基础知识
VueX作用
VueX是一个数据仓库,它可以管理多个组件公用的数据。
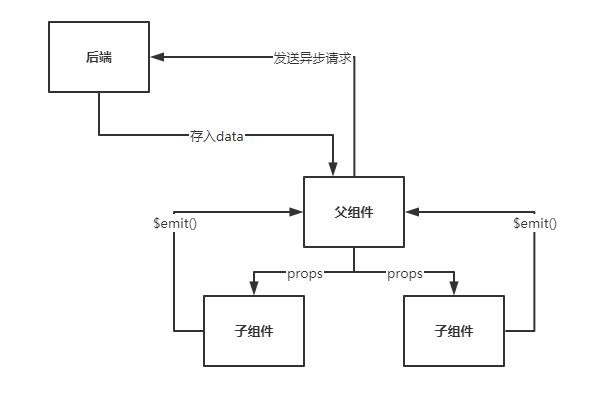
没有学习VueX的时候,子组件要向父级组件传递信息则通过$emit()自定义事件,父组件如果要向子组件传递信息则通过props。
这是一种单向的数据流,操纵起来比较麻烦。
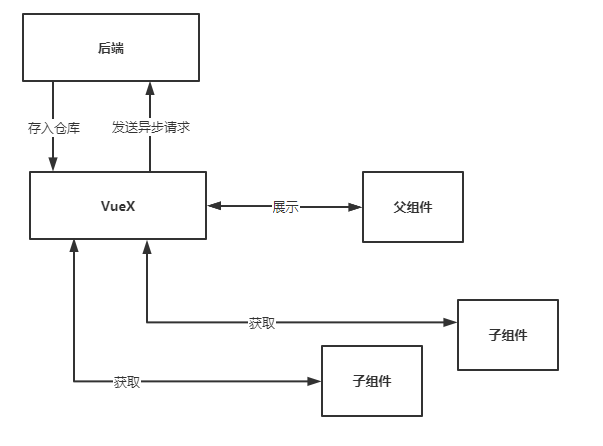
有了VueX一切都变得简单了,你只需要从VueX这个实例中中读取、操纵、修改模块仓库数据即可。
安装Vuex
这里是VueX官方文档提供的安装方法:
直接下载:
https://unpkg.com/vuex
CDN引入:
<script src="/path/to/vue.js"></script>
<script src="/path/to/vuex.js"></script>
NPM安装:
npm install vuex --save
state
定义仓库
使用state来定义一个仓库:
// 定义一个购物车模块,包含state仓库
const cart = {
state: {
commodity: [
{id: 1, name: "苹果手机", price: 399, num: 10},
{id: 2, name: "苹果电脑", price: 1399, num: 21},
]
},
}
// 实例化出Vuex对象使用模块化管理该购物车模块
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart,
}
})
// 根组件中注册Vuex实例
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store,
})
获取数据
如果想要拿到这个数据仓库,则组件要通过计算属性进行获取:
return this.$store.state.模块名.仓库内容
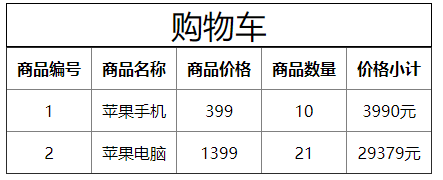
如下所示,子组件购物车进行内容展示:
<style>
th, td {
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cart></cart>
</div>
<!--购物车子组件模板-->
<template id="cart">
<div>
<table v-if="goods.length>0" border="1px" :style="{borderCollapse:'collapse'}">
<caption :style="{border:'1px solid #000',fontSize:'2rem'}">购物车</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>商品编号</th>
<th>商品名称</th>
<th>商品价格</th>
<th>商品数量</th>
<th>价格小计</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="item in goods">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td>{{item.num}}</td>
<td>{{item.num * item.price}}元</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h1 v-else>购物车没有任何商品</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script src="vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 定义一个购物车模块,包含state仓库
const cart = {
state: {
commodity: [
{id: 1, name: "苹果手机", price: 399, num: 10},
{id: 2, name: "苹果电脑", price: 1399, num: 21},
]
},
}
// 实例化出Vuex对象使用模块化管理该购物车模块
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart,
}
})
// 定义子组件
Vue.component("cart",{
template:`#cart`,
// 通过计算属性获取仓库内容
computed:{
goods(){
return this.$store.state.cart.commodity;
}
}
})
// 根组件中注册Vuex实例
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store,
})
</script>
</body>
getters
数据计算
如果我们要对仓库内容进行很复杂的计算,如在购物车下方添加上一个总价的话就需要在购物车模块中添加getters,并在其中定义方法。
它类似与仓库的计算属性,使用也很简单,子组件通过计算属性调用getters中定义的方法:
this.$store.getters.模块getters中定义的方法名
在getters中定义方法时,有一个必要参数state,它指向当前模块中的仓库state,如下所示:
const cart = {
state: {
...
