最近工作中需要写一个一致性哈希的代理,在网上找到了twemproxy,结合网上资料先学习一下源码。
一、Twemproxy简介
Twemproxy是memcache与redis的代理,由twitter公司开发并且目前已经开源。研究这个对于理解网络通信有很大的帮助。
亮点有以下:
1、twemproxy自己创建并维护和后端server(即reids实例)的长连接,保证长连接对于来自不同client但去向同一server的复用。
2、自动识别异常状态的server,保证之后的请求不会被转发到该异常server上。但如果此server恢复正常,twemproxy又能识别此server,并恢复正常访问。
3、提供专门的状态监控端口供外部工具获取状态监控信息。
4、真正实现了多阶段处理多请求,其IO 模型值得学习,采用单线程收发包,基于epoll事件驱动模型。
5、支持Zero Copy技术,通过将消息指针在3个队列之间流转。
二、Twemproxy 入口main函数分析
Twemproxy是以c语言编写的,其整体入口在main函数中。
grep “main”,我们可以看到在文件nc.c中的main函数。开篇我们可以看到定义了一个变量,struct instance nci;
下边我们看下这个instance的定义:
1 struct instance { 2 struct context *ctx; /* active context */ 3 int log_level; /* log level */ 4 char *log_filename; /* log filename */ 5 char *conf_filename; /* configuration filename */ 6 uint16_t stats_port; /* stats monitoring port */ 7 int stats_interval; /* stats aggregation interval */ 8 char *stats_addr; /* stats monitoring addr */ 9 char hostname[NC_MAXHOSTNAMELEN]; /* hostname */ 10 size_t mbuf_chunk_size; /* mbuf chunk size */ 11 pid_t pid; /* process id */ 12 char *pid_filename; /* pid filename */ 13 unsigned pidfile:1; /* pid file created? */ 14 };
再来看一下context的定义:
1 struct context { 2 uint32_t id; /* unique context id */ 3 struct conf *cf; /* configuration */ 4 struct stats *stats; /* stats */ 5 6 struct array pool; /* server_pool[] */ 7 struct event_base *evb; /* event base */ 8 int max_timeout; /* max timeout in msec */ 9 int timeout; /* timeout in msec */ 10 11 uint32_t max_nfd; /* max # files */ 12 uint32_t max_ncconn; /* max # client connections */ 13 uint32_t max_nsconn; /* max # server connections */ 14 };
这个instance就相当于是一个twemproxy实例,一个twemproxy进程对应一个instance,后边整个程序的初始化很多都会用到。这里面 一个instance对应于一个context,而一个context维护一个server pool列表(也就是说一个instance可以包含多个server pool)。
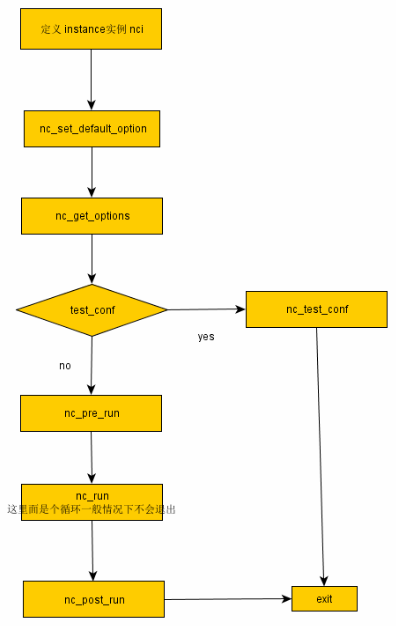
下面先把整个main函数的过程贴出来,加上了一些简要的注释
1 int 2 main(int argc, char **argv) 3 { 4 rstatus_t status; 5 struct instance nci; 6 7 /* 8 * 赋初始值 9 */ 10 nc_set_default_options(&nci); 11 12 /* 13 * 从命令行读入相应参数 14 */ 15 status = nc_get_options(argc, argv, &nci); 16 if (status != NC_OK) { 17 nc_show_usage(); 18 exit(1); 19 } 20 21 if (show_version) { 22 log_stderr("This is nutcracker-%s" CRLF, NC_VERSION_STRING); 23 if (show_help) { 24 nc_show_usage(); 25 } 26 27 if (describe_stats) { 28 stats_describe(); 29 } 30 31 exit(0); 32 } 33 34 /* 35 * 测试配置文件合法性,不必关心 36 */ 37 if (test_conf) { 38 if (!nc_test_conf(&nci)) { 39 exit(1); 40 } 41 exit(0); 42 } 43 44 /* 45 * 初始化log、守护进程、信号、pidfile 46 */ 47 status = nc_pre_run(&nci); 48 if (status != NC_OK) { 49 /* 50 * 失败就对上面的操作进行析构清理,主要就是删除pidfile、关闭log文件描述符 51 */ 52 nc_post_run(&nci); 53 exit(1); 54 } 55 56 nc_run(&nci); 57 58 nc_post_run(&nci); 59 60 exit(1); 61 }
