摘要
本文构建了一个使用工作量证明机制(POW)的类BTC的区块链。将区块链持久化到一个Bolt数据库中,然后会提供一个简单的命令行接口,用来完成一些与区块链的交互操作。这篇文章目的是希望帮助大家理解BTC源码的架构,所以主要专注于的实现原理及存储上,暂时忽略了 “分布式” 这个部分。严格来说还不能算是一个完全意义上的区块链系统。
开发环境
语言:GO;
数据库:BoltDB;
IDE: Goland或其他工具都可以;
系统:不限,本文使用windows。
BoltDB数据库
实际上,选择任何一个数据库都可以,本文先用的是BoltDB。在比特币白皮书中,并没有提到要使用哪一个具体的数据库,它完全取决于开发者如何选择。现在是比特币的一个参考实现,Bitcoin core使用的是是LevelDB。
BoltDB安装及使用可以参考《BoltDB简单使用教程》。
BoltDB有如下优点:
- 非常简单和简约
- 用 Go 实现
- 不需要运行一个服务器
- 能够允许我们构造想要的数据结构
由于 Bolt 意在用于提供一些底层功能,简洁便成为其关键所在。它的API 并不多,并且仅关注值的获取和设置。仅此而已。
Bolt 使用键值存储,数据被存储为键值对(key-value pair,就像 Golang 的 map)。键值对被存储在 bucket 中,这是为了将相似的键值对进行分组(类似 RDBMS 中的表格)。因此,为了获取一个值,你需要知道一个 bucket 和一个键(key)。
注意:Bolt 数据库没有数据类型:键和值都是字节数组(byte array)。鉴于需要在里面存储 Go 的结构(准确来说,也就是存储(块)Block),我们需要对它们进行序列化,也就说,实现一个从 Go struct 转换到一个 byte array 的机制,同时还可以从一个 byte array 再转换回 Go struct。虽然我们将会使用 encoding/gob 来完成这一目标,但实际上也可以选择使用 JSON, XML, Protocol Buffers 等等。之所以选择使用 encoding/gob, 是因为它很简单,而且是 Go 标准库的一部分。
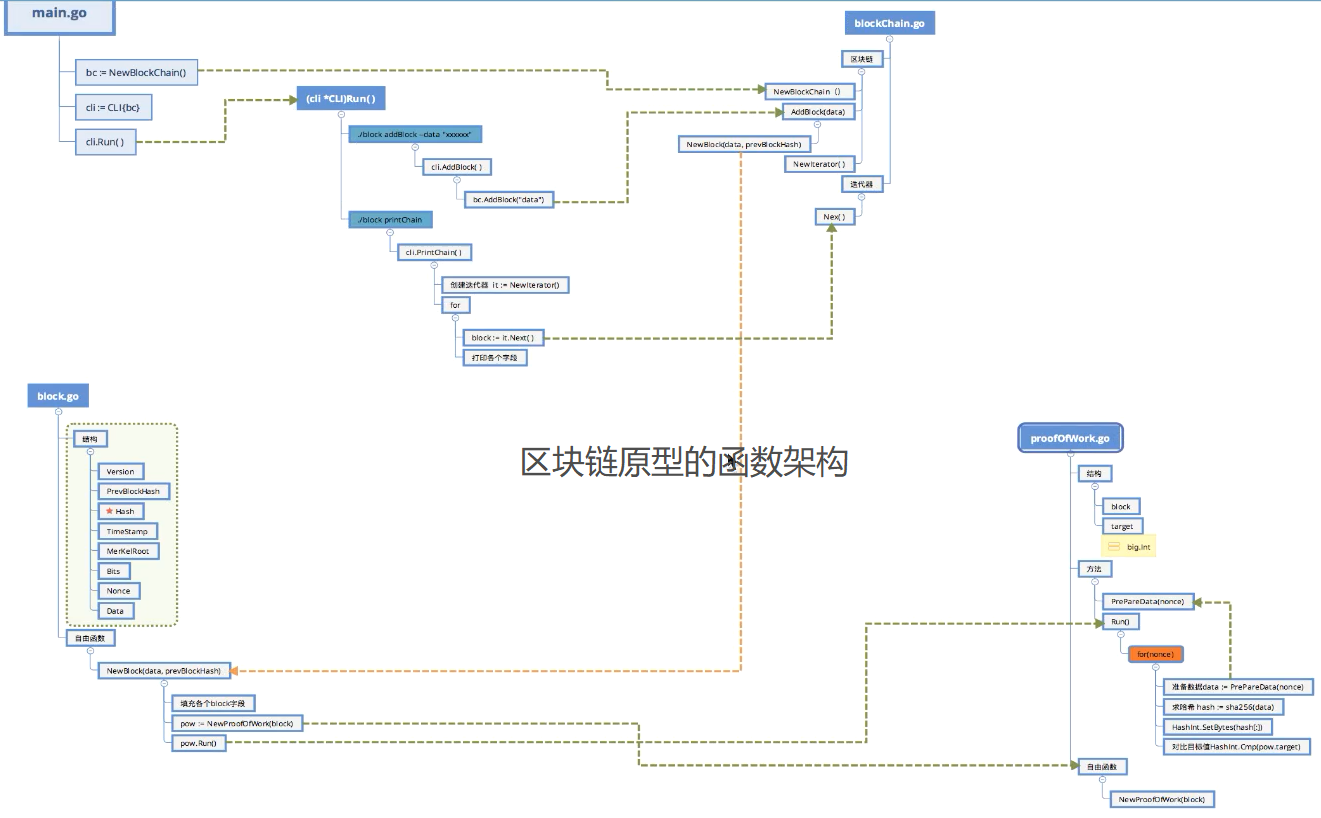
区块链原型的函数架构
系统实现
1.区块文件block.go
该部分主要包括:
对区块结构的定义;创建区块的方法NewBlock();区块的序列化Serialize()与反序列化Deserialize()函数;以及创世区块的生成NewGenesisBlock()。