},
getters: {
totalPrice(state) {
...
}
}
}
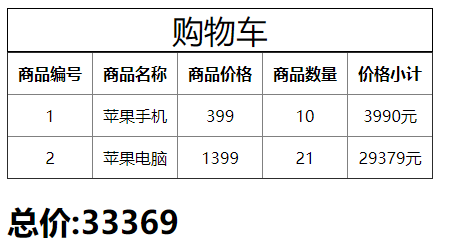
代码如下,我们新增了一个组件用于专门显示总价,而不拘泥于某一个组件。
<style>
th, td {
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cart></cart>
<total-price></total-price>
</div>
<!--购物车子组件模板-->
<template id="cart">
<div>
<table v-if="goods.length>0" border="1px" :style="{borderCollapse:'collapse'}">
<caption :style="{border:'1px solid #000',fontSize:'2rem'}">购物车</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>商品编号</th>
<th>商品名称</th>
<th>商品价格</th>
<th>商品数量</th>
<th>价格小计</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="item in goods">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td>{{item.num}}</td>
<td>{{item.num * item.price}}元</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h1 v-else>购物车没有任何商品</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script src="vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 定义一个购物车模块,包含state仓库
const cart = {
state: {
commodity: [
{id: 1, name: "苹果手机", price: 399, num: 10},
{id: 2, name: "苹果电脑", price: 1399, num: 21},
]
},
getters: {
totalPrice(state) {
return state.commodity.reduce((pre, cur) => {
return pre + cur.price * cur.num;
}, 0);
}
}
}
// 实例化出Vuex对象使用模块化管理该购物车模块
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart,
}
})
// 定义子组件
Vue.component("cart", {
template: `#cart`,
// 通过计算属性获取仓库内容
computed: {
goods() {
return this.$store.state.cart.commodity;
}
}
})
Vue.component("totalPrice", {
template: `
<div><h1>总价:{{ totalPrice }}</h1></div>`,
computed: {
totalPrice() {
return this.$store.getters.totalPrice
}
}
})
// 根组件中注册Vuex实例
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store,
})
</script>
</body>
数量变更
getters作为当前模块对仓库的计算属性,也是被动调用。
当仓库中的商品数量发生改变后它会重新进行计算,如下所示:
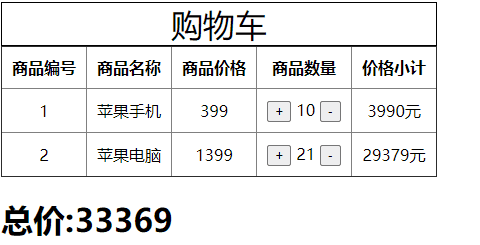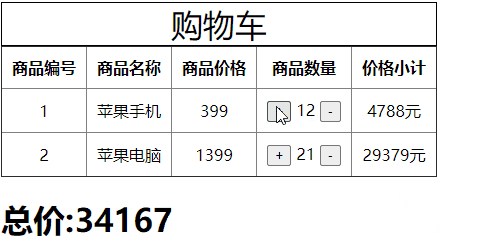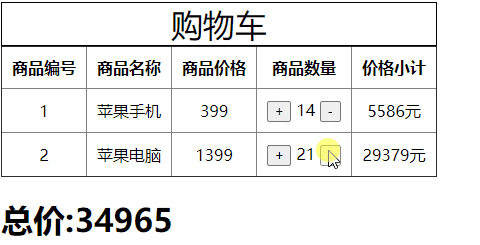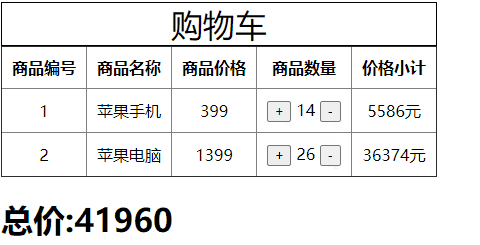
<td><button type="button" @click="item.num++" :style={marginRight:'5px'}>+</button>{{item.num}}<button @click="item.num++" type="button" :style={marginLeft:'5px'}>-</button></td>
mutation
操纵仓库
如果我们要对仓库内容进行变更,如删除购物车中的某一项商品那就需要在购物车模块中添加mutation,并在其中定义方法。
子组件通过methods与$store.commit()调用getters中定义的方法:
this.$store.commit('mutation中定义的方法', 参数)