下面我们进到各个函数里面看一下吧。
1、函数nc_set_default_options
1 static void 2 nc_set_default_options(struct instance *nci) 3 { 4 int status; 5 6 nci->ctx = NULL; 7 8 nci->log_level = NC_LOG_DEFAULT; 9 nci->log_filename = NC_LOG_PATH; 10 11 nci->conf_filename = NC_CONF_PATH; 12 13 nci->stats_port = NC_STATS_PORT; 14 nci->stats_addr = NC_STATS_ADDR; 15 nci->stats_interval = NC_STATS_INTERVAL; 16 17 status = nc_gethostname(nci->hostname, NC_MAXHOSTNAMELEN); 18 if (status < 0) { 19 log_warn("gethostname failed, ignored: %s", strerror(errno)); 20 nc_snprintf(nci->hostname, NC_MAXHOSTNAMELEN, "unknown"); 21 } 22 nci->hostname[NC_MAXHOSTNAMELEN - 1] = '�'; 23 24 nci->mbuf_chunk_size = NC_MBUF_SIZE; 25 26 nci->pid = (pid_t)-1; 27 nci->pid_filename = NULL; 28 nci->pidfile = 0; 29 }
这个是用来设置上述instance实例nci的各项参数的默认值。
2、函数nc_get_options
1 static rstatus_t 2 nc_get_options(int argc, char **argv, struct instance *nci) 3 { 4 int c, value; 5 6 opterr = 0; 7 8 for (;;) { 9 c = getopt_long(argc, argv, short_options, long_options, NULL); 10 if (c == -1) { 11 /* no more options */ 12 break; 13 } 14 15 switch (c) { 16 case 'h': 17 show_version = 1; 18 show_help = 1; 19 break; 20 21 case 'V': 22 show_version = 1; 23 break; 24 25 case 't': 26 test_conf = 1; 27 break; 28 29 case 'd': 30 daemonize = 1; 31 break; 32 33 case 'D': 34 describe_stats = 1; 35 show_version = 1; 36 break; 37 38 case 'v': 39 value = nc_atoi(optarg, strlen(optarg)); 40 if (value < 0) { 41 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -v requires a number"); 42 return NC_ERROR; 43 } 44 nci->log_level = value; 45 break; 46 47 case 'o': 48 nci->log_filename = optarg; 49 break; 50 51 case 'c': 52 nci->conf_filename = optarg; 53 break; 54 55 case 's': 56 value = nc_atoi(optarg, strlen(optarg)); 57 if (value < 0) { 58 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -s requires a number"); 59 return NC_ERROR; 60 } 61 if (!nc_valid_port(value)) { 62 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -s value %d is not a valid " 63 "port", value); 64 return NC_ERROR; 65 } 66 67 nci->stats_port = (uint16_t)value; 68 break; 69 70 case 'i': 71 value = nc_atoi(optarg, strlen(optarg)); 72 if (value < 0) { 73 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -i requires a number"); 74 return NC_ERROR; 75 } 76 77 nci->stats_interval = value; 78 break; 79 80 case 'a': 81 nci->stats_addr = optarg; 82 break; 83 84 case 'p': 85 nci->pid_filename = optarg; 86 break; 87 88 case 'm': 89 value = nc_atoi(optarg, strlen(optarg)); 90 if (value <= 0) { 91 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -m requires a non-zero number"); 92 return NC_ERROR; 93 } 94 95 if (value < NC_MBUF_MIN_SIZE || value > NC_MBUF_MAX_SIZE) { 96 log_stderr("nutcracker: mbuf chunk size must be between %zu and" 97 " %zu bytes", NC_MBUF_MIN_SIZE, NC_MBUF_MAX_SIZE); 98 return NC_ERROR; 99 } 100 101 nci->mbuf_chunk_size = (size_t)value; 102 break; 103 104 case '?': 105 switch (optopt) { 106 case 'o': 107 case 'c': 108 case 'p': 109 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -%c requires a file name", 110 optopt); 111 break; 112 113 case 'm': 114 case 'v': 115 case 's': 116 case 'i': 117 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -%c requires a number", optopt); 118 break; 119 120 case 'a': 121 log_stderr("nutcracker: option -%c requires a string", optopt); 122 break; 123 124 default: 125 log_stderr("nutcracker: invalid option -- '%c'", optopt); 126 break; 127 } 128 return NC_ERROR; 129 130 default: 131 log_stderr("nutcracker: invalid option -- '%c'", optopt); 132 return NC_ERROR; 133 134 } 135 } 136 137 return NC_OK; 138 }
从命令行读入相应参数,如果有则覆盖上一个函数所设置的默认参数。
3、函数nc_test_conf
如果配置了-t选项 则nc_test_conf : 用于对配置文件做检查,以确保配置文件格式的正确。里面的解析用了一坨yaml的东西,不懂……不过我们也不用关心这个。
4、函数nc_pre_run
1 static rstatus_t 2 nc_pre_run(struct instance *nci) 3 { 4 rstatus_t status; 5 6 status = log_init(nci->log_level, nci->log_filename); 7 if (status != NC_OK) { 8 return status; 9 } 10 11 if (daemonize) { 12 status = nc_daemonize(1); 13 if (status != NC_OK) { 14 return status; 15 } 16 } 17 18 nci->pid = getpid(); 19 20 status = signal_init(); 21 if (status != NC_OK) { 22 return status; 23 } 24 25 if (nci->pid_filename) { 26 status = nc_create_pidfile(nci); 27 if (status != NC_OK) { 28 return status; 29 } 30 } 31 32 nc_print_run(nci); 33 34 return NC_OK; 35 }
做了这些事情:初始化log、守护进程、信号、pidfile;其中关于守护进程的实现非常经典,后面会单独写。
5、函数nc_run
1 static void 2 nc_run(struct instance *nci) 3 { 4 rstatus_t status; 5 struct context *ctx; 6 7 ctx = core_start(nci); 8 if (ctx == NULL) { 9 return; 10 } 11 12 /* run rabbit run */ 13 for (;;) { 14 status = core_loop(ctx); 15 if (status != NC_OK) { 16 break; 17 } 18 } 19 20 core_stop(ctx); 21 }
nc_run开始启动proxy;这个函数完成的工作就是调用core_start创建context,然后进入死循环调用core_loop开始整个事件循环的处理,接受请求并处理。当然,core_start以及core_loop这两个函数里边还包含了大量的处理工作,包括:配置文件解析以及读取,相关组件(server_pool,conf,context)的初始化等,这个后面再单独写。
总体来说,启动流程就是这些步骤,如下图:
本文参考自:http://blog.sina.cn/dpool/blog/s/blog_4f8ea2ef0101iill.html?md=gd