1. 原理
压缩
LZ78算法的压缩过程非常简单。在压缩时维护一个动态词典Dictionary,其包括了历史字符串的index与内容;压缩情况分为三种:
- 若当前字符c未出现在词典中,则编码为
(0, c); - 若当前字符c出现在词典中,则与词典做最长匹配,然后编码为
(prefixIndex,lastChar),其中,prefixIndex为最长匹配的前缀字符串,lastChar为最长匹配后的第一个字符; - 为对最后一个字符的特殊处理,编码为
(prefixIndex,)。
如果对于上述压缩的过程稍感费解,下面给出三个例子。例子一,对于字符串“ABBCBCABABCAABCAAB”压缩编码过程如下: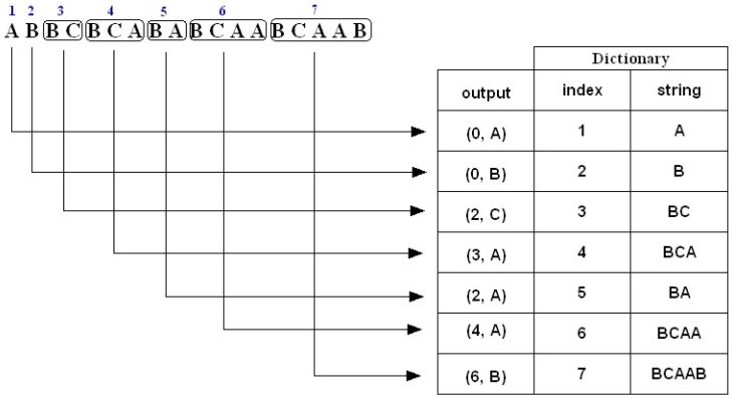
1. A is not in the Dictionary; insert it
2. B is not in the Dictionary; insert it
3. B is in the Dictionary.
BC is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
4. B is in the Dictionary.
BC is in the Dictionary.
BCA is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
5. B is in the Dictionary.
BA is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
6. B is in the Dictionary.
BC is in the Dictionary.
BCA is in the Dictionary.
BCAA is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
7. B is in the Dictionary.
BC is in the Dictionary.
BCA is in the Dictionary.
BCAA is in the Dictionary.
BCAAB is not in the Dictionary; insert it.例子二,对于字符串“BABAABRRRA”压缩编码过程如下: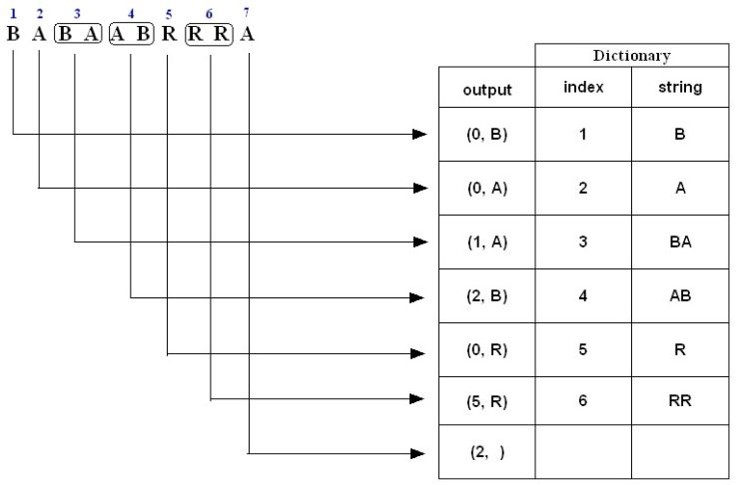
1. B is not in the Dictionary; insert it
2. A is not in the Dictionary; insert it
3. B is in the Dictionary.
BA is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
4. A is in the Dictionary.
AB is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
5. R is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
6. R is in the Dictionary.
RR is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
7. A is in the Dictionary and it is the last input character; output a pair
containing its index: (2, )例子三,对于字符串“AAAAAAAAA”压缩编码过程如下:
1. A is not in the Dictionary; insert it
2. A is in the Dictionary
AA is not in the Dictionary; insert it
3. A is in the Dictionary.
AA is in the Dictionary.
AAA is not in the Dictionary; insert it.
4. A is in the Dictionary.
AA is in the Dictionary.
AAA is in the Dictionary and it is the last pattern; output a pair containing its index: (3, )解压缩
解压缩能更根据压缩编码恢复出(压缩时的)动态词典,然后根据index拼接成解码后的字符串。为了便于理解,我们拿上述例子一中的压缩编码序列(0, A) (0, B) (2, C) (3, A) (2, A) (4, A) (6, B)来分解解压缩步骤,如下图所示:
前后拼接后,解压缩出来的字符串为“ABBCBCABABCAABCAAB”。
LZ系列压缩算法
LZ系列压缩算法均为LZ77与LZ78的变种,在此基础上做了优化。
- LZ77:LZSS、LZR、LZB、LZH;
- LZ78:LZW、LZC、LZT、LZMW、LZJ、LZFG。
其中,LZSS与LZW为这两大阵容里名气最响亮的算法。LZSS是由Storer与Szymanski [2]改进了LZ77:增加最小匹配长度的限制,当最长匹配的长度小于该限制时,则不压缩输出,但仍然滑动窗口右移一个字符。Google开源的Snappy压缩算法库大体遵循LZSS的编码方案,在其基础上做了一些工程上的优化。
2. 实现
Python 3.5实现LZ78算法:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# A simplified implementation of LZ78 algorithm
# @Time : 2017/1/13
# @Author : rain
def compress(message):
tree_dict, m_len, i = {}, len(message), 0
while i < m_len:
# case I
if message[i] not in tree_dict.keys():
yield (0, message[i])
tree_dict[message[i]] = len(tree_dict) + 1
i += 1
# case III
elif i == m_len - 1:
yield (tree_dict.get(message[i]), '')
i += 1
else:
for j in range(i + 1, m_len):
# case II
if message[i:j + 1] not in tree_dict.keys():
yield (tree_dict.get(message[i:j]), message[j])
tree_dict[message[i:j + 1]] = len(tree_dict) + 1
i = j + 1
break
# case III
elif j == m_len - 1:
yield (tree_dict.get(message[i:j + 1]), '')
i = j + 1
def uncompress(packed):
unpacked, tree_dict = '', {}
for index, ch in packed:
if index == 0:
unpacked += ch
tree_dict[len(tree_dict) + 1] = ch
else:
term = tree_dict.get(index) + ch
unpacked += term
tree_dict[len(tree_dict) + 1] = term
return unpacked
if __name__ == '__main__':
messages = ['ABBCBCABABCAABCAAB', 'BABAABRRRA', 'AAAAAAAAA']
for m in messages:
pack = compress(m)
unpack = uncompress(pack)
print(unpack == m)