在getters中定义方法时,有两个必要参数state与param,分别指向当前仓库和传入的数据,如下所示:
const cart = {
state: {
...
},
getters: {
totalPrice(state) {
...
}
},
mutations:{
del(state, param) {
...
}
}
}
代码如下,我们要删除购物车中的某一项商品。
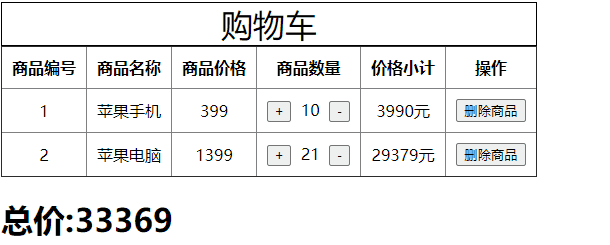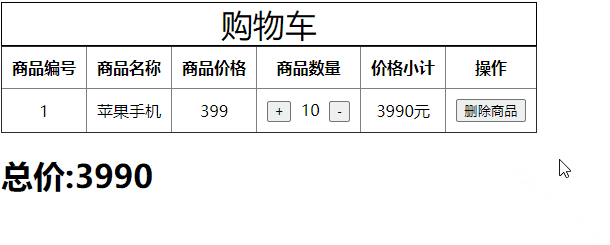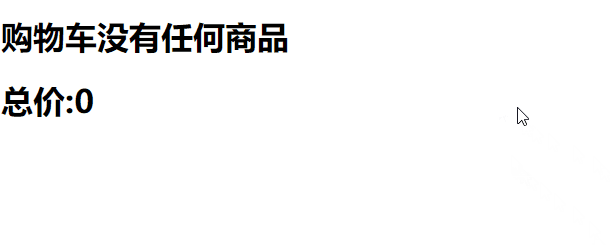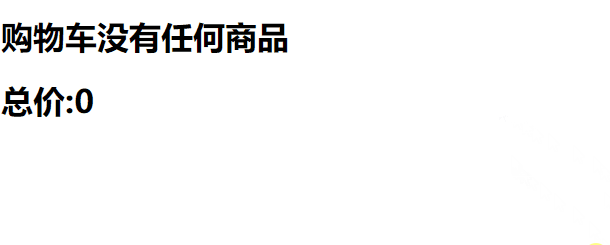
<style>
th, td {
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cart></cart>
<total-price></total-price>
</div>
<!--购物车子组件模板-->
<template id="cart">
<div>
<table v-if="goods.length>0" border="1px" :style="{borderCollapse:'collapse'}">
<caption :style="{border:'1px solid #000',fontSize:'2rem'}">购物车</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>商品编号</th>
<th>商品名称</th>
<th>商品价格</th>
<th>商品数量</th>
<th>价格小计</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="item in goods">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td>
<button type="button" @click="item.num++" :style={marginRight:'5px'}>+</button>
{{item.num}}
<button @click="item.num++" type="button" :style={marginLeft:'5px'}>-</button>
</td>
<td>{{item.num * item.price}}元</td>
<td>
<button type="button" @click="del(item.id)">删除商品</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h1 v-else>购物车没有任何商品</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script src="vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 定义一个购物车模块,包含state仓库
const cart = {
state: {
commodity: [
{id: 1, name: "苹果手机", price: 399, num: 10},
{id: 2, name: "苹果电脑", price: 1399, num: 21},
]
},
getters: {
totalPrice(state) {
return state.commodity.reduce((pre, cur) => {
return pre + cur.price * cur.num;
}, 0);
}
},
mutations: {
//删除购物车中的商品
del(state, param) {
// param传递过来的参数
for (let i = 0; i < state.commodity.length; i++) {
if (state.commodity[i].id == param) {
state.commodity.splice(i, 1); // splice是响应式的
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 实例化出Vuex对象使用模块化管理该购物车模块
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart,
}
})
// 定义子组件
Vue.component("cart", {
template: `#cart`,
// 通过计算属性获取仓库内容
computed: {
goods() {
return this.$store.state.cart.commodity;
}
},
// 通过methods与commit修改仓库内容
methods: {
del(id) {
this.$store.commit("del", id);
}
}
})
Vue.component("totalPrice", {
template: `
<div><h1>总价:{{ totalPrice }}</h1></div>`,
computed: {
