这篇文章给大家分享的内容是关于Swoft 源码剖析之Swoole和Swoft的一些介绍(Task投递/定时任务篇),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下。
前言
Swoft的任务功能基于Swoole的Task机制,或者说Swoft的Task机制本质就是对Swoole的Task机制的封装和加强。
我的官方群点击此处。
任务投递
//SwoftTaskTask.php class Task { /** * Deliver coroutine or async task * * @param string $taskName * @param string $methodName * @param array $params * @param string $type * @param int $timeout * * @return bool|array * @throws TaskException */ public static function deliver(string $taskName, string $methodName, array $params = [], string $type = self::TYPE_CO, $timeout = 3) { $data = TaskHelper::pack($taskName, $methodName, $params, $type); if(!App::isWorkerStatus() && !App::isCoContext()){ return self::deliverByQueue($data);//见下文Command章节 } if(!App::isWorkerStatus() && App::isCoContext()){ throw new TaskException('Please deliver task by http!'); } $server = App::$server->getServer(); // Delier coroutine task if ($type == self::TYPE_CO) { $tasks[0] = $data; $prifleKey = 'task' . '.' . $taskName . '.' . $methodName; App::profileStart($prifleKey); $result = $server->taskCo($tasks, $timeout); App::profileEnd($prifleKey); return $result; } // Deliver async task return $server->task($data); } }
任务投递Task::deliver()将调用参数打包后根据$type参数通过Swoole的$server->taskCo()或$server->task()接口投递到Task进程。Task本身始终是同步执行的,$type仅仅影响投递这一操作的行为,Task::TYPE_ASYNC对应的$server->task()是异步投递,Task::deliver()调用后马上返回;Task::TYPE_CO对应的$server->taskCo()是协程投递,投递后让出协程控制,任务完成或执行超时后Task::deliver()才从协程返回。
任务执行
//SwoftTaskBootstrapListenersTaskEventListener /** * The listener of swoole task * @SwooleListener({ * SwooleEvent::ON_TASK, * SwooleEvent::ON_FINISH, * }) */ class TaskEventListener implements TaskInterface, FinishInterface { /** * @param SwooleServer $server * @param int $taskId * @param int $workerId * @param mixed $data * @return mixed * @throws InvalidArgumentException */ public function onTask(Server $server, int $taskId, int $workerId, $data) { try { /* @var TaskExecutor $taskExecutor*/ $taskExecutor = App::getBean(TaskExecutor::class); $result = $taskExecutor->run($data); } catch (Throwable $throwable) { App::error(sprintf('TaskExecutor->run %s file=%s line=%d ', $throwable->getMessage(), $throwable->getFile(), $throwable->getLine())); $result = false; // Release system resources App::trigger(AppEvent::RESOURCE_RELEASE); App::trigger(TaskEvent::AFTER_TASK); } return $result; } }
此处是swoole.onTask的事件回调,其职责仅仅是将将Worker进程投递来的打包后的数据转发给TaskExecutor。
Swoole的Task机制的本质是Worker进程将耗时任务投递给同步的Task进程(又名TaskWorker)处理,所以swoole.onTask的事件回调是在Task进程中执行的。上文说过,Worker进程是你大部分HTTP服务代码执行的环境,但是从TaskEventListener.onTask()方法开始,代码的执行环境都是Task进程,也就是说,TaskExecutor和具体的TaskBean都是执行在Task进程中的。
//SwoftTaskTaskExecutor /** * The task executor * * @Bean() */ class TaskExecutor { /** * @param string $data * @return mixed */ public function run(string $data) { $data = TaskHelper::unpack($data); $name = $data['name']; $type = $data['type']; $method = $data['method']; $params = $data['params']; $logid = $data['logid'] ?? uniqid('', true); $spanid = $data['spanid'] ?? 0; $collector = TaskCollector::getCollector(); if (!isset($collector['task'][$name])) { return false; } list(, $coroutine) = $collector['task'][$name]; $task = App::getBean($name); if ($coroutine) { $result = $this->runCoTask($task, $method, $params, $logid, $spanid, $name, $type); } else { $result = $this->runSyncTask($task, $method, $params, $logid, $spanid, $name, $type); } return $result; } }
