Room and Moor
Problem Description
PM Room defines a sequence A = {A1, A2,..., AN}, each of which is either 0 or 1. In order to beat him, programmer Moor has to construct another sequence B = {B1, B2,... , BN} of the same length, which satisfies that:
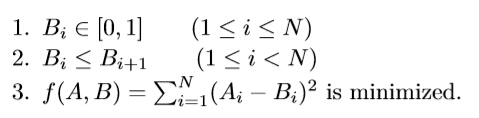
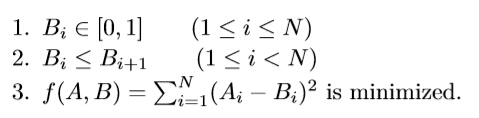
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The number of test cases T(T<=100) occurs in the first line of input.
For each test case:
The first line contains a single integer N (1<=N<=100000), which denotes the length of A and B.
The second line consists of N integers, where the ith denotes Ai.
For each test case:
The first line contains a single integer N (1<=N<=100000), which denotes the length of A and B.
The second line consists of N integers, where the ith denotes Ai.
Output
Output the minimal f (A, B) when B is optimal and round it to 6 decimals.
Sample Input
4 9 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 9 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 4 0 0 1 1 4 0 1 1 1
Sample Output
1.428571 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000
题意:不多说了。
sl: 其实就是一个贪心的思想。
网上讲解很多。比赛时没搞出来。。。呵呵了。
1 // by caonima
2 // hehe
3 #include <cstdio>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <queue>
7 #include <vector>
8 #include <algorithm>
9 using namespace std;
10 const int MAX = 1e6+10;
11 struct node {
12 int one,zero;
13 double val;
14 }v[MAX];
15 stack<node> ans;
16 int a[MAX];
17 void init() {
18 while(!ans.empty()) ans.pop();
19 }
20 int main() {
21 int cas,n;
22 scanf("%d",&cas);
23 while(cas--) {
24 scanf("%d",&n);
25 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
26 scanf("%d",&a[i]);
27 }
28 a[n+1]=1;
29 int L=1,R=n;
30 while(a[L]==0) L++;
31 while(a[R]==1) R--;
32 if(L>=R) printf("0.000000 ");
33 else {
34 int id=0;
35 for(int i=L;i<=R;) {
36 int cnt0=0,cnt1=0;
37 while(a[i]==1) {
38 cnt1++; i++;
39 }
40 while(a[i]==0) {
41 cnt0++; i++;
42 }
43 v[id].one=cnt1; v[id].zero=cnt0;
44 v[id++].val=(double) cnt1/(double)(cnt0+cnt1);
45 }
46 init();
47 for(int i=0;i<id;i++) {
48
49 if(ans.empty()) ans.push(v[i]);
50 else {
51 node vn=ans.top();
52 if(vn.val<=v[i].val) ans.push(v[i]);
53 else {
54 node t=v[i];
55 while(true) {
56 node vx=ans.top();
57 if(vx.val>t.val) {
58 t.one+=vx.one; t.zero+=vx.zero;
59 t.val=(double) t.one/(double)(t.one+t.zero);
60 ans.pop();
61 }
62 else {
63 ans.push(t);
64 break;
65 }
66 if(ans.empty()) {
67 ans.push(t);
68 break;
69 }
70 }
71 }
72 }
73 }
74 double res=0;
75 while(!ans.empty()) {
76 node vn=ans.top();
77 ans.pop();
78 res+=vn.val*vn.val*vn.zero+(1-vn.val)*(1-vn.val)*vn.one;
79 }
80 printf("%.6lf ",res);
81 }
82
83 }
2 // hehe
3 #include <cstdio>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <queue>
7 #include <vector>
8 #include <algorithm>
9 using namespace std;
10 const int MAX = 1e6+10;
11 struct node {
12 int one,zero;
13 double val;
14 }v[MAX];
15 stack<node> ans;
16 int a[MAX];
17 void init() {
18 while(!ans.empty()) ans.pop();
19 }
20 int main() {
21 int cas,n;
22 scanf("%d",&cas);
23 while(cas--) {
24 scanf("%d",&n);
25 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
26 scanf("%d",&a[i]);
27 }
28 a[n+1]=1;
29 int L=1,R=n;
30 while(a[L]==0) L++;
31 while(a[R]==1) R--;
32 if(L>=R) printf("0.000000 ");
33 else {
34 int id=0;
35 for(int i=L;i<=R;) {
36 int cnt0=0,cnt1=0;
37 while(a[i]==1) {
38 cnt1++; i++;
39 }
40 while(a[i]==0) {
41 cnt0++; i++;
42 }
43 v[id].one=cnt1; v[id].zero=cnt0;
44 v[id++].val=(double) cnt1/(double)(cnt0+cnt1);
45 }
46 init();
47 for(int i=0;i<id;i++) {
48
49 if(ans.empty()) ans.push(v[i]);
50 else {
51 node vn=ans.top();
52 if(vn.val<=v[i].val) ans.push(v[i]);
53 else {
54 node t=v[i];
55 while(true) {
56 node vx=ans.top();
57 if(vx.val>t.val) {
58 t.one+=vx.one; t.zero+=vx.zero;
59 t.val=(double) t.one/(double)(t.one+t.zero);
60 ans.pop();
61 }
62 else {
63 ans.push(t);
64 break;
65 }
66 if(ans.empty()) {
67 ans.push(t);
68 break;
69 }
70 }
71 }
72 }
73 }
74 double res=0;
75 while(!ans.empty()) {
76 node vn=ans.top();
77 ans.pop();
78 res+=vn.val*vn.val*vn.zero+(1-vn.val)*(1-vn.val)*vn.one;
79 }
80 printf("%.6lf ",res);
81 }
82
83 }
84 }