JSP:Java Server Page(通俗来说就是动态页面,支持Java代码的页面),实际JSP文件就是一个继承Servlet的Java类。
Html:是静态页面
新建一个JSP文件
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> 欢迎使用JSP </body> </html>
运行效果
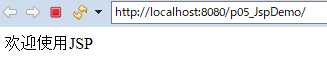
为什么说JSP是一个Java类呢?
通过查看apache-tomcat-9.0.30workCatalinalocalhostp05_JspDemoorgapachejsp

查看index_jsp.java
package org.apache.jsp; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import javax.servlet.jsp.*; public final class index_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent, org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceImports { ... .... public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response) throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException { if (!javax.servlet.DispatcherType.ERROR.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) { final java.lang.String _jspx_method = request.getMethod(); if ("OPTIONS".equals(_jspx_method)) { response.setHeader("Allow","GET, HEAD, POST, OPTIONS"); return; } if (!"GET".equals(_jspx_method) && !"POST".equals(_jspx_method) && !"HEAD".equals(_jspx_method)) { response.setHeader("Allow","GET, HEAD, POST, OPTIONS"); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, "JSPではGET、POST、またはHEADのみが許可されます。 JasperはOPTIONSも許可しています。"); return; } } final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext; javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null; final javax.servlet.ServletContext application; final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config; javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null; final java.lang.Object page = this; javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null; javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null; try { response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8"); pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, true, 8192, true); _jspx_page_context = pageContext; application = pageContext.getServletContext(); config = pageContext.getServletConfig(); session = pageContext.getSession(); out = pageContext.getOut(); _jspx_out = out; out.write(" "); out.write("<!DOCTYPE html> "); out.write("<html> "); out.write("<head> "); out.write("<meta charset="UTF-8"> "); out.write("<title>Insert title here</title> "); out.write("</head> "); out.write("<body> "); out.write("欢迎使用JSP "); out.write("</body> "); out.write("</html>"); } catch (java.lang.Throwable t) { if (!(t instanceof javax.servlet.jsp.SkipPageException)){ out = _jspx_out; if (out != null && out.getBufferSize() != 0) try { if (response.isCommitted()) { out.flush(); } else { out.clearBuffer(); } } catch (java.io.IOException e) {} if (_jspx_page_context != null) _jspx_page_context.handlePageException(t); else throw new ServletException(t); } } finally { _jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context); } } }
发现JSP文件最后编译成Java类文件其中HTML标签是通过Java代码的out.write()方法输入的。
查看index.jsp中的代码,分为两部分
一、HTML标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> 欢迎使用JSP </body> </html>
二、指令(page、include、taglib)
①、page指令
用于定义jsp页面的各种属性,不管page指令出如今什么位置。他的作用都是整个页面,可是最好放在开头。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
* language:页面中支持镶嵌代码的语言
* contentType:设置文件类型和字符编码
* pageEncoding:设置编码
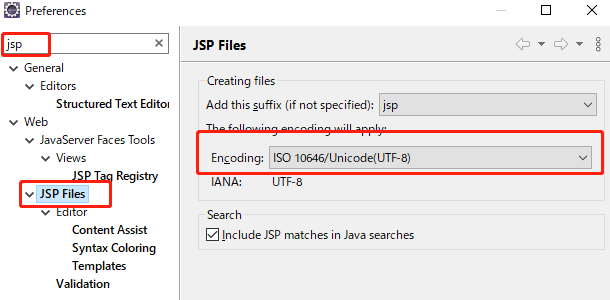
每次新建JSP文件都要修改其编码的话,可以通过eclipse工具的菜单Window=>Preferences
* extends://继承的包
* import:须要导入的包(能够用逗号分开写。也能够另写一个import)
* session:假设为true,jsp页面会自己主动创建一个session,假设为false则不会。
* buffer:缓冲区能够设置为无。也能够自己设置,或者使用默认设置:8kb.("none | 8kb | sizekb")
* autoFlush:自己主动刷新。
* isThreadSafe:是否线程安全
* errorPage:errorPage属性的设置值必须使用相对路径。假设以"/"开头,表示相对于当前的web应用程序的根文件夹(注意不是网站根文件夹),否则,相对于当前页面。
* isErrorPage:将一个页面声明为错误页面。
②、include指令
包含另外一个jsp的内容进来(把另外一个页面的所有内容拿过来一起输出。 所有的标签元素都包含进来。)
<body> 欢迎使用JSP <%@ include file="index01.jsp" %> </body>

③、taglib指令
三、JSP 动作标签
<jsp:include page=""></jsp:include> <jsp:param value="" name=""/> <jsp:forward page=""></jsp:forward>
* jsp:include
动态包含
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> 欢迎使用JSP<br /> <%@ include file="index01.jsp" %><br /> <jsp:include page="index02.jsp"></jsp:include> </body> </html>
查看Java源码

