C. k-Tree
time limit per test
1 secondmemory limit per test
256 megabytesinput
standard inputoutput
standard outputQuite recently a creative student Lesha had a lecture on trees. After the lecture Lesha was inspired and came up with the tree of his own which he called a k-tree.
A k-tree is an infinite rooted tree where:
- each vertex has exactly k children;
- each edge has some weight;
- if we look at the edges that goes from some vertex to its children (exactly k edges), then their weights will equal 1, 2, 3, ..., k.
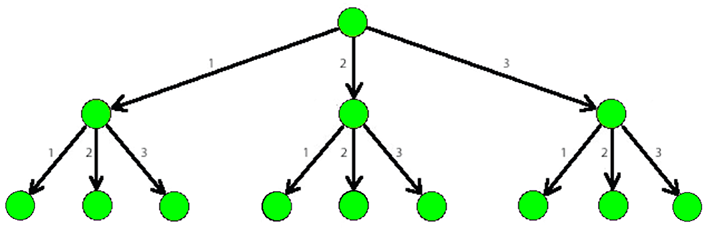
The picture below shows a part of a 3-tree.
Help Dima find an answer to his question. As the number of ways can be rather large, print it modulo1000000007 (109 + 7).
Input
A single line contains three space-separated integers: n, k and d (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 100; 1 ≤ d ≤ k).
Output
Print a single integer — the answer to the problem modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Sample test(s)
input
3 3 2
output
3
input
3 3 3
output
1
input
4 3 2
output
6
input
4 5 2
output
7
神奇的动态规划啊啊啊啊啊啊,
两个状态,dp[n][0,1] 0,1代表是否选超过d的。
dp[i+j][0]+=dp[i][0] j<d
dp[i+j][1]+=dp[i][0] j>=d
dp[i+j][1]+=dp[i][1]
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define MOD 1000000007
LL n,k,d,dp[110][2];
int main()
{
scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&n,&k,&d);
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[0][0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=k;j++)
{
if(i+j>n) continue;
if(j<d) dp[i+j][0]+=dp[i][0];
else dp[i+j][1]+=dp[i][0];
dp[i+j][1]+=dp[i][1];
dp[i+j][0]=dp[i+j][0]%MOD;
dp[i+j][1]=dp[i+j][1]%MOD;
}
}
printf("%I64d",dp[n][1]);
return 0;
}