totalPrice() {
return this.$store.getters.totalPrice
}
}
})
// 根组件中注册Vuex实例
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store,
})
</script>
</body>
actions
异步请求
在上面我们都是模拟的数据,如果要异步向后端请求数据则可以通过在模块中定义actions与方法。
在actions中定义方法时,有一个必要参数state,它指向当前的仓库,如下所示:
const cart = {
state: {
...
},
getters: {
totalPrice(state) {
...
}
},
mutations:{
del(state, param) {
...
}
}
actions: {
load(state) {
...
}
}
}
模块里actions中的方法需要通过$store.dispatch('方法名')触发,一般来说请求数据的流程如下:
- 在组件的钩子函数如created()或者mounted()中触发模块内actions中定义的异步请求数据方法load
- load方法再通过$store.commit()触发模块下mutation中定义的操纵仓库的方法,完成数据的更新
代码演示:
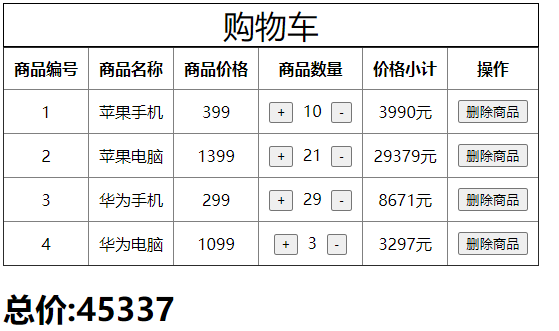
后端返回的数据:
return JsonResponse(
[
{"id": 1, "name": "苹果手机", "price": 399, "num": 10},
{"id": 2, "name": "苹果电脑", "price": 1399, "num": 21},
{"id": 3, "name": "华为手机", "price": 299, "num": 29},
{"id": 4, "name": "华为电脑", "price": 1099, "num": 3},
],safe=False,
)
Vue代码中,使用axios发送异步请求:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
完整代码如下:
<style>
th, td {
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cart></cart>
<total-price></total-price>
</div>
<!--购物车子组件模板-->
<template id="cart">
<div>
<table v-if="goods.length>0" border="1px" :style="{borderCollapse:'collapse'}">
<caption :style="{border:'1px solid #000',fontSize:'2rem'}">购物车</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>商品编号</th>
<th>商品名称</th>
<th>商品价格</th>
<th>商品数量</th>
<th>价格小计</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="item in goods">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td>
<button type="button" @click="item.num++" :style={marginRight:'5px'}>+</button>
{{item.num}}
<button @click="item.num++" type="button" :style={marginLeft:'5px'}>-</button>
</td>
<td>{{item.num * item.price}}元</td>
<td>
<button type="button" @click="del(item.id)">删除商品</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h1 v-else>购物车没有任何商品</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="vuex.js"></script>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 定义一个购物车模块,包含state仓库
const cart = {
state: {
commodity: []
},
getters: {
totalPrice(state) {
return state.commodity.reduce((pre, cur) => {
return pre + cur.price * cur.num;
}, 0);
}
},
mutations: {
//删除购物车中的商品
del(state, param) {
// param传递过来的参数