//定义一个区块的结构Block type Block struct { //版本号 Version int64 //父区块头哈希值 PreBlockHash []byte //当前区块的Hash值, 为了简化代码 Hash []byte //Merkle根 MerkleRoot []byte //时间戳 TimeStamp int64 //难度值 Bits int64 //随机值 Nonce int64 //交易信息 Data []byte } //提供一个创建区块的方法 func NewBlock(data string, preBlockHash []byte) *Block { var block Block block = Block{ Version: 1, PreBlockHash: preBlockHash, //Hash TODO MerkleRoot: []byte{}, TimeStamp: time.Now().Unix(), Bits: targetBits, Nonce: 0, Data: []byte(data)} //block.SetHash() pow := NewProofOfWork(&block) nonce, hash := pow.Run() block.Nonce = nonce block.Hash = hash return &block } // 将 Block 序列化为一个字节数组 func (block *Block) Serialize() []byte { var buffer bytes.Buffer encoder := gob.NewEncoder(&buffer) err := encoder.Encode(block) CheckErr("Serialize", err) return buffer.Bytes() } // 将字节数组反序列化为一个 Block func Deserialize(data []byte) *Block { if len(data) == 0 { return nil } var block Block decoder := gob.NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(data)) err := decoder.Decode(&block) CheckErr("Deserialize", err) return &block } //创世块 func NewGenesisBlock() *Block { return NewBlock("Genesis Block", []byte{}) }
2.区块链blockChain.go
该部分内容主要包括:
-
定义一个区块链结构BlockChain结构体;
-
提供一个创建BlockChain的方法NewBlockChain();
我们希望NewBlockchain实现的功能有:
- 打开一个数据库文件
- 检查文件里面是否已经存储了一个区块链
- 如果已经存储了一个区块链:
- 创建一个新的
Blockchain实例- 设置
Blockchain实例的 tip 为数据库中存储的最后一个块的哈希- 如果没有区块链:
- 创建创世块
- 存储到数据库
- 将创世块哈希保存为最后一个块的哈希
- 创建一个新的
Blockchain实例,初始时 tail 指向创世块( tail存储的是最后一个块的哈希值)
