTitle(String msg){return msg+" "+TEST_FAILURE_MSG;}
}
测试效果:
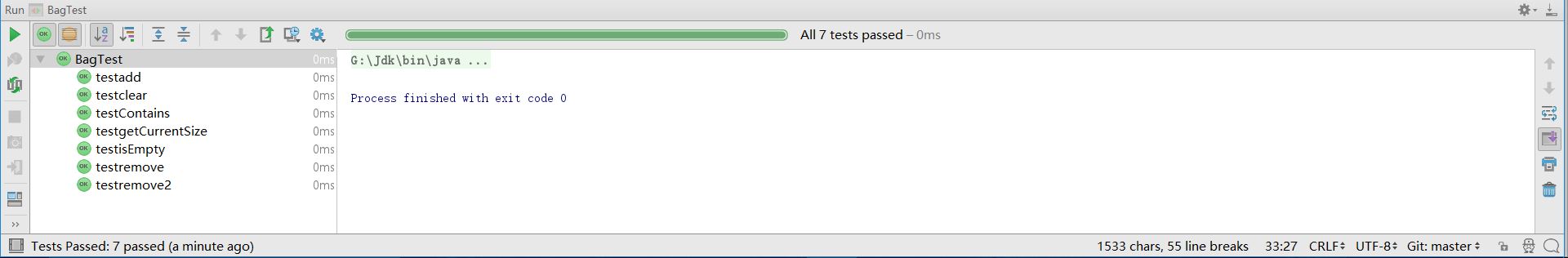
- 实验四:使用链表实现List的基本方法.照葫芦画瓢,我也创建一个接口用于承载List方法。
/**
* Created by Funny_One on 2017/9/25.
*/
public interface LinkedBagInterface<T> {
public boolean isEmpty();
/** Adds a new entry to this bag.
16 @param newEntry The object to be added as a new entry.
17 @return True if the addition is successful, or false if not. */
public boolean add(T newEntry);
/** Removes one unspecified entry from this bag, if possible.
21 @return Either the removed entry, if the removal
22 was successful, or null. */
public T remove();
/** Removes one occurrence of a given entry from this bag, if possible.
26 @param anEntry The entry to be removed.
27 @return True if the removal was successful, or false if not. */
public boolean remove (T anEntry);
/** Removes all entries from this bag. */
public void clear();
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* Created by Funny_One on 2017/9/25.
*/
public class LinkedBag<T> implements LinkedBagInterface<T>{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
boolean judge = true;
if (list.size()==0){
judge=true;
}else {
judge = false;
}
return judge;
}
@Override
public boolean add(Object newEntry) {
boolean judge = true;
if(list.add(newEntry)){
judge = true;
}else{
judge = false;
}
return judge;
}
@Override
public T remove() {
T a = (T) list.remove(0);
return a;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object anEntry) {
list.remove(anEntry);
return true;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
list.clear();
}
}
import junit.framework.TestCase;
/**
* Created by Funny_One on 2017/9/25.
