题目描述
In an effort to better manage the grazing patterns of his cows, Farmer John has installed one-way cow paths all over his farm. The farm consists of N fields, conveniently numbered 1..N, with each one-way cow path connecting a pair of fields. For example, if a path connects from field X to field Y, then cows are allowed to travel from X to Y but not from Y to X.
Bessie the cow, as we all know, enjoys eating grass from as many fields as possible. She always starts in field 1 at the beginning of the day and visits a sequence of fields, returning to field 1 at the end of the day. She tries to maximize the number of distinct fields along her route, since she gets to eat the grass in each one (if she visits a field multiple times, she only eats the grass there once).
As one might imagine, Bessie is not particularly happy about the one-way restriction on FJ's paths, since this will likely reduce the number of distinct fields she can possibly visit along her daily route. She wonders how much grass she will be able to eat if she breaks the rules and follows up to one path in the wrong direction. Please compute the maximum number of distinct fields she can visit along a route starting and ending at field 1, where she can follow up to one path along the route in the wrong direction. Bessie can only travel backwards at most once in her journey. In particular, she cannot even take the same path backwards twice.
约翰有n块草场,编号1到n,这些草场由若干条单行道相连。奶牛贝西是美味牧草的鉴赏家,她想到达尽可能多的草场去品尝牧草。
贝西总是从1号草场出发,最后回到1号草场。她想经过尽可能多的草场,贝西在通一个草场只吃一次草,所以一个草场可以经过多次。因为草场是单行道连接,这给贝西的品鉴工作带来了很大的不便,贝西想偷偷逆向行走一次,但最多只能有一次逆行。问,贝西最多能吃到多少个草场的牧草。
输入输出格式
输入格式:INPUT: (file grass.in)
The first line of input contains N and M, giving the number of fields and the number of one-way paths (1 <= N, M <= 100,000).
The following M lines each describe a one-way cow path. Each line contains two distinct field numbers X and Y, corresponding to a cow path from X to Y. The same cow path will never appear more than once.
输入:
第一行:草场数n,道路数m。
以下m行,每行x和y表明有x到y的单向边,不会有重复的道路出现。
输出格式:OUTPUT: (file grass.out)
A single line indicating the maximum number of distinct fields Bessie
can visit along a route starting and ending at field 1, given that she can
follow at most one path along this route in the wrong direction.
输出:
一个数,逆行一次最多可以走几个草场。
输入输出样例
说明
SOLUTION NOTES:
Here is an ASCII drawing of the sample input:
v---3-->6
7 | |
^ v |
| 1 |
| | v
| v 5
4<--2---^Bessie can visit pastures 1, 2, 4, 7, 2, 5, 3, 1 by traveling
backwards on the path between 5 and 3. When she arrives at 3 she
cannot reach 6 without following another backwards path.
....调了一节晚自习,不想说话QAQ
这道题是求在一个有向图中从1开始最多逆行一次后回到1可经过的最大牧场数。
思路:
tarjan缩点后,最终路径一定是由1所在点集A到达点集B逆行一次到达点集C后回到A(其中B,C不是必须存在)。形如:
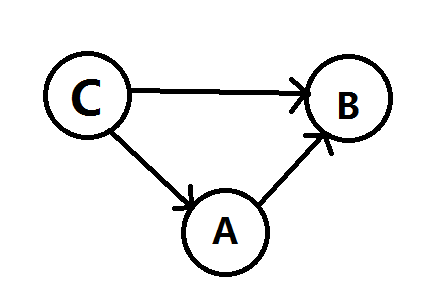
把边存正反两套,由A向外延正边把每个能到达的B和A到B之间的点数记录下来,再延反边找到每个C,同时找出每个C能延正边到达的B。 A+C+B的最大值即为所求
做法
- tarjan缩点
- 将缩点重新构图,同时存下每条边的反边
- 用两遍dfs找出所有找BC时可以经过的边
- 穷举每一条边找出每一个点的入度
- 进行第一遍拓扑排序标记每一个可达的B并求出每个A到B经过的最大点数
- 第二遍拓扑排序找出A延反边到达的C同时穷举每个C能到达的B求出最大值
- happy end
我又双叒叕一次把tarjan写崩了(QAQ)一通乱改后dfs也崩了(内牛满面
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int x,y,cnt,i,m,n,j,k,ver[2][100001],nex[2][100001],head[2][100001],ss[2][100001];
int ans,dfn[100001],low[100001],sta[100001],top,u,f[100001],size[100001],maxx,r[2][100001];
bool vis[100001],b[2][100001];
void add(int x,int y)
{
cnt+=1;
ver[0][cnt]=y; ver[1][cnt]=x;
nex[0][cnt]=head[0][x]; nex[1][cnt]=head[1][y];
head[0][x]=head[1][y]=cnt;
}
void tarjan(int x)
{
cnt+=1; low[x]=dfn[x]=cnt;
vis[x]=1; sta[++top]=x;
for(int i=head[0][x];i;i=nex[0][i])
{
int t=ver[0][i];
if(!dfn[t])
{
tarjan(t);
low[x]=min(low[x],low[t]);
}
else if(vis[t]) low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[t]);
}
if(dfn[x]==low[x])
{
u+=1;
do
{
f[sta[top]]=u;
size[u]+=1;
vis[sta[top]]=0;
}while(sta[top--]!=x);
}
}
void dfs(int x,int y)
{
for(int i=head[y][x];i;i=nex[y][i])
if(!b[y][i])
{
b[y][i]=1;
dfs(ver[y][i],y);
}
}
void topo(int x)
{
vis[x]=1;
for(int i=head[0][x];i;i=nex[0][i])
{
int t=ver[0][i];
r[0][t]-=1;
ss[0][t]=max(ss[0][t],ss[0][x]+size[t]);
if(!r[0][t]) topo(t);
}
}
void topp(int x)
{
for(int i=head[0][x];i;i=nex[0][i])
if(vis[ver[0][i]]) ans=max(ans,ss[1][x]+ss[0][ver[0][i]]);
for(int i=head[1][x];i;i=nex[1][i])
{
int t=ver[1][i];
r[1][t]-=1;
ss[1][t]=max(ss[1][t],ss[1][x]+size[t]);
if(!r[1][t]) topp(t);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y);
}
cnt=0;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++) if(!dfn[i])tarjan(i);
cnt=0;
memset(head,0,sizeof(head)); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
if(f[ver[0][i]]!=f[ver[1][i]])
add(f[ver[1][i]],f[ver[0][i]]);
dfs(f[1],0); dfs(f[1],1); m=cnt; cnt=0;
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int g=ver[0][i],h=ver[1][i];
if(b[0][i]) r[0][g]+=1;
if(b[1][i]) r[1][h]+=1;
}
topo(f[1]);
topp(f[1]);
printf("%d",ans+size[f[1]]);
}