任务执行思路很简单,将Worker进程发过来的数据解包还原成原来的调用参数,根据$name参数找到对应的TaskBean并调用其对应的task()方法。其中TaskBean使用类级别注解@Task(name="TaskName")或者@Task("TaskName")声明。
值得一提的一点是,@Task注解除了name属性,还有一个coroutine属性,上述代码会根据该参数选择使用协程的runCoTask()或者同步的runSyncTask()执行Task。但是由于而且由于Swoole的Task进程的执行是完全同步的,不支持协程,所以目前版本请该参数不要配置为true。同样的在TaskBean中编写的任务代码必须的同步阻塞的或者是要能根据环境自动将异步非阻塞和协程降级为同步阻塞的
从Process中投递任务
前面我们提到:
Swoole的Task机制的本质是Worker进程将耗时任务投递给同步的Task进程(又名TaskWorker)处理。
换句话说,Swoole的$server->taskCo()或$server->task()都只能在Worker进程中使用。
这个限制大大的限制了使用场景。 如何能够为了能够在Process中投递任务呢?Swoft为了绕过这个限制提供了Task::deliverByProcess()方法。其实现原理也很简单,通过Swoole的$server->sendMessage()方法将调用信息从Process中投递到Worker进程中,然后由Worker进程替其投递到Task进程当中,相关代码如下:
//SwoftTaskTask.php /** * Deliver task by process * * @param string $taskName * @param string $methodName * @param array $params * @param string $type * @param int $timeout * @param int $workId * * @return bool */ public static function deliverByProcess(string $taskName, string $methodName, array $params = [], int $timeout = 3, int $workId = 0, string $type = self::TYPE_ASYNC): bool { /* @var PipeMessageInterface $pipeMessage */ $server = App::$server->getServer(); $pipeMessage = App::getBean(PipeMessage::class); $data = [ 'name' => $taskName, 'method' => $methodName, 'params' => $params, 'timeout' => $timeout, 'type' => $type, ]; $message = $pipeMessage->pack(PipeMessage::MESSAGE_TYPE_TASK, $data); return $server->sendMessage($message, $workId); }
数据打包后使用$server->sendMessage()投递给Worker:
//SwoftBootstrapServerServerTrait.php /** * onPipeMessage event callback * * @param SwooleServer $server * @param int $srcWorkerId * @param string $message * @return void * @throws InvalidArgumentException */ public function onPipeMessage(Server $server, int $srcWorkerId, string $message) { /* @var PipeMessageInterface $pipeMessage */ $pipeMessage = App::getBean(PipeMessage::class); list($type, $data) = $pipeMessage->unpack($message); App::trigger(AppEvent::PIPE_MESSAGE, null, $type, $data, $srcWorkerId); }
$server->sendMessage后,Worker进程收到数据时会触发一个swoole.pipeMessage事件的回调,Swoft会将其转换成自己的swoft.pipeMessage事件并触发.
//SwoftTaskEventListenersPipeMessageListener.php /** * The pipe message listener * * @Listener(event=AppEvent::PIPE_MESSAGE) */ class PipeMessageListener implements EventHandlerInterface { /** * @param SwoftEventEventInterface $event */ public function handle(EventInterface $event) { $params = $event->getParams(); if (count($params) < 3) { return; } list($type, $data, $srcWorkerId) = $params; if ($type != PipeMessage::MESSAGE_TYPE_TASK) { return; } $type = $data['type']; $taskName = $data['name']; $params = $data['params']; $timeout = $data['timeout']; $methodName = $data['method']; // delever task Task::deliver($taskName, $methodName, $params, $type, $timeout); } }
swoft.pipeMessage事件最终由PipeMessageListener处理。在相关的监听其中,如果发现swoft.pipeMessage事件由Task::deliverByProcess()产生的,Worker进程会替其执行一次Task::deliver(),最终将任务数据投递到TaskWorker进程中。
一道简单的回顾练习:从Task::deliverByProcess()到某TaskBean 最终执行任务,经历了哪些进程,而调用链的哪些部分又分别是在哪些进程中执行?
