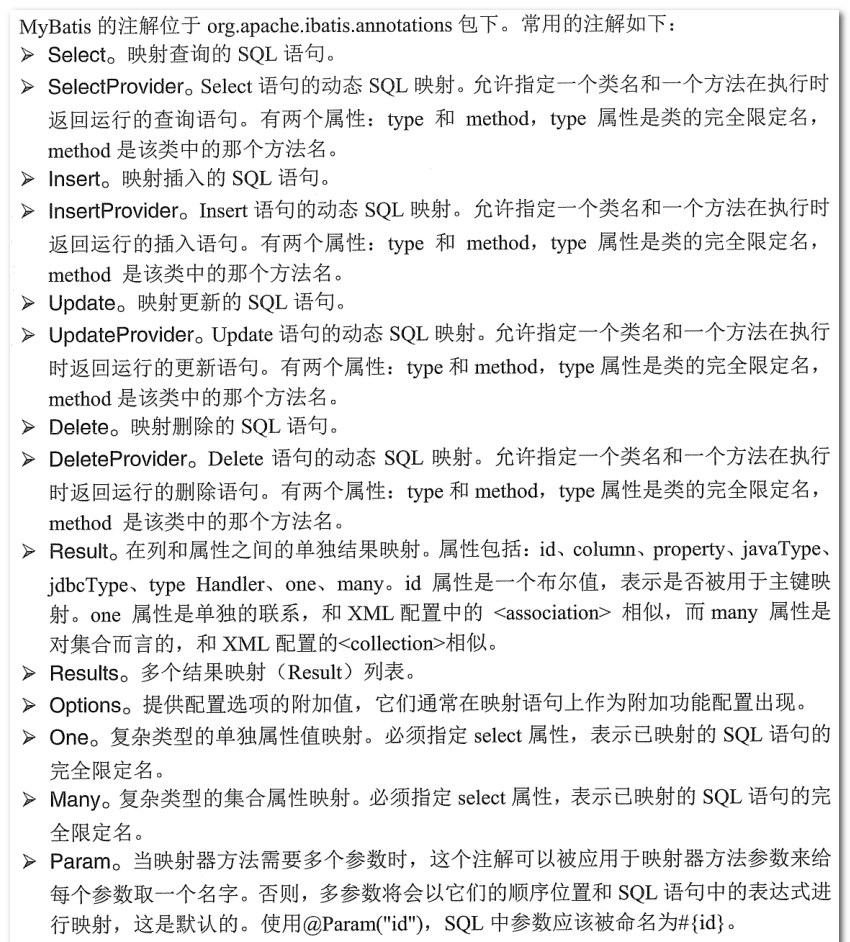
1、常用的注解。
2、@insert、@delete、@update、@select完成常见的CRUD操作。
import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Options; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Result; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Results; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update; import com.lfy.bean.User; public interface UserMapper { @Insert("INSERT INTO TB_USER(name,sex,age) VALUES(#{name},#{sex},#{age})") @Options(useGeneratedKeys=true,keyProperty="id") // @SelectKey(before=false,keyProperty="id",resultType=Integer.class, // statement="SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() AS id") int saveUser(User user); //@Param指定参数的名称,如果没有,则按顺序对应语句中的参数
@Delete("DELETE FROM TB_USER WHERE id = #{id}") int removeUser(@Param("id") Integer id); @Update("UPDATE TB_USER SET name = #{name},sex = #{sex},age = #{age} WHERE id = #{id}") void modifyUser(User user); //如果属性列的名称一致,可以省略@Result
@Select("SELECT * FROM TB_USER WHERE id = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(id=true,column="id",property="id"), @Result(column="name",property="name"), @Result(column="sex",property="sex"), @Result(column="age",property="age") }) User selectUserById(@Param("id") Integer id); @Select("SELECT * FROM TB_USER ") List<User> selectAllUser(); }
public class InsertTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义SqlSession变量 SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { // 创建SqlSession实例 sqlSession = FKSqlSessionFactory.getSqlSession(); // 创建UserMapper实例 UserMapper um = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); // 创建User对象并设置属性 User user = new User(); user.setName("test"); user.setSex("男"); user.setAge(18); // 插入数据 um.saveUser(user); // 查看插入数据生成的主键 System.out.println("插入数据生成的主键id为:" + user.getId()); // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { // 回滚事务 sqlSession.rollback(); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { // 关闭SqlSession if(sqlSession != null) sqlSession.close(); } } }
2、1对1。
public interface CardMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM TB_CARD WHERE ID = #{id} ") Card selectCardById(Integer id); }
public interface PersonMapper { //TB_PERSON表中有个字段card_id
@Select("SELECT * FROM TB_PERSON WHERE ID = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(id=true,column="id",property="id"), @Result(column="name",property="name"), @Result(column="sex",property="sex"), @Result(column="age",property="age"), @Result(column="card_id",property="card", one=@One( select="com.lfy.mapping.CardMapper.selectCardById", fetchType=FetchType.EAGER)) }) Person selectPersonById(Integer id); }
one属性表示是一对一关联关系,@One注解的select属性表示需要关联执行的SQL语句,fetchType表示查询的类型是立即加载还是懒加载。
3、1对多
public interface StudentMapper { // 根据班级id查询班级所有学生 @Select("SELECT * FROM TB_STUDENT WHERE CLAZZ_ID = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(id=true,column="id",property="id"), @Result(column="name",property="name"), @Result(column="sex",property="sex"), @Result(column="age",property="age") }) List<Student> selectByClazzId(Integer clazz_id); }
public interface ClazzMapper { // 根据id查询班级信息 @Select("SELECT * FROM TB_CLAZZ WHERE ID = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(id=true,column="id",property="id"), @Result(column="code",property="code"), @Result(column="name",property="name"), @Result(column="id",property="students", many=@Many( select="com.lfy.mapping.StudentMapper.selectByClazzId", fetchType=FetchType.LAZY)) }) Clazz selectById(Integer id); }
column="id"表示会将id作为查询条件,传递到查询班级下所有学生的查询中。many属性表示是一对多关联关系
4、多对多
订单只会属于某一用户,订单对用户是1对1关系;订单里面会有很多商品,一个订单对商品是1对多的关系。所以查询订单信息利用上面两种关联关系组合查询。
public interface OrderMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM TB_ORDER WHERE ID = #{id}") @Results({ @Result(id=true,column="id",property="id"), @Result(column="code",property="code"), @Result(column="total",property="total"), @Result(column="user_id",property="user", one=@One(select="com.lfy.mapping.UserMapper.selectById", fetchType=FetchType.EAGER)), @Result(column="id",property="articles", many=@Many(select="com.lfy.mapping.ArticleMapper.selectByOrderId", fetchType=FetchType.LAZY)) }) Order selectById(Integer id); }
5、动态SQL
比较繁琐,不够直观简便,暂放弃整理。