概论: 在操作系统中,线程可以划分优先级,优先级高的获得的CPU资源较多,也就是CPU优先执行优先级较高的线程。在JAVA中线程的优先级
分1~~10个10个等级。大于或者小于会报异常。
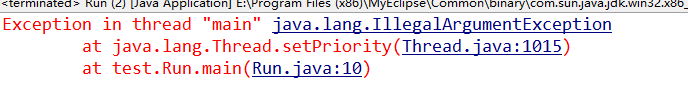
一、线程优先级具有继承性
A 线程启动 B线程,则线程B的优先级与A的是一样的。。
public class MyThread1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("MyThread1 run priority=" + this.getPriority()); MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2(); thread2.start(); } }
public class MyThread2 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("MyThread2 run priority=" + this.getPriority()); } }
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("main thread begin priority=" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); \获取线程的优先级 //Thread.currentThread().setPriority(6); \设置线程的优先级 System.out.println("main thread end priority=" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1(); thread1.start(); } }
结果:

二、线程优先级具规则性
public class MyThread1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); long addResult = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) { Random random = new Random(); random.nextInt(); addResult = addResult + i; } } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("★★★★★thread 1 use time=" + (endTime - beginTime)); } }
public class MyThread2 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); long addResult = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) { Random random = new Random(); random.nextInt(); addResult = addResult + i; } } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("☆☆☆☆☆thread 2 use time=" + (endTime - beginTime)); } }
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { MyThread1 thread1 = new MyThread1(); thread1.setPriority(1); thread1.start(); MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2(); thread2.setPriority(10); thread2.start(); } } }
结果: 高优先级的线程总是大部分先执行完,运行速度比较快,并不代表全部执行完,线程的优先级与线程的执行顺序无关。出现这样的结果优先级相差10倍造成的。修改为相近的优先级再看看,如下图。
高优先级的线程总是大部分先执行完,运行速度比较快,并不代表全部执行完,线程的优先级与线程的执行顺序无关。出现这样的结果优先级相差10倍造成的。修改为相近的优先级再看看,如下图。

三、线程优先级具具有随机性
多次运行优先级相近的代码,你会发现会有如下结果出现。。可以证实线程的优先级具有随机性。

守护线程(daemon)
概念:任何一个守护线程都是整个JVM中所有非守护线程的“保姆”。。只要当前实例中存在一个非守护线程没有结束,守护线程就在工作。当最后一个非守护线程结束
时,守护线程才会结束工作。(典型,GC垃圾回收器)