区别一:
<%@ include file="index01.jsp" %>不会把index01.jsp编译成Java文件<br /> <jsp:include page="index02.jsp"></jsp:include>把index02.jsp编译成Java文件
区别二:
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request,
final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response) throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException { ... ... try { ... ... out.write(" "); out.write("<!DOCTYPE html> "); out.write("<html> "); out.write("<head> "); out.write("<meta charset="UTF-8"> "); out.write("<title>Insert title here</title> "); out.write("</head> "); out.write("<body> "); out.write("欢迎使用JSP<br /> "); out.write(" ");
//静态包含(index01.jsp) out.write("<!DOCTYPE html> "); out.write("<html> "); out.write("<head> "); out.write("<meta charset="UTF-8"> "); out.write("<title>Insert title here</title> "); out.write("</head> "); out.write("<body> "); out.write("index01.jsp页面 "); out.write("</body> "); out.write("</html>"); out.write("<br /> ");
//动态包含(index02.jsp) org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspRuntimeLibrary.include(request, response, "index02.jsp", out, false); out.write(" "); out.write("</body> "); out.write("</html>"); } ... ... }
动态包含是:将包含页面(index02.jsp)运行结果输出显示
* jsp:forward
请求转发
index.jsp页面代码
<body> 欢迎使用JSP<br /> <jsp:forward page="index03.jsp"></jsp:forward> </body>
等同于
<% request.getRequestDispatcher("index03.jsp").forward(request, response); %>
其效果是访问index.jsp页面会跳转到index03.jsp页面
* jsp:param
参数,页面之间访问(jsp:include或jsp:forward)所需要的参数
index.jsp页面代码
<body> 欢迎使用JSP<br /> <jsp:forward page="index03.jsp"> <jsp:param value="zhangsan" name="name"/> </jsp:forward> </body>
index.jsp页面代码
<body> 欢迎<%= request.getParameter("name") %><br /> index03.jsp页面 </body>
结果

四、JSP内置对象
所谓内置对象,可以直接在jsp页面中使用的对象
* 四个作用域对象
①、作用域:对象的应用(存取值)范围 setAttribute( 存值) 和 getAttribute(取值)
- pageContext
- request
- session
- application
②、用法代码演示:
使用作用域来存储数据 <br> <% pageContext.setAttribute("name", "page"); request.setAttribute("name", "request"); session.setAttribute("name", "session"); application.setAttribute("name", "application"); %> 取出四个作用域中的值 <br> <%=pageContext.getAttribute("name")%><br> <%=request.getAttribute("name")%><br> <%=session.getAttribute("name")%><br> <%=application.getAttribute("name")%><br>
③、作用域范围
* pageContext 【PageContext】范围:当前页面
* request 【HttpServletRequest】范围:一次请求
* session 【HttpSession】范围:一次会话(同一个Session ID)
* application 【ServletContext】范围:整个工程,服务器关闭就不能使用
验证实例:
Ⅰ、验证pageContext作用域为当前页面
index.jsp代码
<body> 使用作用域来存储数据 <br> <% pageContext.setAttribute("name", "page"); request.setAttribute("name", "request"); session.setAttribute("name", "session"); application.setAttribute("name", "application"); request.getRequestDispatcher("index04.jsp").forward(request, response); %> </body>
index04.jsp代码
<body> <h3>Index04.jsp页面</h3> 取出四个作用域中的值 <br> pageContext:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("name")%><br> request:<%=request.getAttribute("name")%><br> session:<%=session.getAttribute("name")%><br> application:<%=application.getAttribute("name")%><br> </body>
结果:

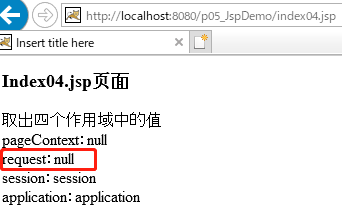
Ⅱ、验证request作用域为一次请求
index.jsp代码(index04.jsp代码不变)
<body> 使用作用域来存储数据 <br> <% pageContext.setAttribute("name", "page"); request.setAttribute("name", "request"); session.setAttribute("name", "session"); application.setAttribute("name", "application"); //request.getRequestDispatcher("index04.jsp").forward(request, response); response.sendRedirect("index04.jsp"); %> </body>
结果:
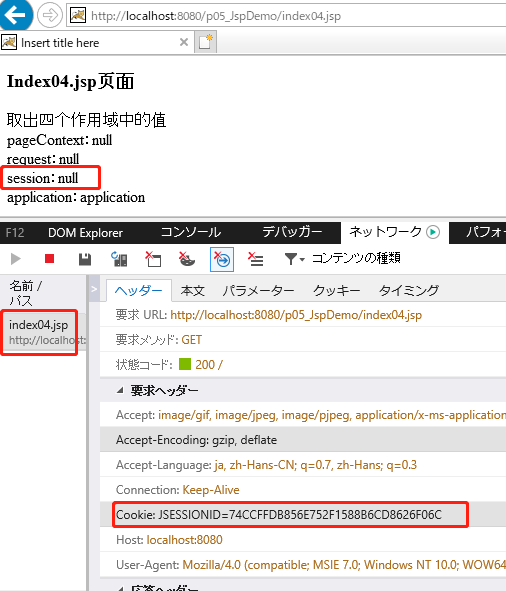
Ⅲ、验证session作用域为一次会话(同一Session ID)
使用开发者(F12)查看Session ID 
关闭浏览器重新访问index04.jsp
* 其他内置对象
- out 【JspWriter】
- response 【HttpServletResponse】
- exception 【Throwable】
- page 【Object】 ---就是这个jsp翻译成的java类的实例对象
- config 【ServletConfig】