- 提供一个添加区块的方法AddBlock(data string);
- 迭代器对区块进行遍历。
const dbFile = "blockchain.db" const blocksBucket = "bucket" const lastHashKey = "key" //定义一个区块链结构BlockChain type BlockChain struct { //blocks []*Block //数据库的操作句柄 db *bolt.DB //tail尾巴,表示最后一个区块的哈希值 //在链的末端可能出现短暂分叉的情况,所以选择tail其实也就是选择了哪条链 tail []byte } //提供一个创建BlockChain的方法 func NewBlockChain() *BlockChain { // 打开一个 BoltDB 文件 //func Open(path string, mode os.FileMode, options *Options) (*DB, error) db, err := bolt.Open(dbFile, 0600, nil) //utils中的校验函数,校验错误 CheckErr("NewBlockChain1", err) var lastHash []byte err = db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { bucket := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) // 如果数据库中不存在bucket,要去创建创世区块,将数据填写到数据库的bucket中 if bucket == nil { fmt.Println("No existing blockchain found. Creating a new one...") genesis := NewGenesisBlock() bucket, err := tx.CreateBucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) CheckErr("NewBlockChain2", err) err = bucket.Put(genesis.Hash, genesis.Serialize()) CheckErr("NewBlockChain3", err) err = bucket.Put([]byte(lastHashKey), genesis.Hash) CheckErr("NewBlockChain4", err) lastHash = genesis.Hash } else { //直接读取最后区块的哈希值 lastHash = bucket.Get([]byte(lastHashKey)) } return nil }) CheckErr("db.Update", err) return &BlockChain{db, lastHash} } //提供一个添加区块的方法 func (bc *BlockChain) AddBlock(data string) { var preBlockHash []byte err := bc.db.