从Command进程或其子进程中投递任务
//SwoftTaskQueueTask.php /** * @param string $data * @param int $taskWorkerId * @param int $srcWorkerId * * @return bool */ public function deliver(string $data, int $taskWorkerId = null, $srcWorkerId = null) { if ($taskWorkerId === null) { $taskWorkerId = mt_rand($this->workerNum + 1, $this->workerNum + $this->taskNum); } if ($srcWorkerId === null) { $srcWorkerId = mt_rand(0, $this->workerNum - 1); } $this->check(); $data = $this->pack($data, $srcWorkerId); $result = msg_send($this->queueId, $taskWorkerId, $data, false); if (!$result) { return false; } return true; }
对于Command进程的任务投递,情况会更复杂一点。
上文提到的Process,其往往衍生于Http/Rpc服务,作为同一个Manager的子孙进程,他们能够拿到SwooleServer的句柄变量,从而通过$server->sendMessage(),$server->task()等方法进行任务投递。
但在Swoft的体系中,还有一个十分路人的角色: Command。Command的进程从shell或cronb独立启动,和Http/Rpc服务相关的进程没有亲缘关系。因此Command进程以及从Command中启动的Process进程是没有办法拿到SwooleServer的调用句柄直接通过UnixSocket进行任务投递的。
为了为这种进程提供任务投递支持,Swoft利用了Swoole的Task进程的一个特殊功能----消息队列。
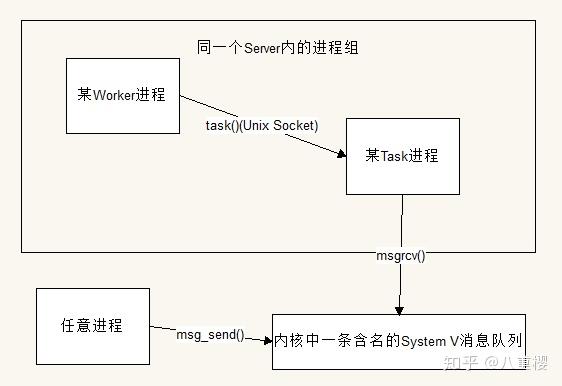
同一个项目中Command和HttpRpcServer 通过约定一个message_queue_key获取到系统内核中的同一条消息队列,然后Comand进程就可以通过该消息队列向Task进程投递任务了。
该机制没有提供对外的公开方法,仅仅被包含在Task::deliver()方法中,Swoft会根据当前环境隐式切换投递方式。但该消息队列的实现依赖Semaphore拓展,如果你想使用,需要在编译PHP时加上--enable-sysvmsg参数。
定时任务
除了手动执行的普通任务,Swoft还提供了精度为秒的定时任务功能用来在项目中替代Linux的Crontab功能.
Swoft用两个前置Process---任务计划进程:CronTimerProcess和任务执行进程CronExecProcess
,和两张内存数据表-----RunTimeTable(任务(配置)表)OriginTable((任务)执行表)用于定时任务的管理调度。
两张表的每行记录的结构如下:
\SwoftTaskCrontabTableCrontab.php /** * 任务表,记录用户配置的任务信息 * 表每行记录包含的字段如下,其中`rule`,`taskClass`,`taskMethod`生成key唯一确定一条记录 * @var array $originStruct */ private $originStruct = [ 'rule' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 100],//定时任务执行规则,对应@Scheduled注解的cron属性 'taskClass' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 255],//任务名 对应@Task的name属性(默认为类名) 'taskMethod' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 255],//Task方法,对应@Scheduled注解所在方法 'add_time' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 11],//初始化该表内容时的10位时间戳 ]; /** * 执行表,记录短时间内要执行的任务列表及其执行状态 * 表每行记录包含的字段如下,其中`taskClass`,`taskMethod`,`minute`,`sec`生成key唯一确定一条记录 * @var array $runTimeStruct */ private $runTimeStruct = [ 'taskClass' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 255],//同上 'taskMethod' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 255],//同上 'minute' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 20],//需要执行任务的时间,精确到分钟 格式date('YmdHi') 'sec' => [SwooleTable::TYPE_STRING, 20],//需要执行任务的时间,精确到分钟 10位时间戳 'runStatus' => [SwooleTABLE::TYPE_INT, 4],//任务状态,有 0(未执行) 1(已执行) 2(执行中) 三种。 //注意:这里的执行是一个容易误解的地方,此处的执行并不是指任务本身的执行,而是值`任务投递`这一操作的执行,从宏观上看换成 _未投递_,_已投递_,_投递中_描述会更准确。 ];
此处为何要使用Swoole的内存Table?
