1.setfill/setw使用
2.定义结构体
3.关于字符串读取
4.排序问题:复试不要求一般用:冒泡排序
5.数字和字符之间转换
6.进制转化:10进制转8进制
7.质数判断
8.字符串拷贝函数strcpy
9.字符串拼接函数strcat
10.字符串比较函数strcmp
11.计算字符串长度函数strlen
12.补充内容:

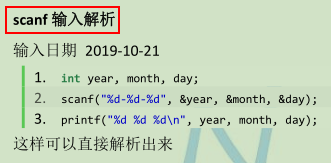






万能头文件:#include <bits/stdc++.h>
基本冒泡排序:
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++){
for(int j=0; j<n-1-i; j++){
if(a[j]>a[j+1]){
int temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
基本二分查找:
int left = 0;
int right = len - 1;
int mid;
while( left<=right){
mid = left + (right - left)/2;//防止溢出
if(find_data == a[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(find_data > a[mid]){
left = mid + 1;
}else{
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;//没有找到
基本选择排序:
从待排序的数据中选出最小的元素放在起始位置,然后再从剩余的未排序元素中寻找到最小的元素,放到已排序的序列的末尾
1.我们的目标是找到最小的数min,放到第一位
2.我们的目标是,找出除了min以外的最小值,让它排在第2位
3.重复2直到结束
for(int i=0; i<a.length-1; i++){//需要几轮,例如a=[1,2,3,4,5]需要4轮,最后一个肯定是最大值
//每轮遍历开始前,默认第一个数为最小值
int min = a[i];
int minIndex = i;
for(int j=i+1; j<a.length; j++){
if(min>a[j]){
min = a[j];
minIndex = j;//记录下标
}
}
//如果最小值改变了,那么交换
if(min!=a[i]){
a[minIndex] = a[i];
a[i] = min;
}
}
基本插入排序:
void insertSort(int a[], int n){
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){//默认第一个元素a[0],只有一个数,有序
int temp = a[i];//存储当前要插入元素
int j = i - 1;
while( j>=0 && temp<a[j] ){//从后往前找合适位置
a[j+1] = a[j];//没找到,元素后移
j--;
}
//此时找到了合适位置
//每次没找到都j--所以最后插在j+1位置
a[j+1] = temp;
}
//打印
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
}
正文:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
// 1.setfill/setw使用
// float f1 = 2.99;
// float f2 = 8.9099;
// int i = 10;
// cout << setfill('*');
// //setw是设置域宽,就是输出数据所占几列
// //如果在默认的情况下,输出的数据不能达到所规定的域宽就用空格填充
// //setfill是设置填充物
// //使用操纵符时,需要包含头文件iomanip
// cout << setw(10) << f1 << endl;
// cout << setw(10) << f2 << endl;
// cout << setw(10) << i << endl;
// 2.定义结构体
// struct Student{
// int id;
// char name[20];
// };
// 可以使用typedef添加别名
// typedef struct Student{
// int id;
// char name[20];
// }Student;
//
// 使用:Student s;
// 3.关于字符串读取
// string str = "hello gy";
// int i = 0;
// while(str[i] != '�'){
// cout << str[i] << endl;
// i++;
// }
// 4.排序问题
// 复试不要求一般用:冒泡排序
// int len = 6;
// int num[] = {5,2,77,1,99,66};
// for(int i=0; i<len-1; i++){
// for(int j=0; j<len-1-i; j++){
// if( num[j]>num[j+1] ){
// int temp = num[j];
// num[j] = num[j+1];
// num[j+1] = temp;
// }
// }
// }
// for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
// cout << num[i] << " ";
// }
// 5.数字和字符之间转换
// 例如:将字符'7'转为数字7
// char a = '7';
// int a_num = a - '0';
// 例如:将数字 5 转换成字符'5'
// int b_num = 5;
// char b = b_num + '0';
// 6.进制转化:10进制转8进制
// int num = 666;
// int result[100];
// int len = 0;
// while(num/8 != 0){
// result[len] = num%8;
// len++;
// num /= 8;
// }
// result[len] = num;
// for(int i=len; i>=0; i--){
// cout << result[i] <<endl;
// }
// 7.质数判断
// int num = 10;
// int temp = sqrt(num);
// bool isZhiShu = true;//默认是质数
// for(int i=2; i<=temp; i++){
// if( num%i==0 ){
// isZhiShu = false;//不是质数
// break;
// }
// }
// if(isZhiShu){
// cout << "是质数" << endl;
// }else{
// cout << "不是质数" << endl;
// }
// 8.字符串拷贝函数strcpy
// char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src);
// 将参数 src 字符串拷贝至参数 dest 所指的地址
// char string[10];
// char *str1 = "abcdefgh";
// //将str1的内容拷贝给string数组
// strcpy(string, str1);
// printf("%s
", string);
// 9.字符串拼接函数strcat
// char *strcat(char *dest, const char *src);
// 作用:返回dest字符串起始地址,并且dest = dest+src
// char str[20];
// char* str1 = "gyy";
// char* str2 = "wgg";
// strcat(str, str1);
// strcat(str, str2);
// printf("%s
", str);
// 10.字符串比较函数strcmp
// int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2);
// 若s1==s2返回0;s1>s2返回大于0;s1<s2返回小于0
// char *a = "aBcDeF";
// char *b = "AbCdEf";
// char *c = "aacdef";
// char *d = "aBcDeF";
// printf("%d
",strcmp(a,b));
// printf("%d",strcmp(a,d));
// 11.计算字符串长度函数strlen
// 计算指定的字符串长度,不包括结束字符'�' a
// size_t strlen(const char *s);
// 返回字符串s的字符数
// 但是sizeof返回的是变量声明后所占的内存数,不是实际长度
// char str[5] = "abcd";
// cout << strlen(str) << endl;//4
// cout << sizeof(str) << endl;//5
return 0;
}