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { bucket := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) if bucket == nil { os.Exit(1) } preBlockHash = bucket.Get([]byte(lastHashKey)) return nil }) CheckErr("AddBlock-View", err) block := NewBlock(data, preBlockHash) err = bc.db.Update(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { bucket := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) if bucket == nil { os.Exit(1) } err = bucket.Put(block.Hash, block.Serialize()) CheckErr("AddBlock1", err) err = bucket.Put([]byte(lastHashKey), block.Hash) CheckErr("AddBlock2", err) bc.tail = block.Hash return nil }) CheckErr("AddBlock-Update", err) } //迭代器,就是一个对象,它里面包含了一个游标,一直向前/后移动,完成整个容器的遍历 type BlockChainIterator struct { currentHash []byte db *bolt.DB } //创建迭代器,同时初始化为指向最后一个区块 func (bc *BlockChain) NewIterator() *BlockChainIterator { return &BlockChainIterator{bc.tail, bc.db} } // 返回链中的下一个块 func (it *BlockChainIterator) Next() (block *Block) { err := it.db.View(func(tx *bolt.Tx) error { bucket := tx.Bucket([]byte(blocksBucket)) if bucket == nil { return nil } data := bucket.Get(it.currentHash) block = Deserialize(data) it.currentHash = block.PreBlockHash return nil }) CheckErr("Next", err) return }