for (let i = 0; i < state.commodity.length; i++) {
if (state.commodity[i].id == param) {
state.commodity.splice(i, 1); // splice是响应式的
break;
}
}
},
// 设置商品
setCommodity(state, param) {
state.commodity = param.commodity
}
},
actions: {
load(store) {
// 通过axios获取数据,然后再交给mutations操纵仓库,填充数据
axios.post("http://127.0.0.1:8000/commodity/getAll/").then(function (response) {
store.commit('setCommodity', {commodity: response.data})
})
}
}
}
// 实例化出Vuex对象使用模块化管理该购物车模块
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart,
}
})
// 定义子组件
Vue.component("cart", {
template: `#cart`,
// 通过计算属性获取仓库内容
computed: {
goods() {
return this.$store.state.cart.commodity;
}
},
// 通过methods与commit修改仓库内容
methods: {
del(id) {
this.$store.commit("del", id);
}
},
// 钩子函数,组件初始化完成后调用,请求后台数据
mounted() {
this.$store.dispatch('load');
}
})
Vue.component("totalPrice", {
template: `
<div><h1>总价:{{ totalPrice }}</h1></div>`,
computed: {
totalPrice() {
return this.$store.getters.totalPrice
}
}
})
// 根组件中注册Vuex实例
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store,
})
</script>
</body>
modules
模块化管理
上面的例子中,我们一直都再做模块化管理。
// 购物车模块
const cart = {
state: {
...
},
getters: {
...
},
mutations: {
...
},
actions: {
...
}
}
// 仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart,
}
})
这代表你可以将购物车模块放到其他的一个文件中。
非模块化
如果使用非模块化管理则是这个样子的:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
...
},
getters: {
...
},
mutations: {
...
},
actions: {
...
}
})
// 根组件
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
store, // 根组件中注册
})
非模块化和模块化还是有一些调用区别的。
调用区别
当使用非模块化管理时,state仓库可以直接调用,而不用加模块名:
// 非模块化
return this.$store.state.仓库内容
// 必须加上模块名
return this.$store.state.模块名.仓库内容
这是因为非模块化管理时,state是全局定义的,而使用模块化管理时state则变成了局部定义,所以要加模块名。
其他的调用方式不变,他们依旧维持全局定义。
命名空间
如果有多个模块,你想在调用某一个模块下的getters/mutation/actions所定义的方法时加上模块名的前缀,则需要添加命名空间。
使用namespaced:true将getters/mutation/actions定义成局部方法:
const cart = {
namespaced:true, // 添加命名空间后,getters/mutation/actions都将变成局部的
state: {
...
},
getters: {
...
},
mutations: {
...
},
actions: {
...
}
}
对应的调用方式也要变:
this.$store.dispatch('actions下定义的方法');
变为
this.$store.dispatch('模块名/actions下定义的方法');
this.$store.getters.getters下定义的方法;
变为
this.$store.getters['模块名/getters下定义的方法'];
this.$store.commit('mutation下定义的方法', 参数)
变为
this.$store.commit('模块名/mutation下定义的方法', 参数)