| 班级 |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 实验要求|
| 实验目标|理解感知器算法原理,能实现感知器算法 |
| 学号 |3180701331|
一.实验目的
-
理解感知器算法原理,能实现感知器算法;
-
掌握机器学习算法的度量指标;
-
掌握最小二乘法进行参数估计基本原理;
-
针对特定应用场景及数据,能构建感知器模型并进行预测。
二.实验内容
-
安装Pycharm,注册学生版。
-
安装常见的机器学习库,如Scipy、Numpy、Pandas、Matplotlib,sklearn等。
-
编程实现感知器算法。
三、实验报告要求
按实验内容撰写实验过程;
报告中涉及到的代码,每一行需要有详细的注释;
按自己的理解重新组织,禁止粘贴复制实验内容!
四、实验代码结果及注释
In [1]:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris//载入Fisher的鸢尾花数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
In[2]:
# load data
iris = load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)//将列名设置为特征
df['label'] = iris.target//利用dataframe做简单的可视化分析
In[3]:
#
df.columns = ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label']// 选择其中的4个特征进行训练
df.label.value_counts()
Out[3]:
2 50
1 50
0 50
Name: label, dtype: int64
In[4]:
plt.scatter(df[:50]['sepal length'], df[:50]['sepal width'], label='0')
plt.scatter(df[50:100]['sepal length'], df[50:100]['sepal width'], label='1')
plt.xlabel('sepal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
plt.legend()
Out[4]:

In [5]:
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0, 1, -1]])//取前100条数据,为了方便展示,取2个特征
In [6]:
X, y = data[:,:-1], data[:,-1]// 数据类型转换,为了后面的数学计算
In [7]:
y = np.array([1 if i == 1 else -1 for i in y])
In [8]:
# 数据线性可分,二分类数据
# 此处为一元一次线性方程
class Model:
def __init__(self):
self.w = np.ones(len(data[0])-1, dtype=np.float32)
self.b = 0//设定初始w/b的值
self.l_rate = 0.1
# self.data = data
def sign(self, x, w, b):
y = np.dot(x, w) + b//求w,b的值
#Numpy中dot()函数主要功能有两个:向量点积和矩阵乘法。
return y
# 随机梯度下降法
#随机梯度下降法(SGD),随机抽取一个误分类点使其梯度下降。根据损失函数的梯度,对w,b进行更新
def fit(self, X_train, y_train): // #随机梯度下降法(SGD),随机抽取一个误分类点使其梯度下降。根据损失函数的梯度,对w,b进行更新
is_wrong = False//误分类点的意思就是开始的时候,超平面并没有正确划分,做了错误分类的数据。
while not is_wrong;
wrong_count = 0误分为0,就不用循环,得到w,b
for d in range(len(X_train)):
X = X_train[d]
y = y_train[d]
if y * self.sign(X, self.w, self.b) <= 0://如果某个样本出现分类错误,即位于分离超平面的错误侧,则调整参数,使分离超平面开始移动,直至误分类点被正确分类。
self.w = self.w + self.l_rate*np.dot(y, X)//通过数据调整w和b
self.b = self.b + self.l_rate*y
wrong_count += 1
if wrong_count == 0:
is_wrong = True
return 'Perceptron Model!'
#线性可分可用随机梯度下降法
def score(self):
pass
In [9]:
#拟合
perceptron = Model()
perceptron.fit(X, y)

In [10]:
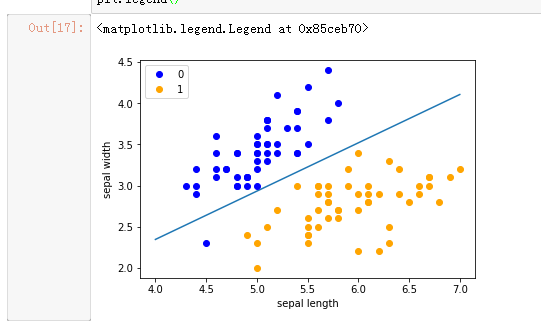
x_points = np.linspace(4, 7,10)
y_ = -(perceptron.w[0]*x_points + perceptron.b)/perceptron.w[1]
plt.plot(x_points, y_)
plt.plot(data[:50, 0], data[:50, 1], 'bo', color='blue', label='0')
plt.plot(data[50:100, 0], data[50:100, 1], 'bo', color='orange', label='1')
plt.xlabel('sepal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
plt.legend()

In [11]:
#定义感知机
from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron
In [12]:
#使用训练数据进行训练
clf = Perceptron(fit_intercept=False, max_iter=1000, shuffle=False)
#得到训练结果,权重矩阵
clf.fit(X, y)

In [13]:
# Weights assigned to the features.输出特征权重矩阵
print(clf.coef_)
[[ 74.6 -127.2]]
In [14]:
# 超平面的截距 Constants in decision function.
print(clf.intercept_)
[0.]
In [15]:
x_ponits = np.arange(4, 8)
y_ = -(clf.coef_[0][0]*x_ponits + clf.intercept_)/clf.coef_[0][1]
plt.plot(x_ponits, y_)
plt.plot(data[:50, 0], data[:50, 1], 'bo', color='blue', label='0')
plt.plot(data[50:100, 0], data[50:100, 1], 'bo', color='orange', label='1')
plt.xlabel('sepal length')
plt.ylabel('sepal width')
plt.legend()
五、实验小结
通过对本次感知机及其应用实验,我了解到了最小二乘估计法是对超定系统进行回归分析得到近似解的一种标准方法,即方程多于未知数。感知机模型的参数从输入层向输出层单向传播,整个网络中无反馈。感知机是最简单形式是因为只包含一层传播。其所涉及到的学习方法、损失函数求解以及优化方法是机器学习的核心思想。
在整个解中,最小二乘法使每个方程结果中残差的平方和最小化。感知机是一种分类学习器,他也是很多复杂算法的基础。