3.工作量证明机制POW.go
该部分主要包括:
创建POW的方法NewProofOfWork(block *Block) ;
计算哈希值的方法 Run() (int64, []byte);
//定义一个工作量证明的结构ProofOfWork type ProofOfWork struct { block *Block //目标值 target *big.Int } //难度值常量 const targetBits = 20 //创建POW的方法 func NewProofOfWork(block *Block) *ProofOfWork { //000000000000000... 01 target := big.NewInt(1) //0x1000000000000...00 target.Lsh(target, uint(256-targetBits)) pow := ProofOfWork{block: block, target: target} return &pow } //给Run()准备数据 func (pow *ProofOfWork) PrepareData(nonce int64) []byte { block := pow.block tmp := [][]byte{ /* 需要将block中的不同类型都转化为byte,以便进行连接 */ IntToByte(block.Version), block.PreBlockHash, block.MerkleRoot, IntToByte(block.TimeStamp), IntToByte(nonce), IntToByte(targetBits), block.Data} //func Join(s [][]byte, sep []byte) []byte data := bytes.Join(tmp, []byte{}) return data } //计算哈希值的方法 func (pow *ProofOfWork) Run() (int64, []byte) { /*伪代码 for nonce { hash := sha256(block数据 + nonce) if 转换(Hash)< pow.target{ 找到了 }else{ nonce++ } } return nonce,hash{:} */ //1.拼装数据 //2.哈希值转成big.Int类型 var hash [32]byte var nonce int64 = 0 var hashInt big.Int fmt.Println("Begin Minding...") fmt.Printf("target hash : %x ", pow.target.Bytes()) for nonce < math.MaxInt64 { data := pow.PrepareData(nonce) hash = sha256.Sum256(data) hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:]) // Cmp compares x and y and returns: // // -1 if x < y // 0 if x == y // +1 if x > y // //func (x *Int) Cmp(y *Int) (r int) { if hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1 { fmt.Printf("found hash :%x,nonce :%d ,", hash, nonce) break } else { //fmt.Printf("not found nonce,current nonce :%d,hash : %x ", nonce, hash) nonce++ } } return nonce, hash[:] } //校验函数 func (pow *ProofOfWork) IsValid() bool { var hashInt big.Int data := pow.PrepareData(pow.block.Nonce) hash := sha256.Sum256(data) hashInt.SetBytes(hash[:]) return hashInt.Cmp(pow.target) == -1 }
4.命令函交互CLI.go
注意这部分需要使用标准库里面的 flag 包来解析命令行参数;
首先,创建两个子命令: addblock 和 printchain, 然后给 addblock 添加 --data 标志。printchain 没有标志;
然后,检查用户输入的命令并解析相关的 flag 子命令;
最后检查解析是哪一个子命令,并调用相关函数执行。
具体如下:
//因为是多行的,所以用反引号`···`包一下,可以实现多行字符串的拼接,不需要转义! //命令行提示 const usage = ` Usage: addBlock -data BLOCK_DATA "add a block to the blockchain" printChain "print all the blocks of the blockchain" ` const AddBlockCmdString = "addBlock" const PrintChainCmdString = "printChain" //输出提示函数 func (cli *CLI) printUsage() { fmt.Println("Invalid input!") fmt.Println(usage) os.Exit(1) } //参数检查函数 func (cli *CLI) validateArgs() { if len(os.Args) < 2 { fmt.Println("invalid