在Android中,消息的传递控制主要是通过两个方法共同配合使用来对用户的触摸消息进行分发的,下面就来看看这两个方法;
- onInterceptTouchEvent:此方法定义于ViewGroup中,顾名思义,这个方法是用于ViewGroup拦截(intercept)触摸消息的;
- onTouchEvent:此方法定义于View中,用于处理用户的触摸事件;
下面来看这两个方法的定义原型;
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev); public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event);
这两个方法的一个共同点就是都有一个参数MotionEvent用于获取触摸事件的具体信息(比如按下,移动等等消息形态)和函数返回值(用于控制不同场合的触摸处理);
简单说一下MotionEvent,它包含了用户触摸消息的类型,常用的几种触摸消息类型为:ACTION_DOWN,ACTION_MOVE,ACTION_UP,ACTION_CANCEL, 分别表示触摸按下,移动,结束的状态;这几种消息类型不是并发产生的,而是如同触摸发生的次序一样有序产生的,DOWN->MOVE->UP/CANCEL;
下边通过一个例子来研究,分别自定义一个简单的ViewGroup和View,用于跟踪onTouchEvent和onInterceptTouchEvent的执行;
LLinearLayout
public class LLinearLayout extends LinearLayout { public LLinearLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } public LLinearLayout(Context context) { super(context); } private float lastY; @Override public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { String tag = "onInterceptTouchEvent"; Log.w(tag, "" + super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev)); switch (ev.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.w(tag, "ACTION_DOWN"); lastY = ev.getX(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.w(tag, "ACTION_MOVE"); if (ev.getX() - lastY > 20) { Log.w(tag, "ACTION_MOVE>20"); return true; } break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: Log.w(tag, "ACTION_UP"); break; } return false; } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { Log.w("onTouchEvent", "" + super.onTouchEvent(event)); return false; } }
LView
public class LView extends ImageView { public LView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } public LView(Context context) { super(context); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { String tag = "LView.onTouchEvent"; Log.e(tag, "" + super.onTouchEvent(event)); switch (event.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: Log.e(tag, "ACTION_DOWN"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: Log.e(tag, "ACTION_MOVE"); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: Log.e(tag, "ACTION_UP"); break; } return false; } }
在xml文件中将LView加入LLinearLayout中,通过一系列更改来一控究竟;
step1:
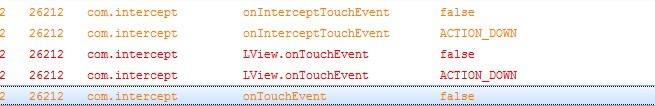
通过上面的Log信息,可以看出,触摸事件先被LLinearLayout拦截到(onInterceptTouchEvent),在这个Demo中,该方法返回值为false,接着就将Touch事件传递给LView,LView的onTouchEvent响应了此次触摸事件,并且也返回false;然后Touch事件再传递给LLinearLayout的onTouchEvent进行处理;
从上面我们可以简单的看出,Touch事件先被LLinearLayout拦截到,然后传递给LView,LView执行onTouchEvent处理逻辑;然后LLinearLayout再执行自己的onTouchEvent处理逻辑;@1
step2:将上面LLinearLayout的onInterceptTouchEvent方法返回值改为true,再次运行程序;

相比上面的Log信息,可以看到消息没有传递到LView;到这里,应该可以得出一个小小的结论了吧;
ViewGroup里面的onInterceptTouchEvent返回值,返回true表示拦截Touch事件,不再将Touch事件传递给ViewGroup里面的子View;
WVPJ6SJ[D]}DW)9AJNJCP.jpg)
step3: 回到step1,将LView中onTouchEvent返回值改为true,再次运行程序,手指从屏幕右滑到左;
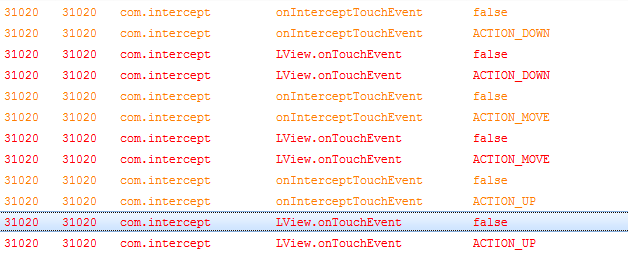
从Log信息中,可以看出,LView的onTouchEvent返回值为true时,LView的触摸事件从DOWN传递到了MOVE,再传递到UP;当然,整个过程都是先由LLinearLayout的onInterceptTouchEvent先接收到Touch事件,在这里,并没有拦截Touch事件,而是将Touch事件传递给子View;细心的朋友可能会发现,在这里,并没有执行到LLinearLayout的onTouchEvent方法,why?其实是因为LView的onTouchEvent事件返回了true,表示处理消耗了此事件,不再继续传递,也就不执行到LLinearLayout的onTouchEvent方法;
结论:View的onTouchEvent返回值表示是否将继续传递Touch事件,比如如果返回true,触摸形态将会从DOWN传递到MOVE再到UP(这里这个说法其实不严谨,这里指的是整个onTouchEvent方法返回值都是true,而没有分段返回,比如在MOVE形态时返回了false);
step4:继续step3,运行程序,手指从屏幕左滑到右;
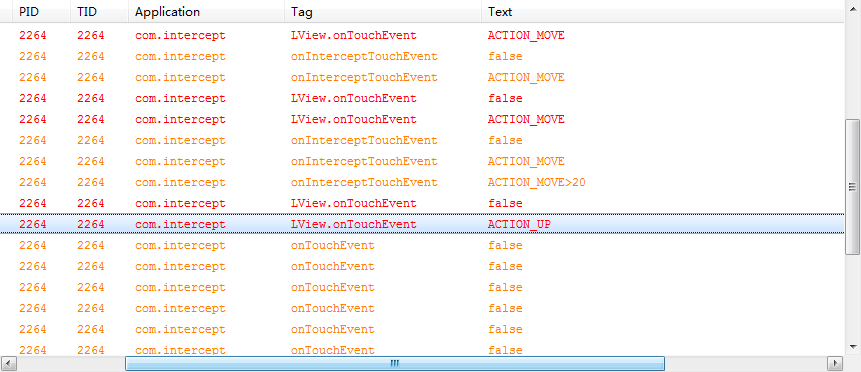
在LLinearLayout的onInterceptTouchEvent中,如果MOVE消息向右滑动距离大于20,则将拦截Touch事件,所以,在事件被拦截后,将不会再像step3中,MOVE消息会在LView的onTouchEvent中不断传递,而是被中断,触摸形态变为到ACTION_UP即手指抬起(其实这里这样说是不对的,准确的说是触摸形态变为ACTION_CANCEL,因为我将UP和CANCEL处理为一类,所以如上图,打印出来的Log信息为ACTION_UP,实际上它本质是ACTION_CANCEL);然后由于ACTION_MOVE被拦截,所以在手指MOVE的时候LLinearLayout的onTouchEevent不断被调用;
结尾总结:
ViewGroup里的onInterceptTouchEvent默认值是false,只有当返回值是false的时候,Touch事件才传给子View,然后调用到子View的onTouchEvent;返回值为true的时候,将拦截用户Touch事件,子View则捕获不到触摸事件;
View的onTouchEvent方法,当返回值为true的时候,事件将继续往下传递,由ACTION_DOWN传递到ACTION_MOVE再到ACTION_UP,反之如果返回值为false,则只会捕获到MotionEvent的ACTION_DOWN形态;