Swoft的的定时任务管理是分别由 任务计划进程 和 任务执行进程 进程负责的。两个进程的运行共同管理定时任务,如果使用进程间独立的array()等结构,两个进程必然需要频繁的进程间通信。而使用跨进程的Table(本文的Table,除非特别说明,都指Swoole的SwooleTable结构)直接进行进程间数据共享,不仅性能高,操作简单 还解耦了两个进程。
为了Table能够在两个进程间共同使用,Table必须在Swoole Server启动前创建并分配内存。具体代码在SwoftTaskBootstrapListeners->onBeforeStart()中,比较简单,有兴趣的可以自行阅读。
背景介绍完了,我们来看看这两个定时任务进程的行为
//SwoftTaskBootstrapProcessCronTimerProcess.php /** * Crontab timer process * * @Process(name="cronTimer", boot=true) */ class CronTimerProcess implements ProcessInterface { /** * @param SwoftProcessProcess $process */ public function run(SwoftProcess $process) { //code.... /* @var SwoftTaskCrontabCrontab $cron*/ $cron = App::getBean('crontab'); // Swoole/HttpServer $server = App::$server->getServer(); $time = (60 - date('s')) * 1000; $server->after($time, function () use ($server, $cron) { // Every minute check all tasks, and prepare the tasks that next execution point needs $cron->checkTask(); $server->tick(60 * 1000, function () use ($cron) { $cron->checkTask(); }); }); } } //SwoftTaskCrontabCrontab.php /** * 初始化runTimeTable数据 * * @param array $task 任务 * @param array $parseResult 解析crontab命令规则结果,即Task需要在当前分钟内的哪些秒执行 * @return bool */ private function initRunTimeTableData(array $task, array $parseResult): bool { $runTimeTableTasks = $this->getRunTimeTable()->table; $min = date('YmdHi'); $sec = strtotime(date('Y-m-d H:i')); foreach ($parseResult as $time) { $this->checkTaskQueue(false); $key = $this->getKey($task['rule'], $task['taskClass'], $task['taskMethod'], $min, $time + $sec); $runTimeTableTasks->set($key, [ 'taskClass' => $task['taskClass'], 'taskMethod' => $task['taskMethod'], 'minute' => $min, 'sec' => $time + $sec, 'runStatus' => self::NORMAL ]); } return true; }
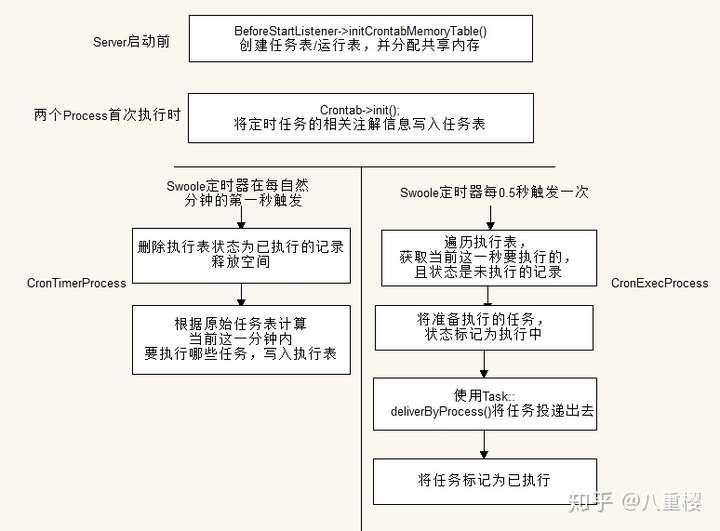
CronTimerProcess是Swoft的定时任务调度进程,其核心方法是Crontab->initRunTimeTableData()。
该进程使用了Swoole的定时器功能,通过SwooleTimer在每分钟首秒时执行的回调,CronTimerProcess每次被唤醒后都会遍历任务表计算出当前这一分钟内的60秒分别需要执行的任务清单,写入执行表并标记为 未执行。
//SwoftTaskBootstrapProcess /** * Crontab process * * @Process(name="cronExec", boot=true) */ class CronExecProcess implements ProcessInterface { /** * @param SwoftProcessProcess $process */ public function run(SwoftProcess $process) { $pname = App::$server->getPname(); $process->name(sprintf('%s cronexec process', $pname)); /** @var SwoftTaskCrontabCrontab $cron */ $cron = App::getBean('crontab'); // Swoole/HttpServer $server = App::$server->getServer(); $server->tick(0.5 * 1000, function () use ($cron) { $tasks = $cron->getExecTasks(); if (!empty($tasks)) { foreach ($tasks as $task) { // Diliver task Task::deliverByProcess($task['taskClass'], $task['taskMethod']); $cron->finishTask($task['key']); } } }); } }
CronExecProcess作为定时任务的执行者,通过SwooleTimer每0.5s唤醒自身一次,然后把 执行表 遍历一次,挑选当下需要执行的任务,通过sendMessage()投递出去并更新该 任务执行表中的状态。
该执行进程只负责任务的投递,任务的实际实际执行仍然在Task进程中由TaskExecutor处理。
定时任务的宏观执行情况如下:
以上内容希望帮助到大家,很多PHPer在进阶的时候总会遇到一些问题和瓶颈,业务代码写多了没有方向感,不知道该从那里入手去提升,对此我整理了一些资料,包括但不限于:分布式架构、高可扩展、高性能、高并发、服务器性能调优、TP6,laravel,YII2,Redis,Swoole、Swoft、Kafka、Mysql优化、shell脚本、Docker、微服务、Nginx等多个知识点高级进阶干货需要的可以免费分享给大家,需要的可以加入我的官方群点击此处。