input!") cli.printUsage() } } func (cli *CLI) Run() { cli.validateArgs() addBlockCmd := flag.NewFlagSet(AddBlockCmdString, flag.ExitOnError) printChainCmd := flag.NewFlagSet(PrintChainCmdString, flag.ExitOnError) //func (f *FlagSet) String(name string, value string, usage string) *string addBlocCmdPara := addBlockCmd.String("data", "", "Block data") switch os.Args[1] { case AddBlockCmdString: //添加动作 err := addBlockCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:]) CheckErr("Run()1", err) if addBlockCmd.Parsed() { if *addBlocCmdPara == "" { fmt.Println("addBlock data not should be empty!") cli.printUsage() } cli.AddBlock(*addBlocCmdPara) } case PrintChainCmdString: //打印输出 err := printChainCmd.Parse(os.Args[2:]) CheckErr("Run()2", err) if printChainCmd.Parsed() { cli.PrintChain() } default: //命令不符合规定,输出提示信息 cli.printUsage() } }
区块链操作演示效果:
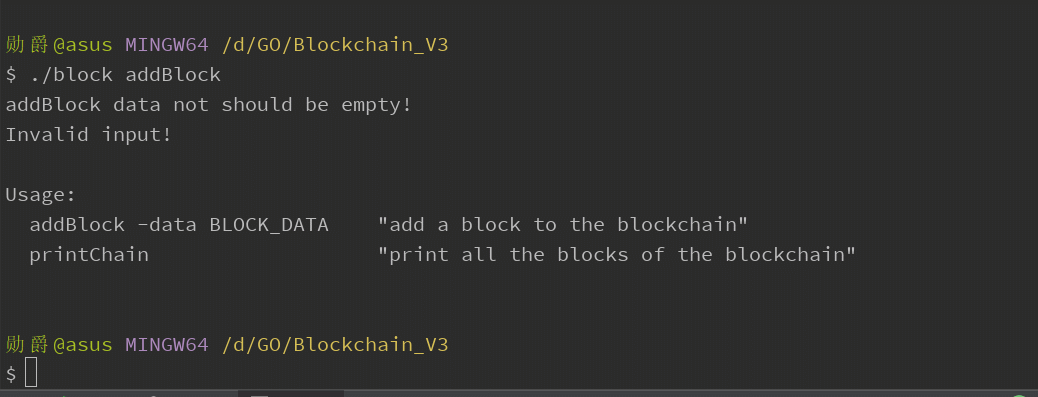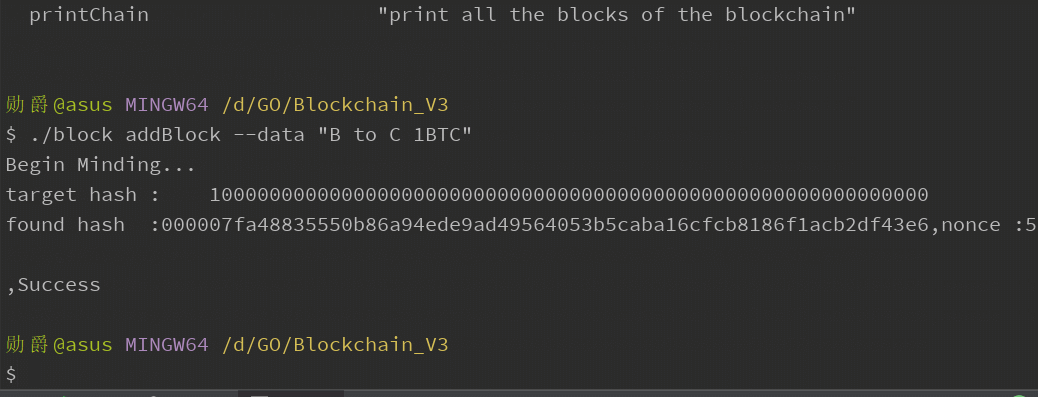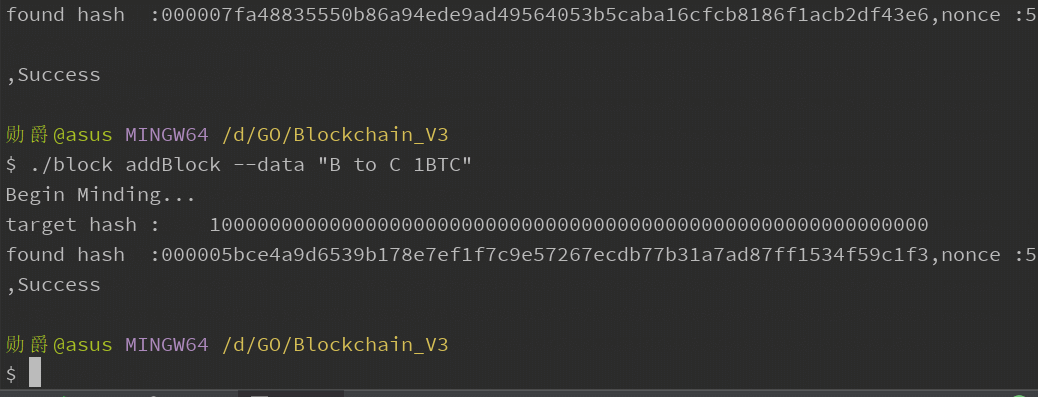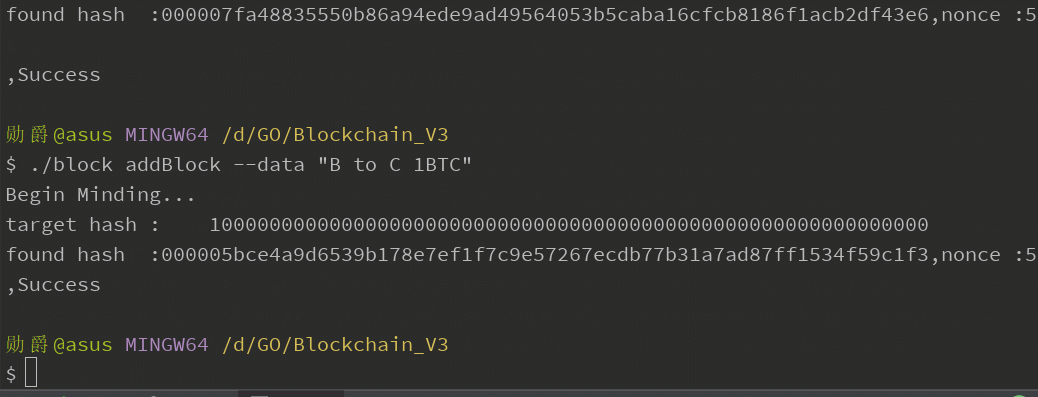
首先 go build 编译程序;输入不带--data参数的错误命令,查看提示。

输入交易信息,查看pow运算:
打印区块链已有区块信息:
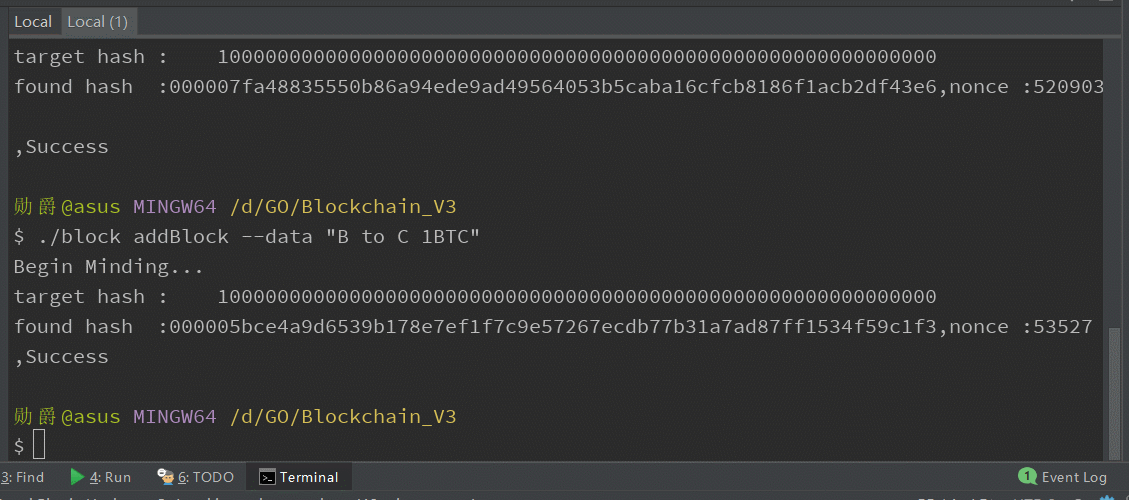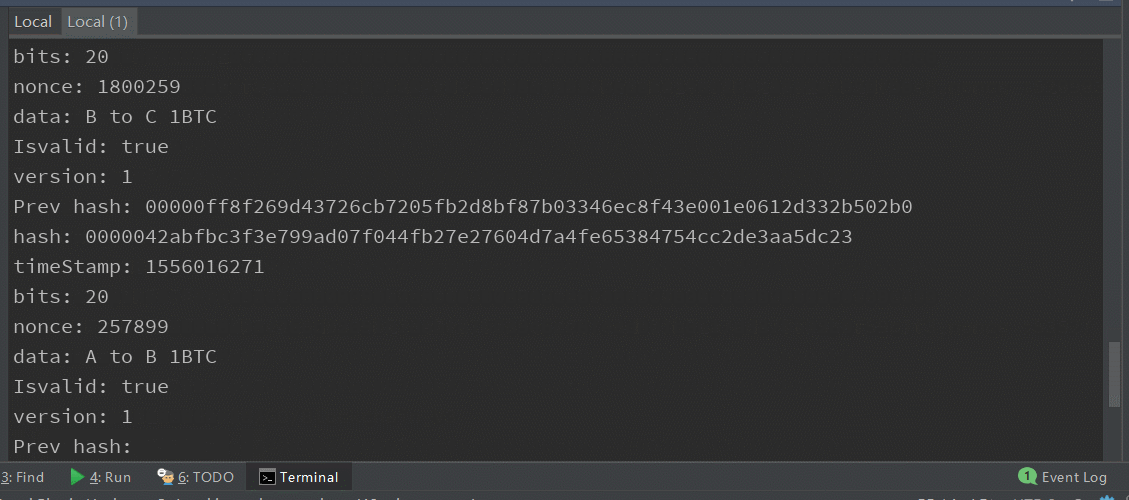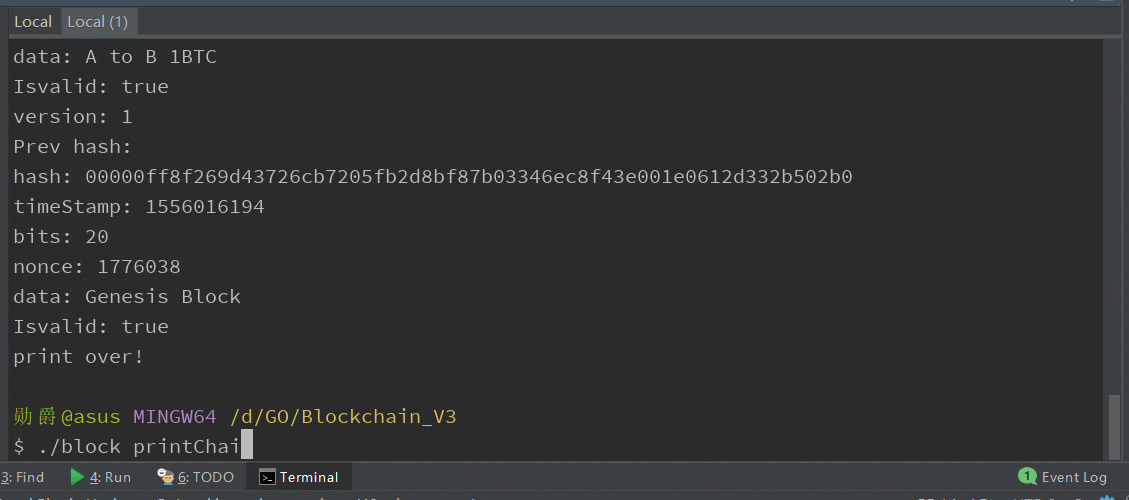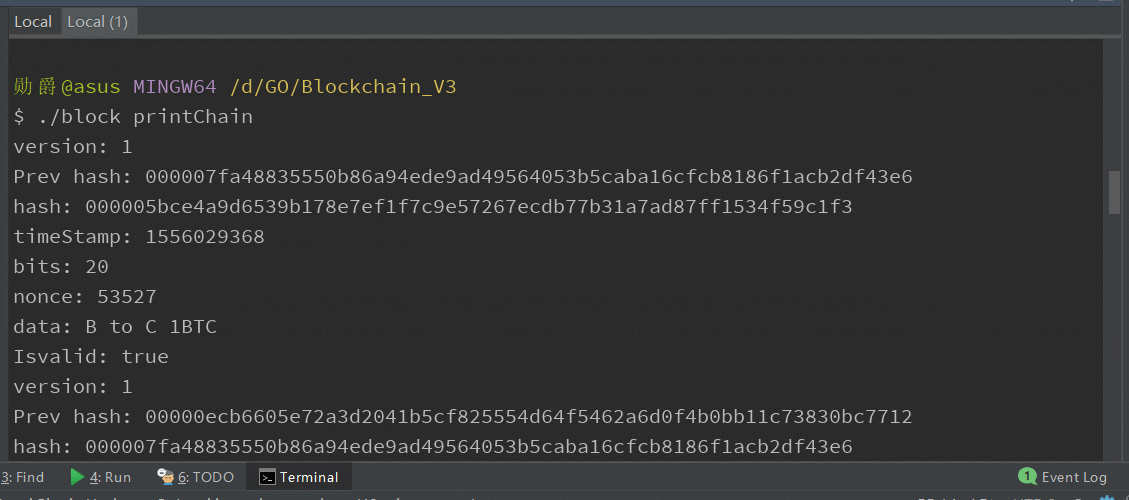
Reference:
最后要感谢Ivan Kuznetsov在GitHub社区的贡献!