*/
public class LinkedBagTest extends TestCase {
LinkedBag list = new LinkedBag();
public void testIsEmpty() throws Exception {
list.add(100);
list.add("String");
assertEquals("",false,list.isEmpty());
list.clear();
assertEquals("",true,list.isEmpty());
}
public void testAdd() throws Exception {
assertEquals("",true,list.add(100));
}
public void testRemove() throws Exception {
list.add(100);
list.add("String");
assertEquals("",false,list.isEmpty());
assertEquals("",100,list.remove());
assertEquals("",true,list.remove("String"));
}
public void testClear() throws Exception {
list.add(100);
list.add("String");
assertEquals("",false,list.isEmpty());
list.clear();
assertEquals("",true,list.isEmpty());
}
}
测试效果:
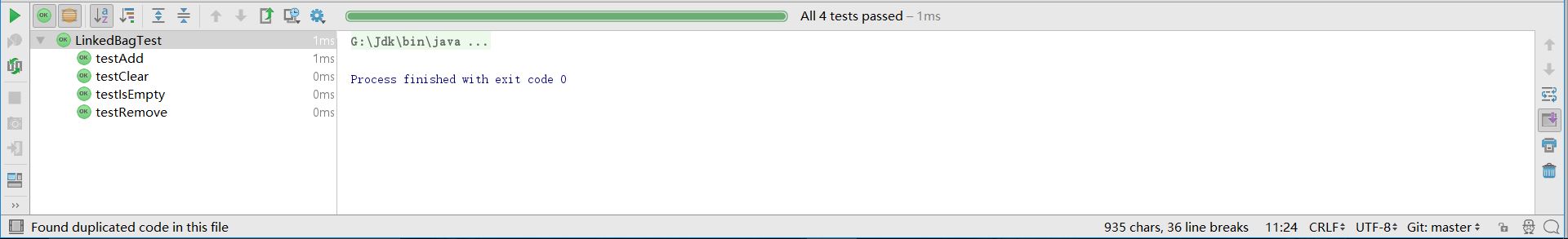
-
实验5:ArrayList与LinkedList的源码阅读理解。
该试验要求我们去阅读ArrayList和LinkedList的源代码,了解是如何实现这两个列表的方法,我选取其中比较主要的几个方法(add,remove) -
ArrayList boolean add(E e)
主要代码有:
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private int size;
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
先分别创建名为elementData和DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA的数组,并生成名为DEFAULT_CAPACITY和size的两个整数型变量。实例化ArrayList的时候会使elementData和DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA这两个数组相等。当调用add的时候,它会内部调用ensureCapacityInternal方法,传入的参数是size+1。在传入任何变量之前,列表长度为0。因此在ensureCapacityInternal中的条件语句成立,选择DEFAULT_CAPACITY或minCapacity(输入的参数)中的较大值,赋值到minCapacity中,在初次传入的时候,较大值为DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10。然后调用ensureExplicitCapacity方法,并将参数minCapacity传进去。ensureExplicitCapacity接收到参数之后,首先在记录列表结构性变化的变量modCount中+1,然后查看这个传入的值与当前数组的长度比较,初次传入的时候数组长度为0,因此会满足条件语句,并调用grow方法,传入参数为minCapacity。在grow方法中,数组会进行自我增长,若数组不够传入的参数大,它就会拿传入的参数作为数组的新长度。因此第一次传入元素的时候,数组会变成10位长度。然后返回到add方法,并将 E e放进数组的第一个空格中,然后size++,等待下一次的调用,从而能够将下一次的调用放进数组的第二个位置中。
- LinkedList boolean add(E e)
主要代码有:
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= SubList.this.size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (offset + i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)];
}
首先需要设置两个节点,一个是第一个节点,另一个是最后一个节点当使用add的方法时,是将元素插入到最后的位置,所以会调用linkLast的方法。在linklLast的方法中,会新建一个节点l等于最后的一个节点,再创建一个新的节点newNode来将元素插入,这个节点的三个参数是:1、上一个节点的值,2、当前节点的值,3、下一个节点的值,由于元素的插入都是从列表的最后插入的,所以下一个节点的值即第三个参数为null。添加好之后将当前节点的值赋给last节点,从而使最后一个节点的值为e。然后进行判断,看l是否为null。若是,当前节点就成为了第一个节点,若不是,节点l的下一个节点就是newNode,然后再列表规模加1,列表结构性变换+1。
- ArrayList E remove(int index)
private int size;
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
//检查是否越界
modCount++;
//列表结构性变化的记录
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//要移除的元素成为oldValue
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
//要复制元素的个数
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//将后面的元素都网上移一格
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
//数组的最后一位变为null并且使长度减一
return oldValue;
//将被移除的元素返回出来
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
- LinkedList E remove(int index)
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
//查看是否会越界
return unlink(node(index));
}
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
//当前节点的值
final Node<E> next = x.next;
//下一个节点的值
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
//上一个节点的值
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
//若没有上一个节点,即为第一个节点,当要断掉第一个节点与第二个节点的联系的时候,将第一个节点的值改为下一个节点的值就好。
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
//移除指定元素所在节点联系的过程
size--;
//列表的长度减少
modCount++;
//记录列表结构性变化的次数增加
return element;
//将元素返回
}
实验知识点
- TDD的用法。
- ArrayList和LinkedList的使用方法
- 泛型的使用
- transient的使用