学习目标
1、深入理解OO程序设计的特征:继承、多态;
2、熟练掌握Java语言中基于类、继承技术构造程序的语法知识;
3、利用继承定义类设计程序,能够设计开发含有1个主类、2个以上用户自定义类的应用程序。
1、实验目的与要求
(1)进一步理解4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途;
(2)掌握Object类的常用API用法;
(3)掌握ArrayList类用法与常用API;
(4)掌握枚举类使用方法;
(5)结合本章知识,理解继承与多态性两个面向对象程序设计特征,并体会其优点;
(6)熟练掌握Java语言中基于类、继承技术构造程序的语法知识(ch1-ch5);
(7)利用已掌握Java语言程序设计知识,学习设计开发含有1个主类、2个以上用户自定义类的应用程序。
一、 理论学习部分
1、(1)访问限制修饰符有:private、protected和public
(2)使用关键字private修饰的成员变量或者方法称为私有变量和私有方法,该成员变量和方法只能在同一个类中被访问,不能够使用类名来操作这个私有变量和私有方法
(3)使用关键字protected修饰的成员变量或者方法称为受保护的成员变量和受保护的方法,在与该类同包的其他类中可以访问该成员变量与方法,可以通过类名来操作这个受保护的变量和受保护的方法,而且子类可以继承父类的受保护的成员变量与受保护的方法,子类可以访问在与子类同一个包中的从父类或者祖先中的继承过来的受保护的成员变量与受保护的方法
(4)使用关键字public修饰的成员变量或者方法称为共有变量和共有方法
(5)不能够使用private和protected来修饰一个类
2、Object:所有类的超类
(1)Object类是Java中所有类的祖先——每一个类都由它扩 展而来。在不给出超类的情况下,Java会自动把Object 作为要定义类的超类。
(2)equals方法、hashCode方法、toString方法
3、a.ArrayList定义
b.添加新元素
c.统计个数
d.调整大小
e.访问
f.增加与删除
4、枚举(enum)类型是Java 5新增的特性,它是一种新的类型,允许用常量来表示特定的数据片断,而且全部都以类型安全的形式来表示。
(2)声明枚举类
(3)为枚举类增加构造函数
(4)Enum类的API
5、继承设计的技巧
① 将公共操作和域放在超类。 ② 不要使用受保护的域。 ③ 使用继承实现“is-a”关系。 ④ 除非所有继承的方法都有意义,否则就不要 使用继承。 ⑤ 在覆盖方法时,不要改变预期的行为。 ⑥ 使用多态,而非类型信息。 ⑦ 不要过多地使用反射。
2、实验内容和步骤
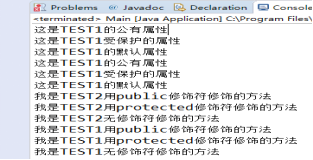
实验1 补充以下程序中主类内main方法体,以验证四种权限修饰符的用法。
public class TEST1 { private String t1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String t2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String t3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String t4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; private void test1() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void tese2() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void tese3() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void tese4() { System.out.println("我是TEST1无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }
public class TEST2 extends TEST1{ private String e1 = "这是TEST2的私有属性"; public String e2 = "这是TEST2的公有属性"; protected String e3 = "这是TEST2受保护的属性"; String e4 = "这是TEST2的默认属性"; public void demo1() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void demo2() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void demo3() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void demo4() { System.out.println("我是TEST2无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { TEST2 test2 = new TEST2(); /*在下面分别调用 demo1 demo2 demo3 demo4 test1 test2 test3 test4方法 和t1 t2 t3 t3 e1 e2 e3 e4属性,好好理解继承和权限修饰符的用法与区别*/
test2.demo1();
test2.demo3();
test2.demo4();
test2.tese2();
test2.tese3();
test2.tese4();
System.out.println(test2.e2); System.out.println(test2.e3); System.out.println(test2.e4); System.out.println(test2.t2); System.out.println(test2.t3); System.out.println(test2.t4); } }
实验2 第五章测试程序反思,继承知识总结。
测试程序1:
编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10(教材174页-177页);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Object类的定义及用法;
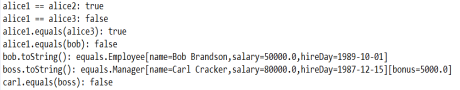
package inheritance; /** * This program demonstrates inheritance. * @version 1.21 2004-02-21 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ManagerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // construct a Manager object Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15);//Manager类定义类对象boss boss.setBonus(5000);//更改器更改 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3];//生成雇员对象 // fill the staff array with Manager and Employee objects用Manager和Employee对象人员子类填充员工数组 staff[0] = boss;//子类对象 staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); staff[2] = new Employee("Tommy Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); } }
package inheritance; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay;//定义属性 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); }//构造器构造Employee对象 public String getName() { return name; }//访问器 public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
package inheritance; public class Manager extends Employee//扩展 { private double bonus;//属性 /** * @param name the employee's name * @param salary the salary * @param year the hire year * @param month the hire month * @param day the hire day */ public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day);//调用的是父类参数 bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary();//用父类的getSalary获得的 return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double b)//更改器 { bonus = b; } }
结果如下:
测试程序2:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-11(教材182页);
Ÿ 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class. * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ArrayListTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array list with three Employee objects ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<>(); staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15)); staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1)); staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15)); // raise everyone's salary by 5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } }
package arrayList; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
结果如下:

测试程序3:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页);
结合运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
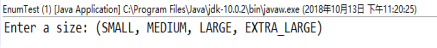
package enums; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates enumerated types. * @version 1.0 2004-05-24 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EnumTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) "); String input = in.next().toUpperCase(); Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); System.out.println("size=" + size); System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation()); if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE) System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _."); } } enum Size { SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; } public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation; }
结果如下:
实验总结:本次实验对上章继承的知识又一次进行了梳理和深化,也进一步理解了public、private、protected、默认4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途,实验方面是在上次实验的基础上进一步了解它的内容和深意,通过注释能更一步了解代码含义,在编程方面感觉还要更加努力,才能进步。